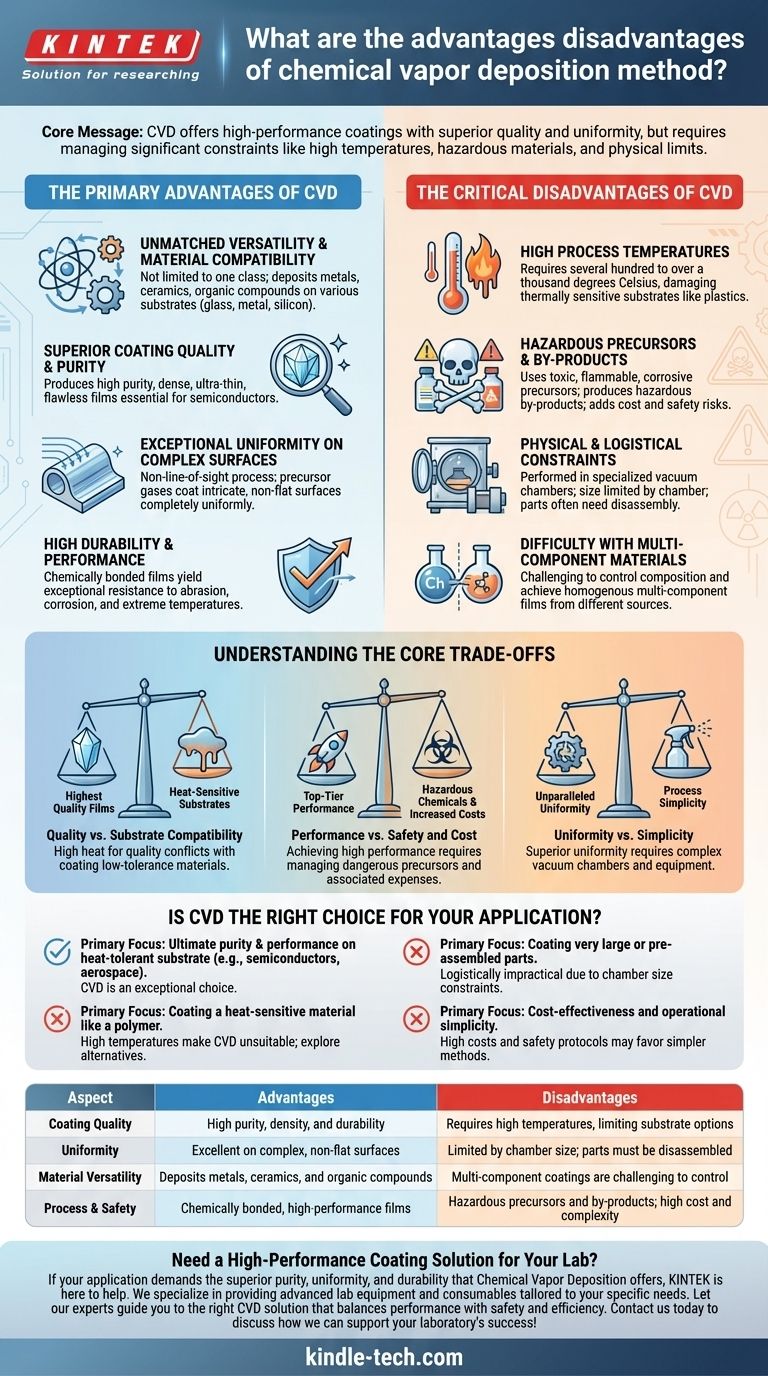
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a powerful and versatile method for creating high-purity, high-performance coatings. Its primary advantages are the exceptional quality, uniformity, and durability of the films it produces, especially on complex surfaces. However, these benefits come at the cost of significant process constraints, including high temperatures, the use of hazardous materials, and physical limitations on the size of the components that can be coated.
Chemical Vapor Deposition offers unparalleled control and quality for creating thin films, making it a cornerstone of high-tech manufacturing. However, its effectiveness is fundamentally tied to a critical trade-off: you must weigh its superior results against the demanding and often hazardous process requirements it entails.
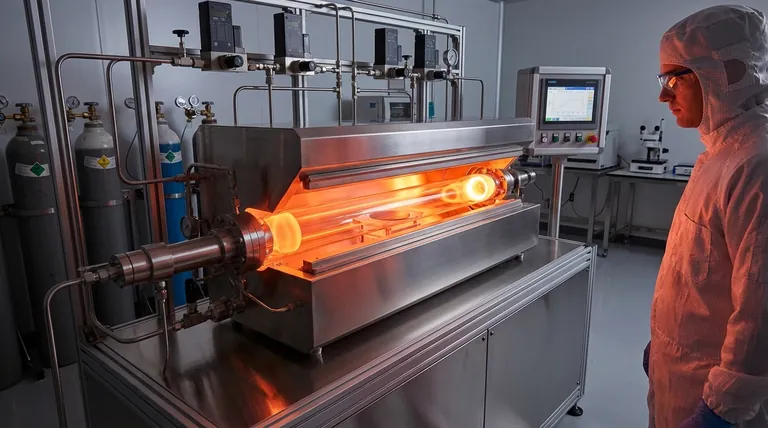

The Primary Advantages of CVD
The power of Chemical Vapor Deposition lies in its use of chemical reactions in a gaseous state, which provides a unique set of benefits for creating advanced materials and coatings.
Unmatched Versatility and Material Compatibility
Because CVD is a chemically driven process, it is not limited to a single class of materials.
It can be used to deposit a wide range of coatings, including metals, ceramics, and organic compounds, onto various substrates like glass, metal, and silicon wafers.
Superior Coating Quality and Purity
CVD is renowned for its ability to produce films with extremely high purity and density.
By precisely controlling the precursor gases and reaction conditions, you can create ultra-thin, flawless layers, which is essential for applications like manufacturing semiconductors and electrical circuits.
Exceptional Uniformity on Complex Surfaces
A key advantage of CVD is that it is a non-line-of-sight process.
The precursor gases flow around and into an object, ensuring that even intricate, complex, and non-flat surfaces receive a completely uniform coating. This is a significant advantage over line-of-sight methods like physical vapor deposition (PVD).
High Durability and Performance
The resulting coatings are not just layered on top; they are chemically bonded to the substrate.
This creates highly durable and adherent films that can be engineered for exceptional resistance to abrasion, corrosion, and extreme temperatures.
The Critical Disadvantages of CVD
The same chemical processes that give CVD its advantages also introduce significant challenges and limitations that must be carefully managed.
High Process Temperatures
Traditional CVD often requires very high temperatures (several hundred to over a thousand degrees Celsius) to initiate the necessary chemical reactions.
This high heat can damage or destroy thermally sensitive substrates, such as plastics or certain metal alloys, severely limiting the types of materials that can be coated.
Hazardous Precursors and By-products
The chemical precursors required for CVD often have high vapor pressure and can be highly toxic, flammable, or corrosive.
Furthermore, the chemical reactions produce by-products that are frequently hazardous themselves. The handling, storage, and neutralization of these chemicals add significant cost, complexity, and safety risks to the process.
Physical and Logistical Constraints
CVD is not a portable technology; it must be performed in a specialized facility with a vacuum chamber.
The size of the object being coated is limited by the size of the chamber. Additionally, components typically must be fully disassembled before coating, adding a logistical step to the manufacturing process.
Difficulty with Multi-Component Materials
While versatile, creating films from multiple chemical sources simultaneously is challenging.
Different precursors have different vapor pressures and reaction rates, making it difficult to control the final composition and achieve a homogenous, multi-component material.
Understanding the Core Trade-offs
Choosing CVD involves balancing its powerful capabilities against its inherent limitations. Your decision will depend entirely on which of these factors is most critical for your project.
Quality vs. Substrate Compatibility
The highest-quality films often demand the highest temperatures. This creates a direct conflict when you need to coat a material that cannot withstand the heat required to achieve the desired coating properties.
Performance vs. Safety and Cost
The most high-performance coatings often rely on the most reactive and hazardous precursors. This means that achieving top-tier durability or purity comes with the increased costs and safety protocols associated with managing dangerous chemicals.
Uniformity vs. Simplicity
CVD’s ability to uniformly coat complex shapes is unparalleled. However, this benefit requires a complex, off-site process involving vacuum chambers and specialized equipment, making it far less simple than other methods like spray coating or dipping for less demanding applications.
Is CVD the Right Choice for Your Application?
To decide, you must align the method's strengths and weaknesses with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity and performance on a heat-tolerant substrate: CVD is an exceptional, often superior, choice for applications like semiconductors, aerospace components, and cutting tools.
- If your primary focus is coating a heat-sensitive material like a polymer: The high temperatures of conventional CVD make it unsuitable, and you should explore low-temperature alternatives or different deposition methods entirely.
- If your primary focus is coating very large or pre-assembled parts: The physical size constraints of the vacuum chamber and the need to coat individual components make CVD logistically impractical.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and operational simplicity: The high equipment cost and stringent safety requirements for handling hazardous materials may make other, simpler coating technologies a more practical fit.
Ultimately, selecting Chemical Vapor Deposition is a strategic decision that hinges on whether your application demands its superior results enough to justify its significant process complexities.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Quality | High purity, density, and durability | Requires high temperatures, limiting substrate options |
| Uniformity | Excellent on complex, non-flat surfaces | Limited by chamber size; parts must be disassembled |
| Material Versatility | Deposits metals, ceramics, and organic compounds | Multi-component coatings are challenging to control |
| Process & Safety | Chemically bonded, high-performance films | Hazardous precursors and by-products; high cost and complexity |
Need a High-Performance Coating Solution for Your Lab?
If your application demands the superior purity, uniformity, and durability that Chemical Vapor Deposition offers, KINTEK is here to help. We specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific needs—whether you're working with semiconductors, aerospace components, or cutting tools.
Let our experts guide you to the right CVD solution that balances performance with safety and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
People Also Ask
- What does CVD method in carbon nanotubes synthesis stand for? Mastering Controlled Nanotube Growth
- What are the advantages of CVD graphene? Achieve High-Quality, Scalable Graphene Films for Industrial Applications
- What are precursors in CVD process? The Essential Ingredient for Thin-Film Success
- Which method of CNTs production leads to high quality nanotubes in large-scale? Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
- What is CVD in nanotechnology? The Key to Atomic-Level Material Fabrication
- What are the techniques of vapor phase? A Guide to PVD, CVD, and Thin Film Deposition Methods
- What is vapor deposition of thin film? A Guide to PVD and CVD Coating Processes
- What are the steps in the CVD method? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition



















