When evaluating metal joining techniques, brazing stands out as a highly versatile process capable of creating strong, clean joints between a wide variety of materials. Its primary advantage is the ability to join dissimilar metals with minimal heat distortion, as the base metals themselves are not melted. However, its effectiveness is highly dependent on the specific metals being joined, and it does not typically achieve the absolute strength of a welded joint.
Brazing's core value is its ability to create precise joints between different types of metals without altering their fundamental properties. This versatility, however, requires careful consideration of base metal compatibility and an acceptance of lower joint strength compared to fusion welding.

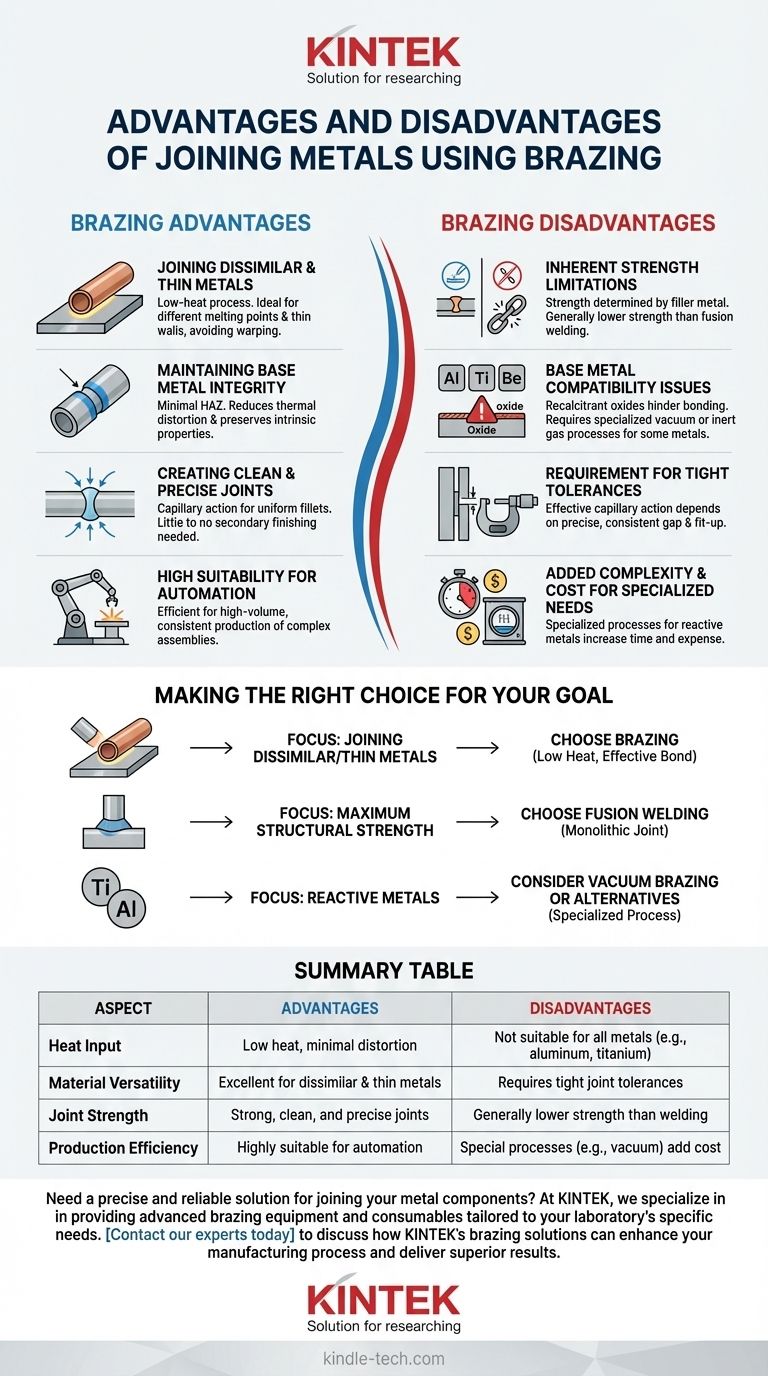
The Core Advantages of Brazing
Brazing operates by heating the base metals and introducing a filler metal that melts at a lower temperature. This filler is drawn into the tight-fitting joint by capillary action, creating a strong metallurgical bond upon cooling. This fundamental principle is the source of its key benefits.
Joining Dissimilar and Thin Metals
Because brazing does not melt the base metals, it is exceptionally well-suited for joining materials with different melting points, such as copper to steel.
This low-heat process also makes it ideal for joining thin-walled tubes or delicate components that would be easily warped or destroyed by the high temperatures of welding.
Maintaining Base Metal Integrity
The temperatures used in brazing are significantly lower than in welding, which drastically reduces the size of the heat-affected zone (HAZ).
This minimizes the risk of thermal distortion, warping, and changes to the base metals' intrinsic properties like hardness or corrosion resistance, preserving the integrity of the original components.
Creating Clean and Precise Joints
The capillary action inherent to brazing pulls the filler metal uniformly throughout the joint, creating a neat, clean fillet.
This results in assemblies that often require little to no secondary finishing, saving time and cost in production environments. The process is also highly controllable and repeatable.
High Suitability for Automation
The brazing process lends itself well to automation. Using controlled atmosphere furnaces or automatic brazing machines allows for high-volume, consistent production of complex assemblies.
This makes it a highly efficient choice for manufacturing applications where repeatability and precision are paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Disadvantages
While versatile, brazing is not a universal solution. Its limitations are critical to understand before selecting it for an application.
Inherent Strength Limitations
A brazed joint's strength is determined by the filler metal, not the fused base metals. Consequently, a brazed joint is generally not as strong as a properly executed welded joint.
For applications demanding the absolute highest level of strength or impact resistance, fusion welding is often the superior choice.
Base Metal Compatibility Issues
Brazing is not effective for all metals under standard conditions. Materials that form strong, stable oxides—often called recalcitrant oxides—are particularly challenging.
Metals like aluminum, titanium, and beryllium require specialized processes such as vacuum brazing or the use of inert gas atmospheres to prevent the formation of these oxides, which would otherwise inhibit the filler metal from bonding. This adds significant complexity and cost.
Requirement for Tight Tolerances
Effective capillary action depends on a precise, consistent gap between the two parts being joined.
This requirement means that component fit-up is critical. Poorly fitting parts will result in weak or incomplete joints, demanding a higher level of precision during the manufacturing and preparation stages.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct joining method requires aligning the process capabilities with your project's most critical outcome.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar metals or thin-walled components: Brazing is an excellent choice due to its low heat input and ability to bond different materials effectively.
- If your primary focus is maximum structural strength: Fusion welding is generally the superior method, as it creates a single, monolithic joint from the base metals.
- If you are working with reactive metals like titanium or aluminum: Be prepared to use specialized brazing processes like vacuum brazing or consider alternative joining technologies.
- If you need high-volume, repeatable production of clean joints: Automated brazing can be a highly efficient and cost-effective solution for complex assemblies.
Ultimately, selecting brazing is a strategic decision that prioritizes joint precision and material versatility over the absolute strength offered by fusion processes.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Input | Low heat, minimal distortion | Not suitable for all metals (e.g., aluminum, titanium) |
| Material Versatility | Excellent for dissimilar & thin metals | Requires tight joint tolerances |
| Joint Strength | Strong, clean, and precise joints | Generally lower strength than welding |
| Production Efficiency | Highly suitable for automation | Special processes (e.g., vacuum) add cost |
Need a precise and reliable solution for joining your metal components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced brazing equipment and consumables tailored to your laboratory's specific needs. Whether you're working with dissimilar metals, thin-walled components, or require automated solutions for high-volume production, our expertise ensures strong, clean, and repeatable joints.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's brazing solutions can enhance your manufacturing process and deliver superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- What is brazing in heat treatment? Achieve Superior Joint Quality and Efficiency
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining



















