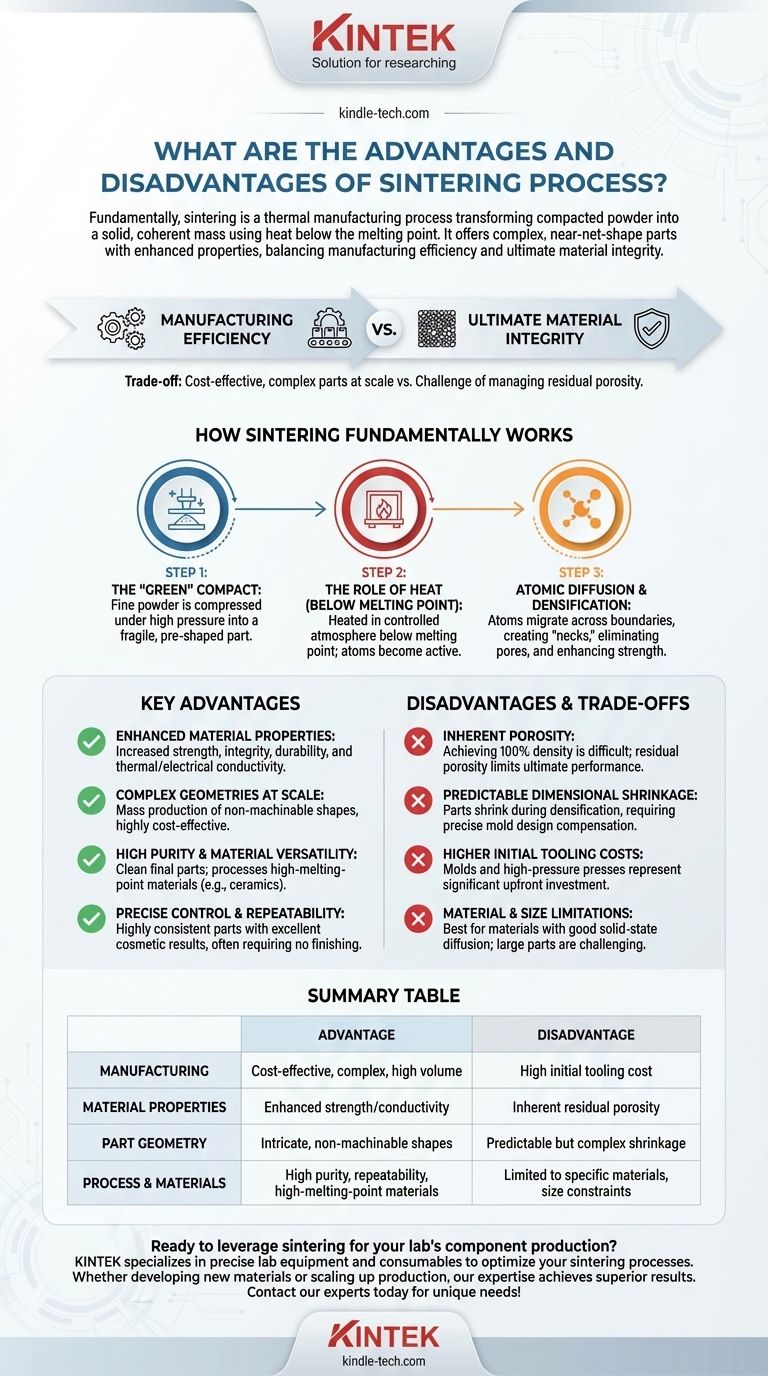
Fundamentally, sintering is a thermal manufacturing process that transforms a compacted powder into a solid, coherent mass using heat below the material's melting point. Its primary advantages are the ability to create complex, near-net-shape parts with enhanced physical properties in a highly repeatable and cost-effective manner for large volumes. The main disadvantage is the challenge of completely eliminating internal porosity, which can limit the ultimate strength and density compared to parts formed from a melt.
The core trade-off of sintering is between manufacturing efficiency and ultimate material integrity. It excels at producing intricate components at scale that would be difficult or expensive to machine, but this comes with the inherent challenge of managing residual porosity.

How Sintering Fundamentally Works
To understand the advantages and limitations, you must first understand the mechanism. Sintering is a process of atomic diffusion, not melting.
The "Green" Compact
The process begins with a fine powder of a specific material, such as a metal or ceramic. This powder is compressed in a die under high pressure to form a fragile, pre-shaped part known as a "green" compact.
The Role of Heat (Below Melting Point)
This green compact is then heated in a controlled-atmosphere furnace to a temperature below its melting point. At this high temperature, the atoms in the powder particles become highly active.
Atomic Diffusion and Densification
At the points where particles touch, atoms begin to migrate or diffuse across the boundaries. This creates "necks" that grow, pulling the particle centers closer together and gradually eliminating the pores between them. This process, called densification, is what gives the final part its strength and improved properties.
Key Advantages of the Sintering Process
The unique mechanism of sintering leads to several significant manufacturing and material benefits.
Enhanced Material Properties
By reducing porosity and bonding particles on an atomic level, sintering significantly improves a material's intrinsic properties. This leads to increased strength, material integrity, and durability. It also enhances thermal and electrical conductivity, as the bonded particles provide a more continuous path for energy to travel.
Complex Geometries at Scale
Sintering allows for the mass production of parts with non-machinable geometries. Because the initial shape is formed in a mold, features that are difficult or impossible to create with traditional cutting tools can be integrated directly into the component. This makes it a highly cost-effective method for large production volumes.
High Purity and Material Versatility
The initial heating stage burns off residual lubricants or binders from the compaction stage, resulting in a clean, high-purity final part. Crucially, because it operates below the melting point, sintering is one of the few viable methods for processing materials with extremely high melting points, such as certain ceramics and refractory metals.
Precise Control and Repeatability
The science behind sintering is well-understood, allowing for precise control over process parameters like temperature, time, and atmosphere. This control leads to highly repeatable and accurate parts, ensuring consistency across large production runs with excellent cosmetic results that often require no finishing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Disadvantages
No process is without limitations. The primary disadvantages of sintering are direct consequences of its powder-based nature.
Inherent Porosity
While sintering dramatically reduces porosity, achieving 100% density is extremely difficult and often not commercially viable. Some level of residual porosity almost always remains, which can act as a stress concentration point and limit the part's ultimate mechanical performance compared to a fully dense, forged, or cast equivalent.
Predictable Dimensional Shrinkage
As the pores are eliminated and the part densifies, it inevitably shrinks. This shrinkage must be precisely calculated and compensated for in the design of the initial mold. Managing this is a critical and sometimes complex aspect of process engineering.
Higher Initial Tooling Costs
The molds and high-pressure presses required to create the initial green compacts represent a significant upfront investment. This makes sintering less economical for small-batch production or prototyping compared to processes like machining.
Material and Size Limitations
The process is best suited for materials that diffuse well in a solid state, primarily certain metals, ceramics, and their composites. Furthermore, very large parts can be challenging to produce due to the difficulty in achieving uniform density and temperature throughout a large volume.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a manufacturing process depends entirely on your project's priorities. Sintering offers a powerful balance of properties and economics when applied correctly.
- If your primary focus is mass production of complex parts: Sintering is an excellent choice due to its high repeatability and cost-effectiveness for non-machinable shapes.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum material density and strength: You must carefully control the sintering process or consider alternative methods like forging or hot isostatic pressing, as residual porosity can be a limiting factor.
- If your primary focus is creating components with controlled porosity (e.g., filters): Sintering offers unique capabilities to engineer specific levels of porosity that are difficult to achieve with other methods.
By understanding these core principles, you can effectively determine if sintering is the optimal path to achieve your specific material and manufacturing objectives.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Cost-effective for complex, high-volume parts | High initial tooling cost for molds/presses |
| Material Properties | Enhanced strength, thermal/electrical conductivity | Inherent residual porosity limits ultimate strength/density |
| Part Geometry | Creates intricate, non-machinable shapes | Predictable but complex-to-manage dimensional shrinkage |
| Process & Materials | High purity, repeatability; works with high-melting-point materials | Limited to materials that diffuse well; size constraints for large parts |
Ready to leverage sintering for your lab's component production? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed to optimize your sintering processes. Whether you are developing new materials or scaling up production of complex parts, our expertise can help you achieve superior results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's unique sintering needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag



















