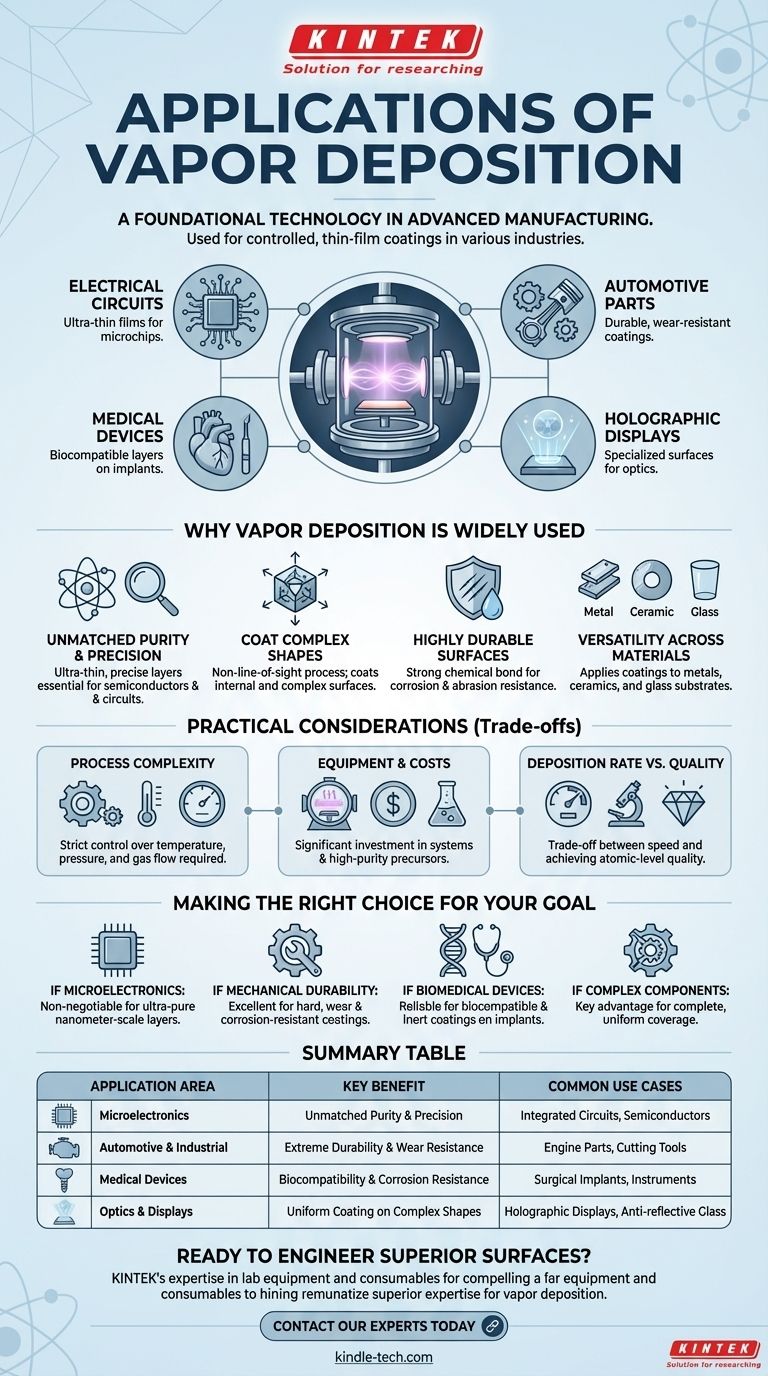
Vapor deposition is a foundational technology in modern advanced manufacturing. It is used to apply highly controlled, thin-film coatings in a variety of industries, with key applications including the creation of electrical circuits, durable coatings for automotive parts, biocompatible layers on medical devices, and even specialized surfaces for holographic displays.
The true value of vapor deposition lies not just in the products it creates, but in its unique ability to deposit exceptionally pure, uniform, and durable films onto surfaces of any shape—a capability that enables the very existence of many high-performance technologies.

Why Vapor Deposition is So Widely Used
The applications of vapor deposition are a direct result of its core technical advantages. The process involves reacting chemical gases in a vacuum chamber, which then deposit a solid material onto a substrate. This method provides a level of control that is difficult to achieve with other coating techniques.
Unmatched Purity and Precision
Vapor deposition allows for the creation of ultra-thin films, often just a few atoms thick. This makes it the go-to process for the semiconductor industry.
The layers of conductive and insulating materials that make up an electrical circuit or microchip require extreme purity and precise thickness, which this process delivers reliably.
The Ability to Coat Complex Shapes
Many coating methods, like spray painting, are "line-of-sight," meaning they can only coat surfaces they can directly "see."
Vapor deposition is a non-line-of-sight process. The precursor gases fill the entire chamber, ensuring that even complex, intricate, and internal surfaces receive a perfectly uniform coating.
Creating Highly Durable and Resistant Surfaces
The deposited films form a strong chemical bond with the substrate, creating coatings that are exceptionally durable.
These layers can be engineered for specific properties like corrosion resistance, abrasion resistance, and tolerance for extreme temperatures, making them ideal for high-stress environments like automotive engines or industrial tools.
Versatility Across Materials
The process is incredibly versatile and is not limited to a single type of substrate.
It can be used to apply high-performance coatings to a wide range of materials, including metals, ceramics, and glass, significantly broadening its industrial applications.
Understanding the Practical Considerations
While powerful, vapor deposition is not a universal solution. As an advisor, it's crucial to understand the trade-offs involved in its implementation.
Process Complexity
Achieving the high purity and precision that vapor deposition is known for requires strict control over variables like temperature, pressure, and the flow of precursor gases. While the concept is straightforward, optimization for high-volume production can be complex.
Equipment and Material Costs
Setting up a vapor deposition system involves significant investment in vacuum chambers, gas handling systems, and heating equipment. Furthermore, the high-purity precursor chemicals required for the process can be expensive.
Deposition Rate vs. Quality
There is often a trade-off between the speed of deposition and the quality of the resulting film. While the process can achieve high deposition rates, producing the most precise, atomically-thin layers for applications like microelectronics often requires slower, more deliberate processing times.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if vapor deposition is the correct approach, align its core strengths with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is microelectronics: This process is non-negotiable for creating the ultra-pure, nanometer-scale layers essential for integrated circuits.
- If your primary focus is mechanical durability: It is an excellent choice for applying hard, wear-resistant, and corrosion-resistant coatings to tools and high-performance parts.
- If your primary focus is biomedical devices: It provides a reliable method for applying biocompatible and inert coatings to implants and surgical instruments.
- If your primary focus is coating complex components: Its non-line-of-sight capability is a key advantage for ensuring complete, uniform coverage on intricate shapes.
Ultimately, understanding these core capabilities allows you to leverage vapor deposition as a fundamental tool for engineering materials with precision at the molecular level.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Benefit | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Microelectronics | Unmatched Purity & Precision | Integrated Circuits, Semiconductors |
| Automotive & Industrial | Extreme Durability & Wear Resistance | Engine Parts, Cutting Tools |
| Medical Devices | Biocompatibility & Corrosion Resistance | Surgical Implants, Instruments |
| Optics & Displays | Uniform Coating on Complex Shapes | Holographic Displays, Anti-reflective Glass |
Ready to Engineer Superior Surfaces with Vapor Deposition?
Vapor deposition is the key to creating ultra-pure, durable, and highly functional coatings that are essential for high-performance technologies. Whether you are developing advanced microelectronics, manufacturing longer-lasting automotive components, or creating safer medical implants, the right equipment is critical to your success.
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for vapor deposition processes, serving the precise needs of R&D and production laboratories. Our expertise can help you select the optimal system to achieve the precise film quality, uniformity, and durability your project demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our vapor deposition solutions can accelerate your innovation and enhance your product performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application



















