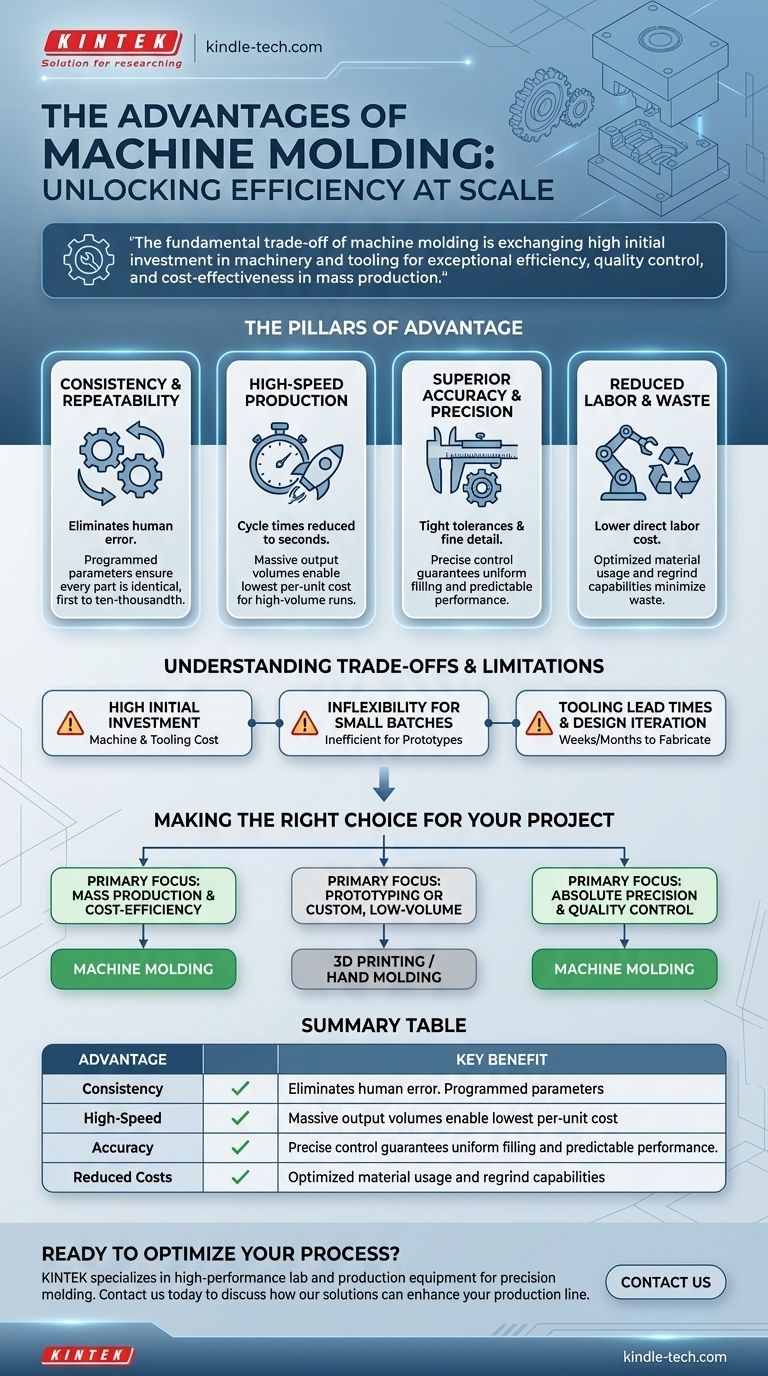
At its core, machine molding offers unparalleled consistency, speed, and precision for manufacturing parts at scale. Compared to manual methods, automation removes human variability, enabling the rapid production of identical components with tight tolerances, which drastically lowers the per-unit cost for high-volume runs.
The fundamental trade-off of machine molding is exchanging high initial investment in machinery and tooling for exceptional efficiency, quality control, and cost-effectiveness in mass production.

The Pillars of Machine Molding Advantage
The benefits of automating the molding process are not isolated; they work together to create a highly efficient production system. Understanding each pillar helps clarify why it is the standard for most modern manufacturing.
Unmatched Consistency and Repeatability
Machine molding operates on a programmed set of parameters—pressure, temperature, and time. Once calibrated, the machine executes these steps identically for every single cycle.
This eliminates the human error and natural variation inherent in hand molding. The first part produced is functionally identical to the ten-thousandth part, ensuring predictable performance and quality.
High-Speed Production Cycles
Automated systems are built for speed. Cycle times—the total time to produce one part—can be reduced to mere seconds, depending on the material and part complexity.
This high throughput allows for massive output volumes that are simply impossible to achieve with manual labor. This speed is a primary driver of the low per-unit cost in mass production.
Superior Dimensional Accuracy and Precision
Machines can exert immense and precisely controlled clamping and injection forces. This ensures the mold cavity is filled completely and uniformly every time.
The result is parts with extremely tight tolerances and fine detail, meeting a level of dimensional accuracy that manual processes struggle to replicate. This is critical for complex assemblies and high-performance applications like medical devices or automotive components.
Reduced Labor Costs and Material Waste
While requiring skilled technicians for setup and maintenance, a single operator can often oversee multiple automated machines. This dramatically reduces the direct labor cost assigned to each part produced.
Furthermore, automated processes are optimized to use the exact amount of material needed, and excess material like runners can often be reground and reused, minimizing waste.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No process is universally superior. The advantages of machine molding are balanced by significant considerations that make it unsuitable for certain applications.
High Initial Investment
The primary barrier to entry is cost. Industrial molding machines represent a significant capital expenditure, often ranging from tens of thousands to millions of dollars.
Beyond the machine itself, each unique part requires its own custom mold, known as tooling. The design and fabrication of this hardened steel tooling is a complex and expensive process.
Inflexibility for Small Batches
The significant time and cost associated with setup and tooling make machine molding highly inefficient for prototypes, one-offs, or very low-volume production runs.
The economic model only works when the high upfront costs are amortized over thousands or millions of identical parts. For small batches, the per-unit cost would be astronomical.
Tooling Lead Times and Design Iteration
Creating the production tooling can take weeks or even months. This lead time must be factored into the project timeline.
Once the tooling is made, modifying the part design is difficult and expensive. It often requires re-machining or fabricating an entirely new mold, discouraging frequent design changes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Selecting the correct molding process requires a clear understanding of your project's specific goals regarding volume, budget, and quality.
- If your primary focus is mass production and cost-efficiency: Machine molding is the definitive choice, as its speed and automation will deliver the lowest cost per part once the initial investment is absorbed.
- If your primary focus is prototyping or custom, low-volume parts: The high setup costs and long lead times make machine molding impractical; 3D printing or hand molding are far better alternatives.
- If your primary focus is absolute precision and quality control: The automated and repeatable nature of machine molding provides a level of consistency and adherence to tolerances that is difficult to achieve manually.
By aligning the process capabilities with your core objective, you can confidently choose the manufacturing path that ensures success.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Consistency & Repeatability | Eliminates human error, produces identical parts every cycle. |
| High-Speed Production | Drastically reduces cycle times for massive output volumes. |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Achieves tight tolerances and fine details for complex parts. |
| Reduced Costs | Lowers per-unit cost and material waste in mass production. |
Ready to Optimize Your Manufacturing Process?
Machine molding is the key to unlocking mass production efficiency, but selecting the right equipment is critical. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab and production equipment, including machinery that supports precision molding processes. Our expertise ensures you get the reliability and accuracy your high-volume projects demand.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how our solutions can enhance your production line, reduce costs, and maintain the superior quality your products require.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Single Punch Manual Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
- Lab Scale Rotary Single Punch Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum drying oven function in the final preparation stage of SnO2/MoS2 catalysts? Ensure Structural Purity
- How does a water bath work? Master Precise and Gentle Heating for Your Lab
- What are the technical advantages of microwave-assisted pyrolysis equipment? Higher Syngas Yield & Lower Tar Residues
- What are inert gases and what are their properties? Essential Stability for Industrial Processes
- How does high-temperature heat treatment affect PVA membranes? Optimizing Stability and Performance
- What is the composition of an evaporator? The 3 Essential Components for Efficient Evaporation
- Why is a laboratory oven required for pre-drying zeolite-titanate photocatalysts? Ensure Structural Integrity
- How to calculate coating thickness? Select the Right Method for Accurate Results



















