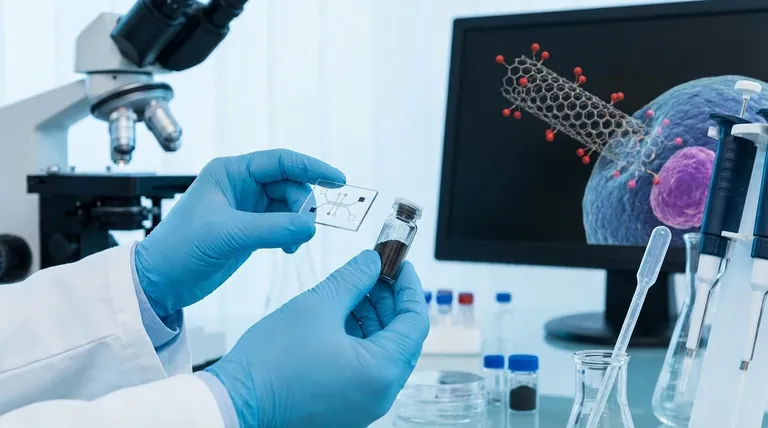
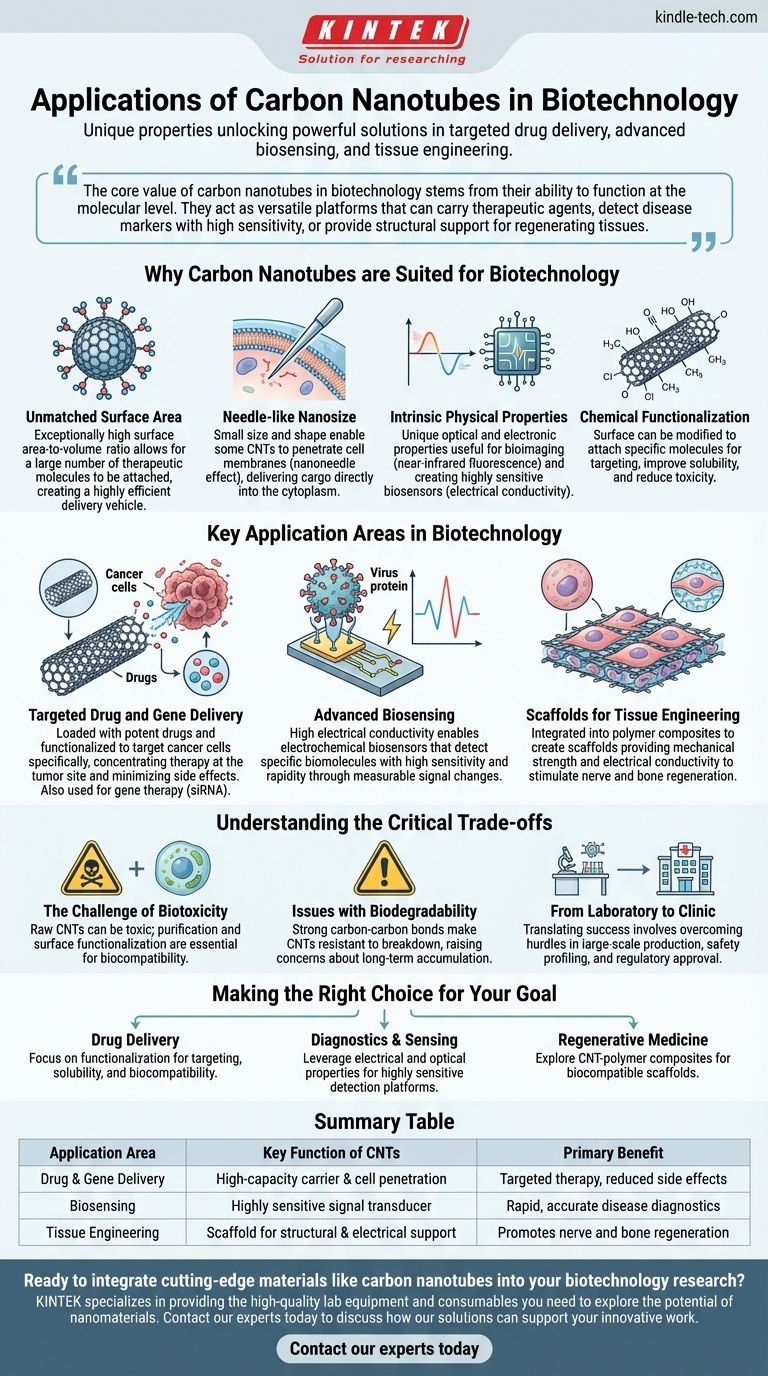
The unique properties of carbon nanotubes have unlocked a range of powerful applications in biotechnology, primarily focused on targeted drug delivery, advanced biosensing, and tissue engineering. Their nanoscale dimensions and high surface area allow them to interact with biological systems in ways that conventional materials cannot, making them a significant tool in modern biomedical research.
The core value of carbon nanotubes in biotechnology stems from their ability to function at the molecular level. They act as versatile platforms that can carry therapeutic agents, detect disease markers with high sensitivity, or provide structural support for regenerating tissues.

Why Carbon Nanotubes are Suited for Biotechnology
The potential of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in medicine and biology is not accidental. It is a direct result of their fundamental physical and chemical characteristics, which allow them to bridge the gap between synthetic materials and living systems.
Unmatched Surface Area
CNTs possess an exceptionally high surface area-to-volume ratio. This allows for a large number of therapeutic molecules, such as drugs or genes, to be attached to their surface, creating a highly efficient delivery vehicle.
Needle-like Nanosize
Their small size and needle-like shape enable some types of CNTs to penetrate cell membranes. This unique ability, often called the "nanoneedle" effect, provides a direct pathway for delivering cargo into the cytoplasm of a target cell.
Intrinsic Physical Properties
CNTs have unique optical and electronic properties. Their intrinsic fluorescence in the near-infrared spectrum is useful for bioimaging, as biological tissues are more transparent in this range. Their electrical conductivity is foundational to their use in highly sensitive biosensors.
Chemical Functionalization
The surface of a carbon nanotube can be chemically modified, or functionalized. This process is critical for attaching specific molecules for targeting (e.g., antibodies that bind to cancer cells), improving solubility in water, and significantly reducing potential toxicity.
Key Application Areas in Biotechnology
While many applications are still in the research phase, the results demonstrate transformative potential across several key domains of biotechnology and medicine.
Targeted Drug and Gene Delivery
CNTs can be loaded with potent chemotherapy drugs and functionalized to target cancer cells specifically. This approach concentrates the therapeutic agent at the tumor site, minimizing damage to healthy surrounding tissues and reducing systemic side effects. They are also used to deliver genetic material like siRNA for gene therapy.
Advanced Biosensing
The high electrical conductivity of CNTs makes them ideal for creating electrochemical biosensors. When a specific biomolecule (like a virus protein or a disease biomarker) binds to a CNT-based sensor, it causes a measurable change in the electrical signal, enabling highly sensitive and rapid diagnostics.
Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering
In regenerative medicine, CNTs can be integrated into polymer composites to create scaffolds for growing new tissue. They provide mechanical strength and electrical conductivity, which can help stimulate the growth and differentiation of cells, particularly for nerve and bone regeneration.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
The promise of CNTs is tempered by significant challenges that must be addressed for safe and effective clinical use. Objectivity requires acknowledging these limitations.
The Challenge of Biotoxicity
In their raw, unmodified state, some carbon nanotubes can be toxic to cells, potentially causing inflammation and oxidative stress. Purification and surface functionalization are absolutely essential steps to ensure biocompatibility and minimize adverse effects.
Issues with Biodegradability
CNTs are composed of strong carbon-carbon bonds, making them resistant to breaking down in the body. This raises concerns about potential long-term accumulation and its consequences, an area of active and critical research.
From Laboratory to Clinic
Translating laboratory success into approved clinical products is a major hurdle. This involves developing methods for large-scale, consistent production, establishing comprehensive safety profiles, and navigating a complex regulatory approval process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The application of carbon nanotubes is highly dependent on the specific objective. Your approach must be tailored to the problem you are trying to solve.
- If your primary focus is drug delivery: Concentrate on surface functionalization techniques that improve targeting, solubility, and biocompatibility.
- If your primary focus is diagnostics and sensing: Leverage the unique electrical and optical properties of CNTs to design highly sensitive detection platforms for specific biomarkers.
- If your primary focus is regenerative medicine: Explore CNT-polymer composites to create biocompatible scaffolds that provide the right structural and electrical cues to promote cell growth.
By understanding both their immense potential and their inherent challenges, researchers can effectively harness carbon nanotubes to engineer the next generation of biomedical solutions.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Function of CNTs | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Drug & Gene Delivery | High-capacity carrier & cell penetration | Targeted therapy, reduced side effects |
| Biosensing | Highly sensitive signal transducer | Rapid, accurate disease diagnostics |
| Tissue Engineering | Scaffold for structural & electrical support | Promotes nerve and bone regeneration |
Ready to integrate cutting-edge materials like carbon nanotubes into your biotechnology research?
KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need to explore the potential of nanomaterials. Whether you are developing new drug delivery systems, creating sensitive diagnostic sensors, or engineering tissues, having the right tools is critical for success.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can support your innovative work and help you navigate the challenges of translating nanomaterial research from the lab to the clinic.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tubes
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Professional Cutting Tools for Carbon Paper Cloth Diaphragm Copper Aluminum Foil and More
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- What are 4 disadvantages of brazing? Understanding the Critical Limitations of This Joining Method
- What are the strengths of brazing? Achieve Strong, Clean, and Precise Metal Joining
- What is the function of a BN inner liner in a graphite mold during Flash Sintering? Master Precise Current Control
- What are the disadvantages of brazing? Understanding the key limitations and trade-offs.
- What are ceramic tubes used for? Essential for Extreme Heat, Insulation & Purity



















