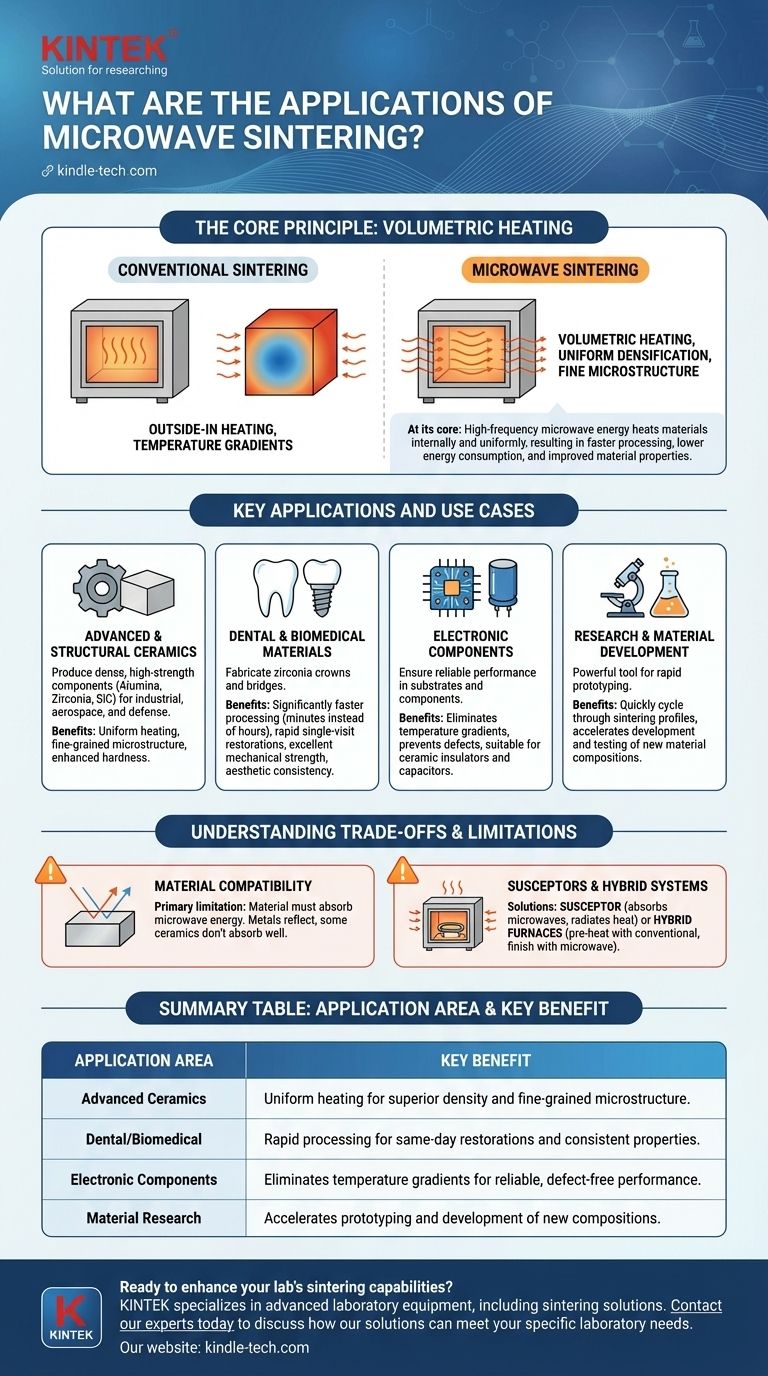
At its core, microwave sintering is a specialized thermal process used to increase the density and strength of materials, primarily advanced ceramics. It leverages high-frequency microwave energy to heat materials internally and uniformly, resulting in significantly faster processing times, lower energy consumption, and improved material properties compared to conventional furnace heating.
The true value of microwave sintering is not just its speed, but its ability to heat a material volumetrically—from the inside out. This unique mechanism produces more uniform microstructures and enables the creation of high-performance components that are often difficult to achieve with traditional methods.

The Core Principle: How Microwave Sintering Works
To understand its applications, you must first understand its mechanism. Unlike a conventional furnace that heats from the outside-in, microwave sintering works on a fundamentally different principle.
From Microwaves to Heat
The process relies on the dielectric properties of a material. When subjected to a microwave electromagnetic field, polar molecules within the material rapidly try to align themselves with the field. This constant molecular friction generates heat directly and simultaneously throughout the entire volume of the material.
The Advantage of Volumetric Heating
Conventional sintering heats the surface of an object first, with heat slowly conducting toward the core. This creates a temperature gradient, which can lead to internal stresses, inconsistent density, and larger grain growth.
Microwave sintering heats the entire object at once, a process known as volumetric heating. This minimizes temperature gradients, promoting uniform densification and a finer, more consistent final microstructure, which often translates to superior mechanical properties.
The Standard Sintering Process
A typical cycle involves placing the material (often a compacted powder, or "green body") into a microwave furnace. The chamber may be evacuated or filled with a specific atmosphere before microwave energy is applied to heat the part to a target temperature, where it is held for a specified time to allow densification to complete before being cooled.
Key Applications and Use Cases
The unique advantages of microwave sintering make it ideal for applications where speed, energy efficiency, and material uniformity are critical.
Advanced and Structural Ceramics
This is the primary application area. Microwave sintering is used to produce dense, high-strength components from materials like alumina, zirconia, and silicon carbide for demanding industrial, aerospace, and defense applications. The rapid, uniform heating preserves a fine-grained microstructure, enhancing hardness and fracture toughness.
Dental and Biomedical Materials
The dental industry uses microwave sintering to fabricate zirconia crowns and bridges. The process is significantly faster than conventional methods—reducing what could take hours to just minutes—allowing for rapid, single-visit restorations. The uniformity also ensures excellent mechanical strength and aesthetic consistency.
Electronic Components
Materials used in electronic substrates and components require exceptional uniformity to ensure reliable performance. Microwave sintering provides this by eliminating the temperature gradients that can cause defects, making it suitable for producing ceramic insulators, capacitors, and other sensitive parts.
Research and Material Development
For materials scientists, microwave sintering is a powerful tool for rapid prototyping. The ability to quickly cycle through different sintering profiles accelerates the development and testing of new material compositions and manufacturing processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, microwave sintering is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is highly dependent on the material and process parameters.
The Challenge of Material Compatibility
The primary limitation is that the material must be able to absorb microwave energy effectively. Metals, for instance, reflect microwaves, while some highly pure or non-polar ceramics do not absorb them well, especially at low temperatures.
The Role of Susceptors and Hybrid Systems
To overcome this, two strategies are used. A susceptor—a material that strongly absorbs microwaves (like silicon carbide)—can be placed alongside the target material to absorb energy and transfer it as radiant heat.
Alternatively, hybrid furnaces combine microwave energy with conventional heating elements. The conventional heaters pre-heat the material to a temperature where it begins to absorb microwaves effectively on its own.
Thermal Management and Cooling
The extreme speed of microwave heating can also present challenges. Rapidly cooling the furnace and the high-density components without introducing thermal shock requires careful engineering and, in some cases, auxiliary cooling systems, which can add complexity to the equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right sintering method depends entirely on your material, production goals, and performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is process speed and energy efficiency: Microwave sintering is an excellent choice for compatible ceramic materials, drastically reducing production cycles.
- If your primary focus is material uniformity and fine microstructure: The volumetric heating of microwaves offers significant advantages for creating high-performance parts with superior mechanical properties.
- If you are working with non-microwave-absorbent materials: You must consider a hybrid system or the use of susceptors, which adds a layer of complexity to the process.
Understanding these principles allows you to move beyond simply choosing a heating method and instead deliberately engineer a process to achieve a specific material outcome.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Benefit of Microwave Sintering |
|---|---|
| Advanced Ceramics | Uniform heating for superior density and fine-grained microstructure. |
| Dental/Biomedical | Rapid processing for same-day restorations and consistent material properties. |
| Electronic Components | Eliminates temperature gradients for reliable, defect-free performance. |
| Material Research | Accelerates prototyping and development of new compositions. |
Ready to enhance your lab's sintering capabilities?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment, including sintering solutions for research and production. Our expertise can help you achieve faster cycle times, improved material properties, and greater energy efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What makes zirconia translucent? The Science Behind Modern Dental Aesthetics
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects



















