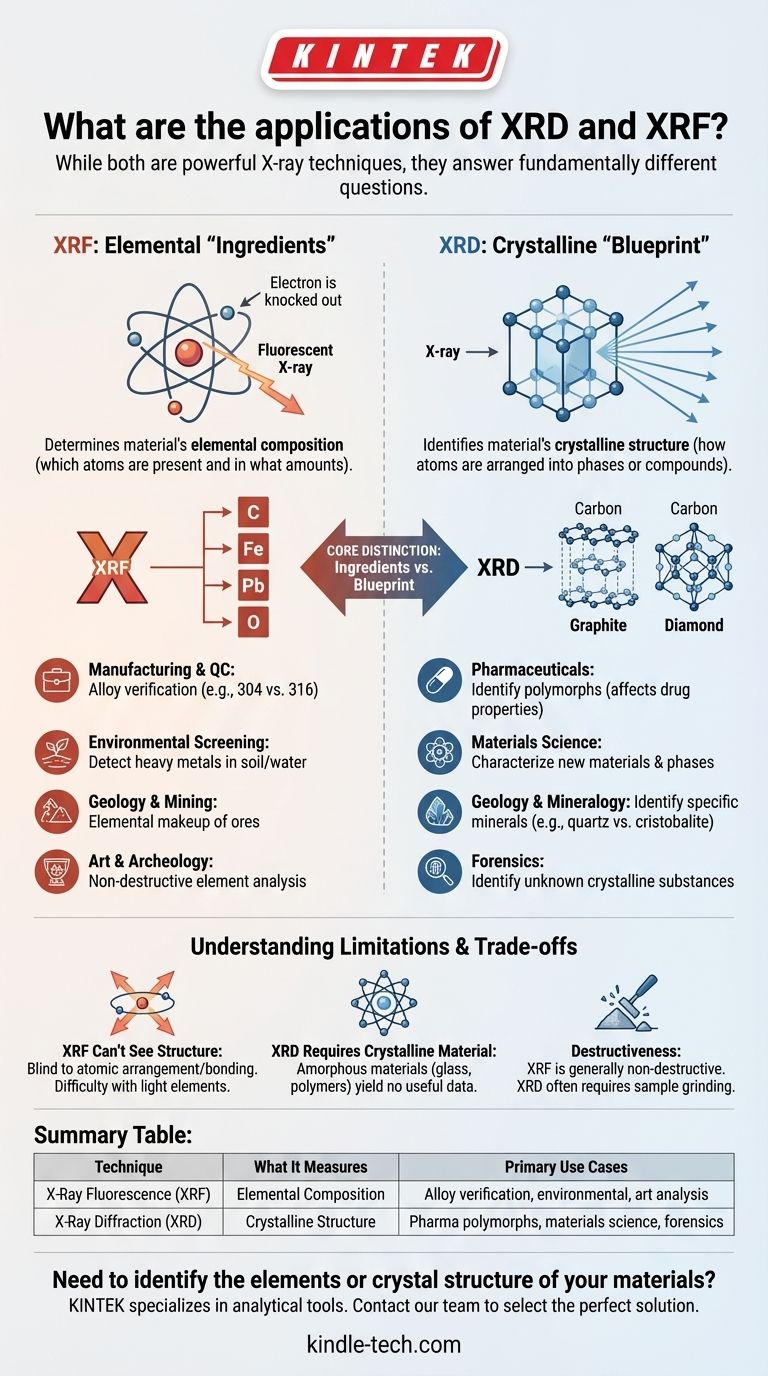
While both XRD and XRF are powerful X-ray techniques, they answer fundamentally different questions about a material. X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) is used to determine a material's elemental composition—identifying which atoms are present and in what amounts. In contrast, X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) is used to identify a material's crystalline structure, revealing how those atoms are arranged into specific phases or compounds.
The core distinction is simple: XRF provides a list of chemical ingredients, while XRD provides the architectural blueprint. An XRF scan tells you a sample contains carbon, but an XRD scan tells you if that carbon is arranged as graphite or diamond.

What Does Each Technique Actually Measure?
To choose the right tool, you must first understand the physical principle each one leverages. Though both use X-rays, they interact with the sample's atoms in completely different ways.
XRF: Identifying the Elemental "Ingredients"
X-Ray Fluorescence is a chemical analysis technique. It works by bombarding a sample with high-energy X-rays, which knock out electrons from the inner shells of the atoms.
When an electron from a higher-energy shell drops down to fill this vacancy, it releases a secondary, "fluorescent" X-ray. The energy of this fluorescent X-ray is a unique fingerprint for each element, allowing for a precise identification of the sample's atomic makeup.
XRD: Revealing the Crystalline "Blueprint"
X-Ray Diffraction is a structural analysis technique. It relies on the principle that a crystalline material—one with a repeating, orderly arrangement of atoms—will diffract an incoming X-ray beam in a predictable pattern.
The atoms in a crystal act as a three-dimensional diffraction grating. By measuring the angles and intensities of the diffracted X-rays, you generate a pattern that is a unique fingerprint for a specific crystal structure. This allows you to identify the exact phase or compound, not just the elements it contains.
Core Applications in Practice
The difference between measuring elements and measuring structure leads to distinct and complementary applications across science and industry.
Common Uses for XRF (Elemental Analysis)
Because it quickly identifies elements, XRF is the go-to tool for rapid chemical verification.
- Manufacturing & Quality Control: Verifying the elemental composition of metal alloys, such as checking if stainless steel meets grade specifications (e.g., 304 vs. 316).
- Environmental Screening: Rapidly detecting heavy metals like lead, mercury, or arsenic in soil, water, or consumer products.
- Geology & Mining: Determining the elemental makeup of rocks and ores during exploration to assess economic value.
- Art & Archeology: Analyzing the elements in pigments, metals, and ceramics to determine authenticity and provenance without damaging the object.
Common Uses for XRD (Structural Analysis)
Because it identifies crystalline phases, XRD is critical for understanding how a material is actually constructed.
- Pharmaceuticals: Identifying the specific polymorph (crystal form) of a drug, which can drastically affect its solubility, stability, and bioavailability.
- Materials Science: Characterizing new materials, identifying phases in alloys, and measuring residual stress or crystal size in manufactured components.
- Geology & Mineralogy: Precisely identifying the minerals present in a rock sample. XRF might tell you a rock contains Si and O, but XRD will tell you if it's quartz, cristobalite, or tridymite—all with the same chemistry but different structures.
- Forensics: Identifying unknown crystalline substances, such as illicit drugs, explosives, or unknown powders found at a crime scene.
Understanding the Limitations and Trade-offs
Neither technique is universally superior; their effectiveness depends entirely on the question you are asking. Understanding their limitations is key to avoiding incorrect conclusions.
XRF Can't See Structure
The primary limitation of XRF is that it is blind to the way atoms are bonded and arranged. It cannot distinguish between polymorphs (graphite vs. diamond) or different mineral phases with similar chemistries. It also has difficulty detecting very light elements (those with atomic numbers below sodium).
XRD Requires Crystalline Material
The primary limitation of XRD is that it requires your sample to be at least partially crystalline. Amorphous materials, like glass or most polymers, do not have the ordered atomic structure needed to produce a sharp diffraction pattern and will not yield useful phase information.
Destructiveness and Sample Preparation
XRF is generally considered non-destructive and often requires little to no sample preparation, making it ideal for finished parts or priceless artifacts. XRD, on the other hand, often yields the best results when the sample is ground into a fine, homogenous powder, which is an inherently destructive process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct technique comes down to defining your analytical goal with precision.
- If your primary focus is determining chemical composition: Choose XRF to identify the elements present and their relative quantities (e.g., "Does this metal contain lead?").
- If your primary focus is identifying the crystalline phase or compound: Choose XRD to understand how atoms are structurally arranged (e.g., "Is this white powder titanium dioxide in the anatase or rutile form?").
- If your primary focus is comprehensive material characterization: Use both techniques. XRF will provide the bulk elemental chemistry, while XRD will identify the specific crystalline compounds formed by those elements.
Understanding this fundamental difference—elements versus structure—is the key to unlocking the right answers for your analytical challenge.
Summary Table:
| Technique | What It Measures | Primary Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) | Elemental Composition | Alloy verification, environmental screening, geology, art analysis |
| X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) | Crystalline Structure | Pharmaceutical polymorphs, materials science, mineral identification, forensics |
Need to identify the elements or crystal structure of your materials?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the right analytical tools for your laboratory's unique challenges. Whether you need to verify the composition of an alloy with XRF or identify a specific drug polymorph with XRD, our experts can help you select the perfect solution.
Contact our team today to discuss your application and discover how our equipment can enhance your research and quality control processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Barium Fluoride BaF2 Substrate Window
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of quenching effect? Harnessing Molecular Interactions to Control Fluorescence
- Have other labs successfully stored samples at -70°C? Proven Long-Term Preservation for Biological Materials
- What is the advantage of sintered glass filter? Achieve Superior Purity and Precision in Your Lab Filtration
- How thick is sputter coating SEM? Optimize Image Quality with 2-20 nm Coatings
- What role do laboratory grinding and polishing systems play in nitriding? Ensure Superior Mirror-Finish & Ion Penetration
- What is the difference between sintering and annealing? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thermal Process
- What are the three types of graphite? A Guide to Natural and Synthetic Graphite for Industrial Use
- What is the process of sputtering in a vacuum? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition



















