At its core, microwave sintering provides a fundamentally faster, more energy-efficient, and more uniform method for densifying materials compared to conventional furnace heating. By using microwave energy to heat the material from within, it dramatically reduces processing time, saves energy, and can produce materials with superior microstructures and properties.
The primary advantage of microwave sintering is not just speed, but control. It leverages a unique volumetric heating mechanism to achieve rapid, uniform densification, which in turn inhibits unwanted grain growth and unlocks superior final material properties that are often impossible to achieve with traditional methods.

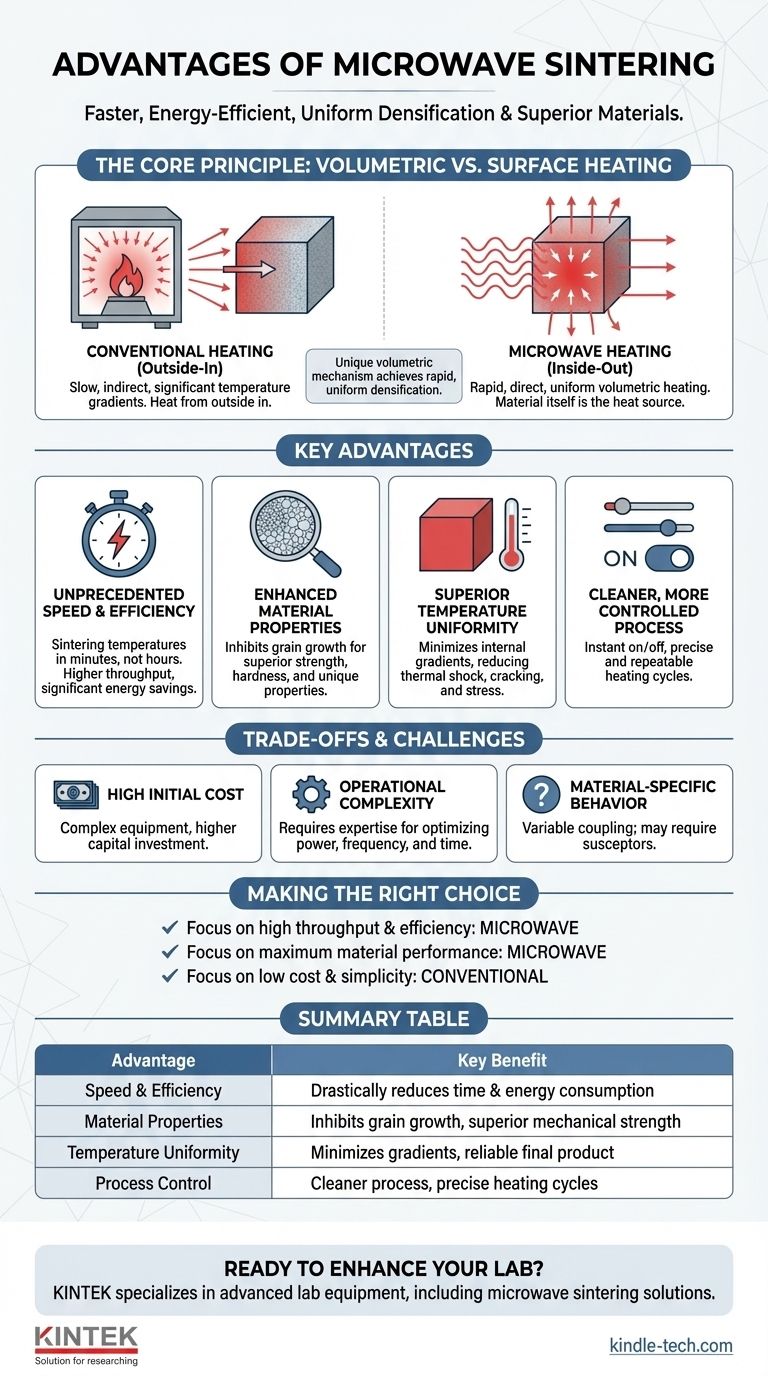
The Core Principle: Volumetric vs. Surface Heating
To understand the advantages, you must first grasp the fundamental difference in how heat is delivered. Conventional sintering is a slow, indirect process.
Conventional Heating: Outside-In
Traditional furnaces heat a material from the outside in, relying on thermal conduction to slowly bring the core of the part up to temperature. This creates significant temperature gradients, where the surface is much hotter than the interior.
This process is slow, inefficient, and can introduce thermal stresses into the material.
Microwave Heating: Inside-Out
Microwave sintering is a form of volumetric heating. It uses an electromagnetic field to energize the molecules throughout the entire volume of the material simultaneously.
The material itself becomes the source of the heat. This results in rapid, uniform temperature elevation with minimal internal gradients.
The Role of Dielectric Loss
This process works because many ceramic materials exhibit dielectric loss. When exposed to a high-frequency microwave field, the material's internal structure resists the rapidly changing electric field, generating friction and thus, heat.
For materials that don't respond well to microwaves, like certain forms of zirconia, special susceptor materials are used. These materials absorb microwave energy efficiently and convert it to thermal energy, which then heats the target material through radiation and conduction.
Key Advantages Explained
This unique heating mechanism translates directly into several significant operational and material science advantages.
Unprecedented Speed and Efficiency
Because the entire part heats at once, sintering temperatures are reached in minutes rather than hours. This drastically shortens the overall processing time.
This speed directly translates to higher production throughput and significant energy savings, as the equipment is running for a fraction of the time required by a conventional furnace.
Enhanced Material Properties
The rapid heating rate is crucial for controlling the final microstructure of the material. It allows the material to densify quickly while effectively inhibiting grain growth.
Smaller, more uniform grains typically result in materials with superior mechanical strength, hardness, and in some cases, improved translucency or conductivity. This allows for the creation of advanced ceramic products that cannot be made using slower, conventional methods.
Superior Temperature Uniformity
By heating the entire volume at once, microwave sintering minimizes the internal temperature gradients that plague conventional methods. This uniformity reduces the risk of thermal shock, cracking, and internal stresses.
The result is a more homogenous, reliable final product with greater structural integrity.
A Cleaner, More Controlled Process
Microwave heating is a clean process that can be turned on and off almost instantly. This provides a high degree of control over the heating cycle, allowing for precise and repeatable processing profiles.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, microwave sintering is not a universal solution. Acknowledging its limitations is critical for making an informed decision.
High Initial Equipment Cost
Microwave sintering furnaces are technologically complex and generally have a higher upfront capital cost compared to traditional resistance-heated furnaces.
Operational Complexity
Mastering the technology requires a higher level of expertise. The ideal microwave power, frequency, and cycle time must be carefully tuned for different materials and geometries, making the operation more complex than a standard furnace.
Material-Specific Behavior
As noted, not all materials couple with microwave energy in the same way. This requires careful material characterization and may necessitate the use of susceptors, adding another variable to the process.
Thermal Management
While the heating is fast, effectively and rapidly cooling the furnace chamber and the material can be a challenge. This may require auxiliary cooling systems, adding to the system's complexity and cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right sintering method depends entirely on your project's primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and energy efficiency: Microwave sintering is the superior choice due to its dramatically reduced cycle times and lower energy consumption per part.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum material performance: Microwave sintering's ability to create fine-grained microstructures makes it essential for developing advanced materials with top-tier strength and unique properties.
- If your primary focus is minimizing upfront cost and operational simplicity: A conventional furnace may be more practical, especially for low-volume production or for materials that do not require highly optimized microstructures.
Ultimately, adopting microwave sintering is a strategic decision to leverage a more advanced heating technology for superior material outcomes and process efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Speed & Efficiency | Drastically reduces processing time and energy consumption compared to conventional furnaces. |
| Material Properties | Inhibits grain growth, leading to superior mechanical strength and microstructural uniformity. |
| Temperature Uniformity | Minimizes internal gradients and thermal stresses for a more reliable final product. |
| Process Control | Offers a cleaner process with precise, repeatable heating cycles. |
Ready to enhance your lab's material processing capabilities?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including microwave sintering solutions. Our expertise can help you achieve faster production times, significant energy savings, and unlock superior material properties for your advanced ceramics and other materials.
Contact our experts today to discuss how microwave sintering can transform your R&D or production workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different sintering methods? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material & Application
- What is the SPS process of spark plasma sintering? A Guide to Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What is the mechanism of SPS process? A Deep Dive into Rapid, Low-Temperature Sintering
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts
- What are the parameters for spark plasma sintering? Master Speed, Pressure & Temperature Control



















