At its core, spark plasma sintering (SPS) is a specialized manufacturing technique used to create highly dense, high-performance materials that are difficult or impossible to produce with conventional methods. Its primary applications involve processing advanced ceramics, refractory metals with extremely high melting points, and novel composite materials where preserving a unique microstructure is critical.
The true value of spark plasma sintering lies in its ability to consolidate materials at lower temperatures and in a fraction of the time. This unique combination of speed and control makes it the ideal choice for fabricating advanced materials while preserving delicate nano-scale or amorphous structures.

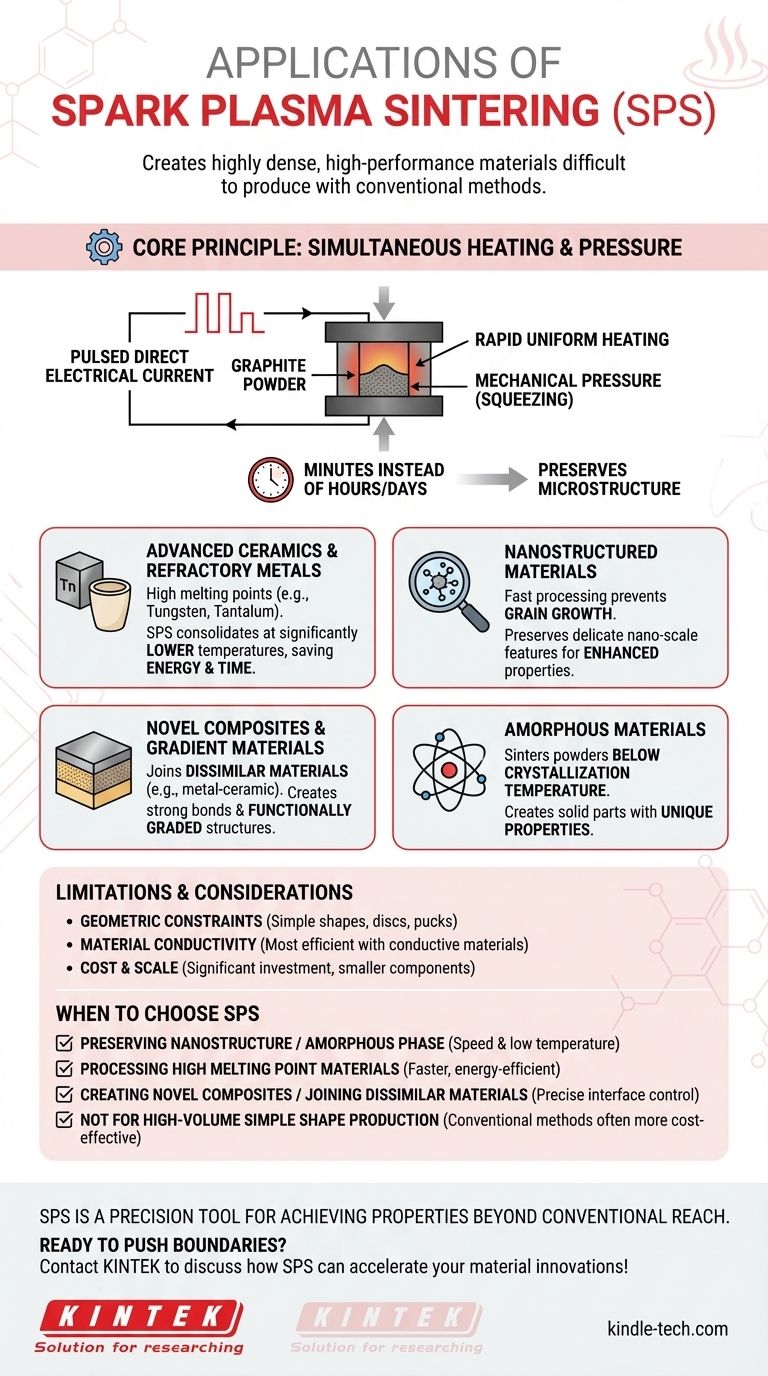
The Core Principle: Why SPS Is Different
To understand its applications, you must first understand how SPS works. Unlike a traditional furnace that slowly heats a material from the outside in, SPS uses a different approach.
Simultaneous Heating and Pressure
A pulsed direct electrical current is passed directly through a conductive die (typically graphite) and, often, through the material powder itself. This creates rapid, uniform heating throughout the sample.
At the same time, mechanical pressure is applied, squeezing the particles together. This combination of direct heat and pressure dramatically accelerates the sintering process.
The Impact of Speed
The entire process, from heating to cooling, can be completed in minutes rather than the hours or even days required for conventional sintering.
This speed is the key to its unique capabilities. It allows materials to be densified before undesirable changes, like grain growth or phase transitions, can occur, preserving the material's intended properties.
Key Application Areas
The unique characteristics of SPS make it exceptionally well-suited for specific classes of advanced materials.
Advanced Ceramics & Refractory Metals
Materials like tungsten, tantalum, and advanced ceramics have exceptionally high melting points, making them difficult to process.
SPS can consolidate these materials into dense solid forms at temperatures hundreds of degrees lower than their melting point, saving enormous amounts of energy and time.
Nanostructured Materials
Creating materials with nano-scale features is one thing; preserving them during consolidation is another. Conventional high-temperature sintering often destroys these delicate structures.
Because SPS is so fast and operates at lower temperatures, it can sinter nano-crystalline powders into a solid part without destroying their refined microstructure. This is critical for materials with enhanced mechanical or electrical properties.
Novel Composites and Gradient Materials
SPS excels at joining dissimilar materials, such as metals to ceramics, to create advanced composites.
The rapid, localized heating allows for strong bonds to form at the interface without causing extensive, damaging chemical reactions between the different layers. This enables the creation of functionally graded materials where the composition changes gradually across the part.
Amorphous Materials
Amorphous materials, like metallic glasses, lack a crystalline structure. This structure is the source of their unique properties but is easily lost when heated.
The precise temperature control and short processing times of SPS make it possible to sinter these powders below their crystallization temperature, creating solid amorphous parts that were previously impossible to fabricate.
Limitations and Practical Considerations
While powerful, SPS is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Geometric Constraints
The most common SPS setup involves a cylindrical graphite die. This means the technique is best suited for producing simple shapes like discs, pucks, or blocks. Complex, near-net-shape parts are generally not feasible.
Material Conductivity
The process is most efficient when the material being sintered has some electrical conductivity, allowing the current to pass through it directly. While insulating materials like some ceramics can be sintered, they rely solely on heat conducted from the die, which can reduce efficiency.
Cost and Scale
SPS equipment is specialized and represents a significant capital investment compared to conventional furnaces. Furthermore, the process is typically used for smaller, high-value components rather than large-scale industrial production.
When to Choose Spark Plasma Sintering
Your decision to use SPS should be driven by the specific properties you need to achieve in your final material.
- If your primary focus is preserving a nanostructure or amorphous phase: SPS is one of the best available techniques due to its speed and low processing temperatures.
- If your primary focus is processing materials with extremely high melting points: SPS provides a faster, more energy-efficient path to creating dense parts compared to conventional high-temperature methods.
- If your primary focus is creating novel composites or joining dissimilar materials: SPS offers a level of control over the interface between materials that is difficult to achieve with other methods.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of simple shapes from common metals: Conventional sintering or other manufacturing processes are almost always more cost-effective.
Ultimately, spark plasma sintering is a precision tool for achieving material properties that lie beyond the reach of conventional processing.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Benefit of SPS |
|---|---|
| Advanced Ceramics & Refractory Metals | Consolidates materials at significantly lower temperatures. |
| Nanostructured Materials | Preserves delicate nano-scale features during densification. |
| Novel Composites & Gradient Materials | Joins dissimilar materials (e.g., metal-ceramic) with strong bonds. |
| Amorphous Materials | Sinters powders without causing crystallization. |
Ready to push the boundaries of your materials research?
Spark plasma sintering from KINTEK enables you to fabricate advanced materials with precision, preserving critical microstructures that are impossible with conventional methods. Whether you are developing nanostructured ceramics, novel composites, or amorphous metals, our SPS solutions provide the speed and control you need.
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including SPS systems, to serve the evolving needs of research and development laboratories.
Contact our experts today to discuss how SPS can accelerate your material innovations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the mechanism of SPS process? A Deep Dive into Rapid, Low-Temperature Sintering
- What are the parameters for spark plasma sintering? Master Speed, Pressure & Temperature Control
- What are the steps in spark plasma sintering? Achieve Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What is the plasma sintering technique? Achieve Rapid, High-Density Material Fabrication
- What is the SPS process of spark plasma sintering? A Guide to Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification



















