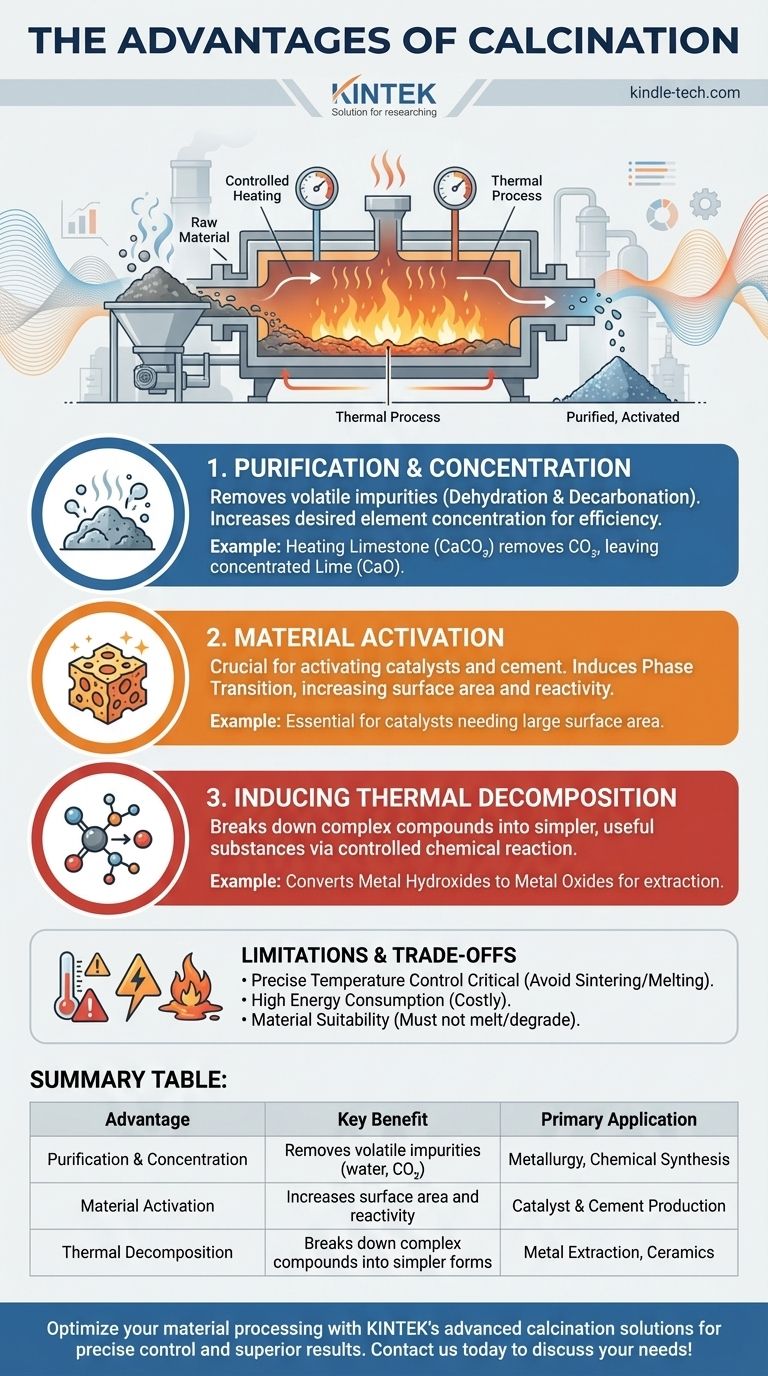
At its core, calcination is a powerful thermal process used to purify, activate, or stabilize solid materials. Its primary advantages are the removal of volatile impurities like water and carbon dioxide, the creation of more reactive material structures, and the production of a chemically stable, concentrated final product.
Calcination is not about melting a material, but fundamentally changing its chemical and physical properties through controlled heating. It is the critical step that transforms a raw ore or compound into a purified, reactive, or stable precursor for industries ranging from cement production to metallurgy.
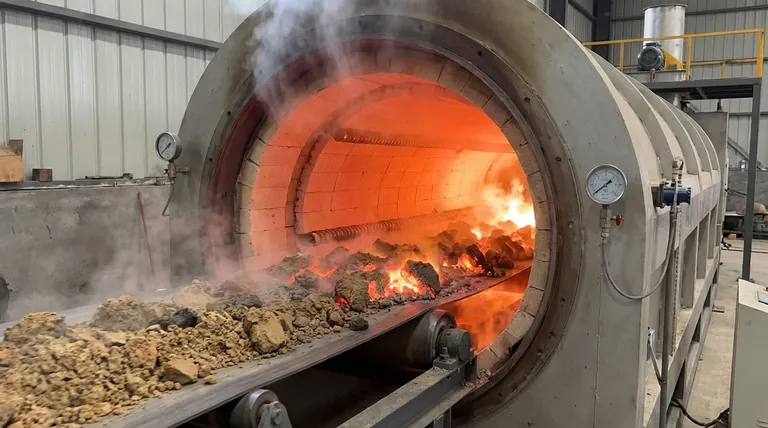

The Core Mechanisms of Calcination
To understand the advantages of calcination, you must first understand the distinct transformations it induces. The process works by heating a material below its melting point in a controlled atmosphere, triggering specific chemical and physical changes.
Advantage 1: Purification and Concentration
The most common application of calcination is to purify a material by driving off volatile components.
This process removes chemically bound water (dehydration) and carbon dioxide (decarbonation). For example, heating limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) removes CO₂, leaving behind a more concentrated lime (calcium oxide, CaO).
By removing these non-essential parts, the concentration of the desired element or compound in the remaining solid increases, making subsequent processing more efficient.
Advantage 2: Material Activation
Calcination is crucial for "activating" materials, particularly for use as catalysts or in cement.
Heating can induce a phase transition, changing the material's internal crystal structure. This often results in a higher surface area and a more porous, reactive state.
This increased reactivity is essential for substances like catalysts, which depend on a large surface area to function effectively, or for cement, which must react with water to harden.
Advantage 3: Inducing Thermal Decomposition
Beyond simply removing volatiles, calcination can break down complex compounds into simpler, more useful substances.
This thermal decomposition is a controlled chemical reaction. For instance, it can be used to convert metal hydroxides into their respective metal oxides, a necessary intermediate step in extracting pure metals from ores.
Understanding the Limitations and Trade-offs
While powerful, calcination is not a universal solution and comes with specific operational challenges that must be managed for a successful outcome.
Precise Temperature Control is Critical
The success of calcination hinges on maintaining a precise temperature. If the temperature is too low, the reaction will be incomplete.
If the temperature is too high, it can cause sintering—where particles begin to fuse together—or even melting. This reduces surface area and can ruin the desired properties of the final product.
High Energy Consumption
Heating materials to the high temperatures required for calcination (often several hundred degrees Celsius) is an energy-intensive and costly process.
This operational expense is a significant factor in the economic viability of using calcination on an industrial scale.
Material Suitability
Calcination is only effective for materials that undergo the desired decomposition or phase transition below their melting point.
It is not a suitable process for materials that melt or degrade into undesirable forms at the required processing temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Calcination is a targeted tool. Its application depends entirely on the desired end-state of your material.
- If your primary focus is purification and concentration: Use calcination to drive off water, carbonates, and other volatile impurities, creating a more concentrated final product for metallurgy or chemical synthesis.
- If your primary focus is creating a reactive material: Employ calcination to induce phase transitions that increase surface area or create active sites, which is essential for manufacturing cements and catalysts.
- If your primary focus is achieving structural stability: Leverage calcination to complete phase changes, creating a uniform, pre-shrunk material that will not change in subsequent high-temperature applications like ceramics.
Ultimately, calcination is a foundational technique for intentionally engineering the properties of solid materials.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Purification & Concentration | Removes volatile impurities (water, CO₂) | Metallurgy, Chemical Synthesis |
| Material Activation | Increases surface area and reactivity | Catalyst & Cement Production |
| Thermal Decomposition | Breaks down complex compounds into simpler forms | Metal Extraction, Ceramics |
Optimize your material processing with KINTEK's advanced calcination solutions. Whether you're purifying ores, activating catalysts, or stabilizing ceramics, our lab equipment delivers precise temperature control and reliable performance. Let our experts help you achieve superior results—contact us today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the drying zone in a rotary kiln? Boost Efficiency with Modern Drying Solutions
- What is a rotary kiln reactor? A Guide to Industrial Thermal Processing
- How does precision temperature control impact TiAl alloy sintering? Master Microstructure Development
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- How does a rotary extractor work? Master Continuous High-Volume Solid Processing



















