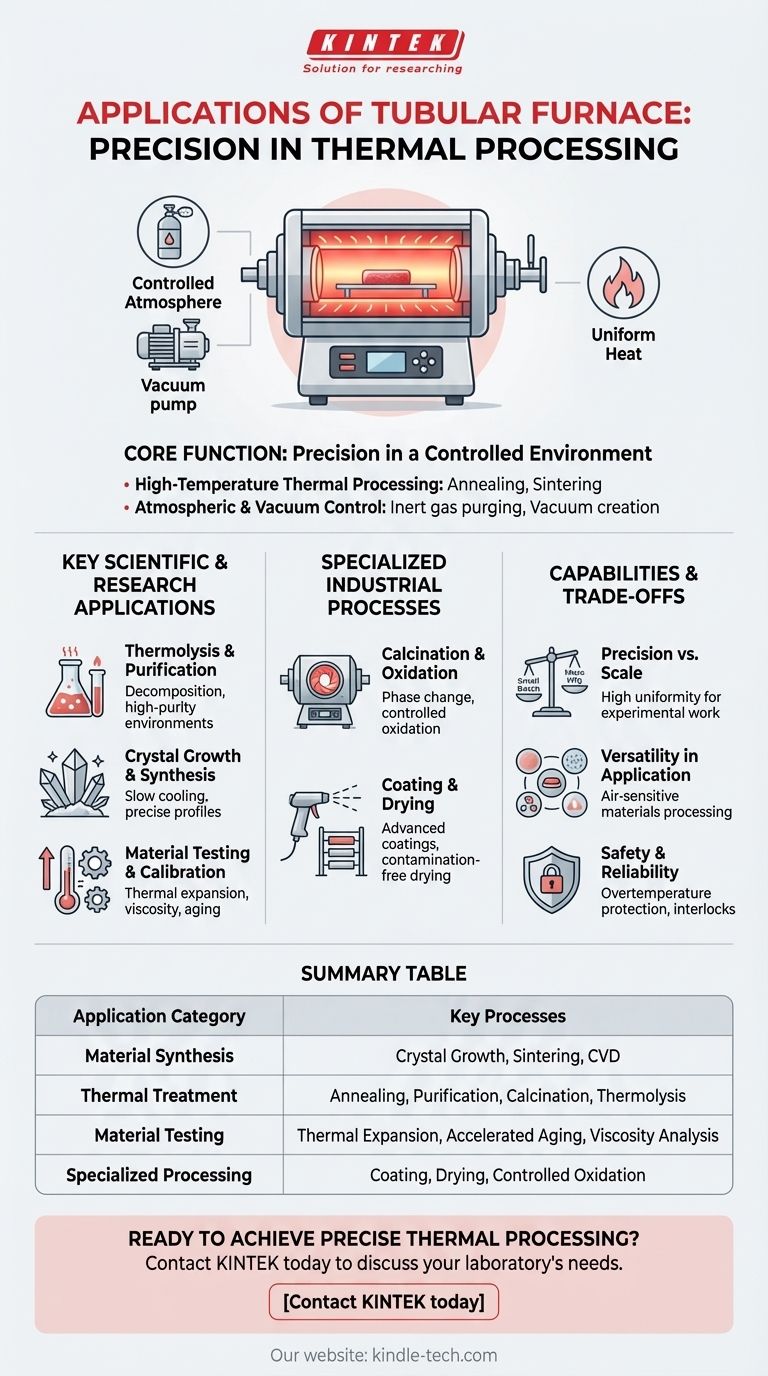
At its core, a tubular furnace is a high-precision heating device used for a wide range of thermal processes on small samples. Its primary applications include material synthesis, purification, annealing, coating, drying, and various forms of material testing within controlled atmospheric or vacuum conditions.
The true value of a tubular furnace isn't just its ability to reach high temperatures, but its capacity to create a highly uniform and precisely controlled environment. This makes it an indispensable tool for scientific research and specialized small-batch production where process repeatability and material purity are paramount.

Core Function: Precision in a Controlled Environment
A tubular furnace provides a cylindrical heating chamber, which is ideal for creating uniform heat distribution around a sample. Its design is optimized for control over the sample's immediate surroundings.
High-Temperature Thermal Processing
The most fundamental application is simply heating materials to very high temperatures. This is required for tasks like annealing metals to increase their ductility, sintering powders into a solid mass, or modeling materials like ores and iron for analysis.
Atmospheric and Vacuum Control
Many materials react with oxygen at high temperatures, leading to unwanted oxidation. Tubular furnaces excel at creating an inert atmosphere by purging the chamber with gases like nitrogen or argon, or by creating a vacuum to remove reactive gases entirely.
Creating Temperature Gradients
Advanced models feature multiple, independently controlled heating zones (e.g., three-zone controls). This allows operators to create precise temperature gradients along the length of the tube, a critical capability for processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and crystal growing.
Key Scientific and Research Applications
These furnaces are fixtures in academic, government, and industrial research labs due to their versatility and precision.
Thermolysis and Purification
Thermolysis is the decomposition of materials using heat. A tube furnace provides the stable, high-temperature environment needed to study these reactions for both organic and inorganic compounds. This is also a common method for purification.
Crystal Growth and Synthesis
Growing high-purity single crystals requires slow, controlled cooling across a precise temperature profile. The excellent thermal uniformity and gradient capabilities of a tube furnace make it ideal for this demanding application.
Material Testing and Calibration
The controlled environment is perfect for testing material properties. Common uses include analyzing thermal expansion, testing sample viscosity at various temperatures, and conducting accelerated aging studies to predict a material's lifespan.
Specialized Industrial Processes
While primarily a research tool, tubular furnaces are also used for developing and executing specialized, small-scale industrial processes.
Calcination and Oxidation
Calcination involves heating a solid to a high temperature to cause a phase change or remove a volatile fraction. Controlled oxidation, where oxygen is intentionally introduced, is another key process. Rotary tube furnaces are often used to ensure the entire sample is processed uniformly.
Coating and Drying
The furnace's ability to maintain a specific temperature for an extended period is leveraged for advanced coating applications and for drying sensitive materials without contamination from combustion byproducts.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Capabilities
While highly capable, a tubular furnace is a specialized instrument. Understanding its strengths and limitations is key to using it effectively.
Precision vs. Scale
The defining advantage of a tubular furnace is its high temperature control accuracy and uniformity. However, this precision is generally applied to small samples, making it ideal for experimental work and small-batch production, not mass manufacturing.
Versatility in Application
The ability to operate with an optional atmosphere or vacuum vastly expands the range of possible applications. This allows for the processing of air-sensitive materials that would be impossible in a standard furnace.
Safety and Reliability
Modern tubular furnaces are designed to be safe and simple to operate. Features like overtemperature protection and safety interlocks that cut power when the door is opened ensure reliable and secure operation in a laboratory setting.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal processing method depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is fundamental materials research: A multi-zone tubular furnace offers unmatched control over atmosphere, temperature uniformity, and thermal gradients for synthesizing novel materials.
- If your primary focus is process development: Use a tubular furnace to test reactions like thermolysis, calcination, or annealing on a small, cost-effective scale before investing in larger equipment.
- If your primary focus is quality control and testing: The device's stability makes it the perfect platform for analyzing material properties like thermal expansion and performing accelerated aging tests.
Ultimately, the tubular furnace is a powerful tool for anyone who needs to subject a sample to a precise and repeatable thermal profile.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes |
|---|---|
| Material Synthesis | Crystal Growth, Sintering, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) |
| Thermal Treatment | Annealing, Purification, Calcination, Thermolysis |
| Material Testing | Thermal Expansion, Accelerated Aging, Viscosity Analysis |
| Specialized Processing | Coating, Drying, Oxidation under controlled atmospheres |
Ready to achieve precise thermal processing for your lab?
A tubular furnace from KINTEK provides the uniform heating, atmospheric control, and temperature gradients essential for advanced material research, synthesis, and testing. Whether you are developing new materials, running quality control tests, or scaling a specialized process, our lab equipment delivers the reliability and accuracy you need.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how a tubular furnace can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and drive your projects forward. Our experts are ready to help you select the ideal solution for your specific application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis



















