At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a sophisticated coating process used to apply a very thin, high-performance film onto a wide range of products. Its applications span industries from aerospace and automotive, where it provides wear resistance to engine components, to medical devices and consumer goods, where it offers a durable, decorative, and biocompatible finish on everything from surgical tools to kitchen faucets.
The true value of PVD coating lies not just in its wide range of applications, but in its ability to fundamentally enhance a product's properties. It is a strategic choice to add specific characteristics—like extreme hardness, corrosion resistance, or a premium aesthetic—that the base material alone cannot provide.

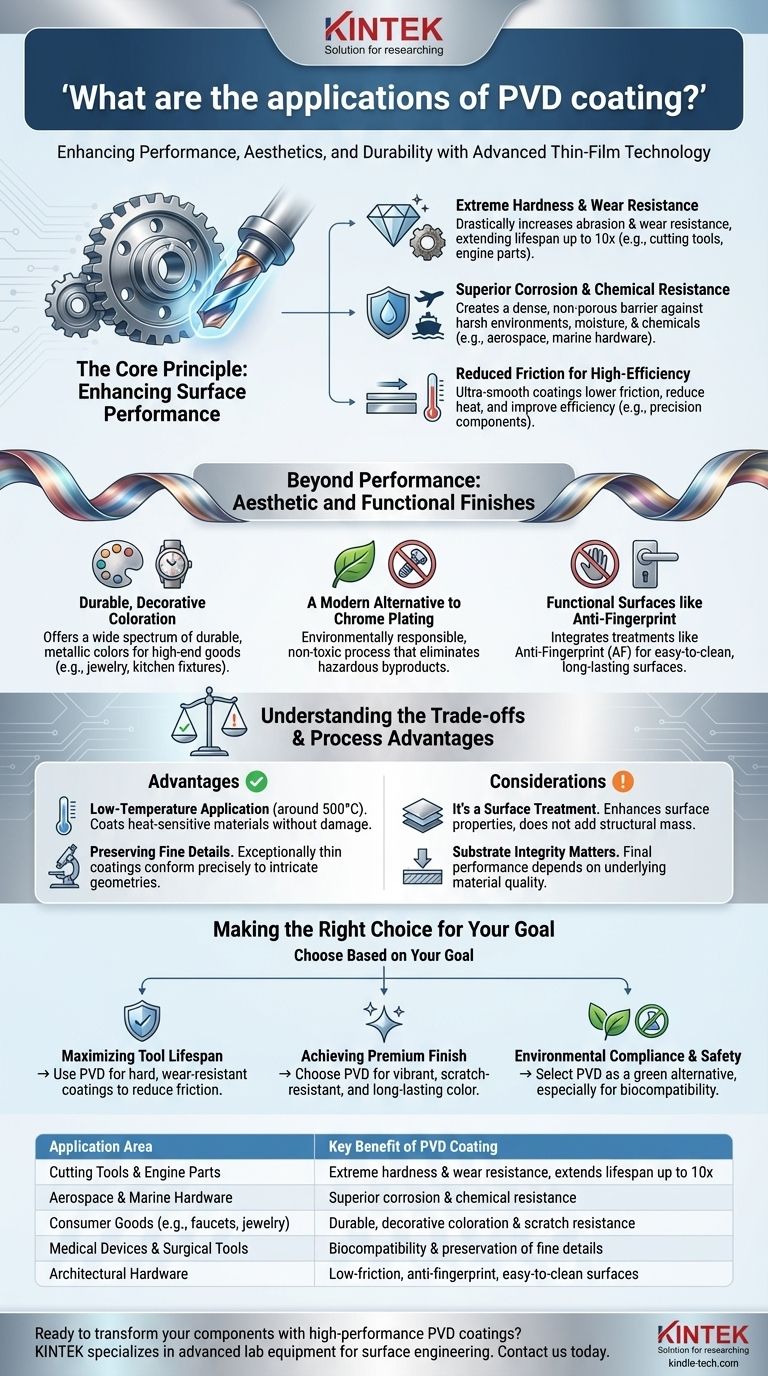
The Core Principle: Enhancing Surface Performance
The primary driver for using PVD is to improve the functional performance of a substrate material. The coating acts as a protective, high-performance armor that dramatically extends the life and reliability of the underlying part.
Extreme Hardness and Wear Resistance
Many applications demand durability far beyond what the base metal can offer. PVD applies a ceramic or composite coating that is exceptionally hard.
This drastically increases resistance to abrasion and wear. It's why PVD is essential for cutting tools, drill bits, and engine components like pistons, where it can extend a product's functional lifespan by up to ten times.
Superior Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
PVD coatings create a dense, non-porous barrier that seals the substrate from its environment. This makes it a critical technology in industries where components are exposed to harsh conditions.
This is particularly valuable in aerospace, automotive, and marine hardware, where parts must resist corrosion from moisture, salt, and other chemical agents.
Reduced Friction for High-Efficiency Components
The coatings are not just hard; they are also incredibly smooth, which significantly reduces the coefficient of friction.
For high-performance applications like engine parts or precision cutting tools, lower friction means less heat generation, improved efficiency, and smoother operation. The thin nature of the coating (typically 3-5μm) also preserves the sharpness of cutting edges.
Beyond Performance: Aesthetic and Functional Finishes
While functional improvement is a key driver, PVD is also widely used for its ability to produce stunning, durable decorative finishes that are both beautiful and practical.
Durable, Decorative Coloration
PVD can deposit a wide spectrum of colors with a metallic luster that is far more durable than traditional paint or plating.
This makes it a popular choice for high-end consumer goods where aesthetics and longevity are paramount, including jewelry, kitchen and bath fixtures, eyeglass frames, musical instruments, and premium writing tools.
A Modern Alternative to Chrome Plating
PVD is often used as a "greener" and superior alternative to traditional electroplating, such as hard chrome.
The PVD process produces no toxic byproducts or hazardous waste, making it an environmentally responsible choice. The resulting finish is also more durable and corrosion-resistant.
Functional Surfaces like Anti-Fingerprint
In modern architectural and product design, maintaining a clean appearance is crucial. PVD coatings can be combined with other treatments, like an anti-fingerprint (AF) coating, directly inside the deposition chamber.
This integrated process creates a long-lasting, easy-to-clean surface ideal for high-touch-point areas like door hardware and appliance panels, where aesthetics must be preserved during daily use.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Process Advantages
Choosing PVD involves understanding its unique process characteristics, which create both significant advantages and certain considerations. It is not a one-size-fits-all solution.
Advantage: Low-Temperature Application
PVD is a relatively low-temperature process, typically operating around 500°C.
This is a major advantage over other coating methods that require high heat, as it allows for the coating of heat-sensitive materials without the risk of thermal damage, distortion, or altering the substrate's core properties.
Advantage: Preserving Fine Details
Because PVD coatings are exceptionally thin, they conform precisely to the original surface geometry.
This is critical for applications like milling cutters and surgical tools, where preserving the sharpness of a blade or the intricate details of a component is non-negotiable.
Consideration: It's a Surface Treatment, Not a Structural Fix
PVD adds incredible surface properties but does not change the bulk characteristics of the substrate. It is a thin film, not a method for adding structural mass.
The integrity of the final product still depends on the strength and quality of the underlying material. The coating enhances, it does not create.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
PVD coating is a versatile tool, and its best application depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing tool or component lifespan: Use PVD to apply hard, wear-resistant coatings to cutting tools, molds, and engine parts to dramatically reduce friction and wear.
- If your primary focus is achieving a premium, durable finish: Choose PVD for consumer products, architectural hardware, or automotive trim to get a vibrant, long-lasting color that resists scratches and fading.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance and safety: Select PVD as a green alternative to traditional plating, especially for medical devices or components where biocompatibility and the absence of toxic chemicals are critical.
Ultimately, adopting PVD is a strategic decision to engineer a better surface, transforming a standard component into a high-performance, durable, and valuable product.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Benefit of PVD Coating |
|---|---|
| Cutting Tools & Engine Parts | Extreme hardness & wear resistance, extends lifespan up to 10x |
| Aerospace & Marine Hardware | Superior corrosion & chemical resistance |
| Consumer Goods (e.g., faucets, jewelry) | Durable, decorative coloration & scratch resistance |
| Medical Devices & Surgical Tools | Biocompatibility & preservation of fine details |
| Architectural Hardware | Low-friction, anti-fingerprint, easy-to-clean surfaces |
Ready to transform your components with high-performance PVD coatings? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for surface engineering. Whether you're in aerospace, medical device manufacturing, or consumer goods, our solutions help you achieve superior durability, aesthetics, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's coating needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















