At its core, sintering is a thermal process that transforms a collection of loose particles into a solid, coherent mass. This is achieved by applying heat and often pressure at a temperature below the material's melting point. The energy drives atoms to diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, fusing them together, increasing density, and dramatically improving the material's strength and other properties.
The central challenge in many advanced manufacturing scenarios is creating dense, strong parts from materials that are difficult to melt or form. Sintering solves this by providing a method to consolidate powders into solid objects without ever reaching a liquid state, saving energy and enabling the fabrication of high-performance components.
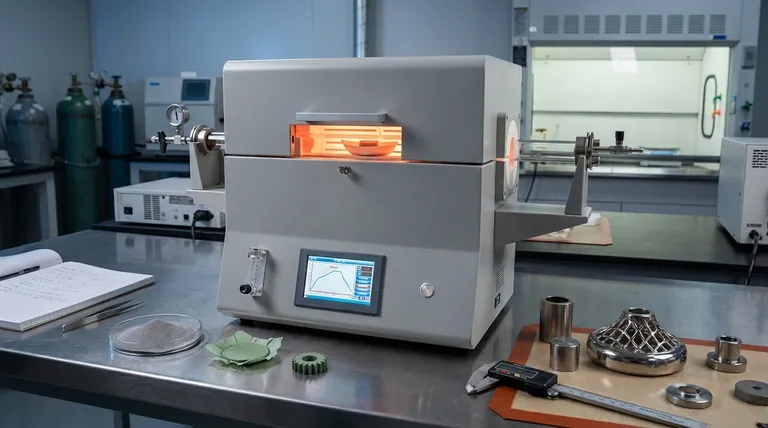

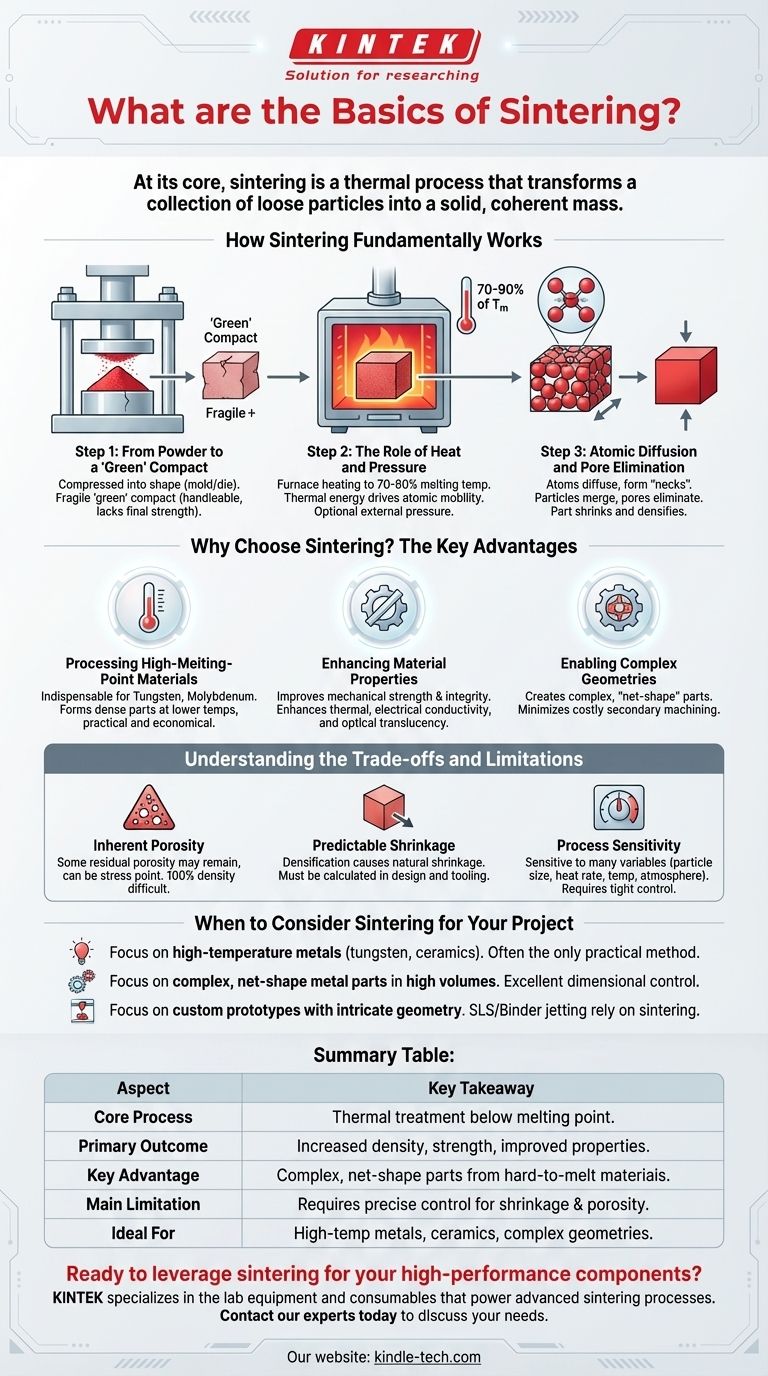
How Sintering Fundamentally Works
Sintering is more than just heating a powder; it is a carefully controlled process of atomic-level bonding that densifies and strengthens a material from the inside out.
Step 1: From Powder to a 'Green' Compact
The process typically begins by compressing the raw powder into a desired shape. This is often done using a hydraulic press with a mold and die set to define the part's geometry. The resulting object is a fragile, lightly compressed part known as a 'green' compact, which has enough integrity to be handled but lacks its final strength.
Step 2: The Role of Heat and Pressure
The 'green' compact is then placed in a furnace. The temperature is raised to a specific point—typically 70-90% of the material's absolute melting temperature. This thermal energy is the primary driver of the process; it gives the atoms within the powder particles enough mobility to move. While not always required, external pressure can also be applied to aid in densification.
Step 3: Atomic Diffusion and Pore Elimination
At sintering temperature, the atoms at the contact points between particles begin to diffuse, forming solid bridges or "necks." As these necks grow, the individual particles start to merge. This process pulls the particle centers closer together, systematically eliminating the empty pore spaces between them and causing the entire component to shrink and densify.
Why Choose Sintering? The Key Advantages
Engineers and manufacturers choose sintering for several distinct and powerful advantages over traditional melting or machining processes.
Processing High-Melting-Point Materials
Sintering is indispensable for materials with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten or molybdenum. Melting these metals requires immense energy and specialized equipment. Sintering allows them to be formed into dense, usable parts at significantly lower temperatures, making it a more practical and economical choice.
Enhancing Material Properties
The primary goal of sintering is to improve a material's physical characteristics. By reducing porosity and creating a dense microstructure, sintering significantly increases mechanical strength and integrity. It can also be used to enhance properties like thermal and electrical conductivity and, in the case of ceramics, optical translucency.
Enabling Complex Geometries and Net-Shape Parts
In powder metallurgy and additive manufacturing, sintering allows for the creation of complex, "net-shape" or near-net-shape parts. This means the component comes out of the furnace very close to its final dimensions, minimizing the need for costly and wasteful secondary machining operations.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, sintering is not without its challenges. A clear understanding of its limitations is crucial for successful application.
Inherent Porosity
Although sintering dramatically reduces porosity, achieving 100% density is difficult and often requires advanced techniques like Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP). Some residual porosity can remain, which may act as a stress concentration point and can be a limiting factor for highly demanding fatigue applications compared to a fully wrought or cast material.
Predictable Shrinkage
As the material densifies, it shrinks. This shrinkage is a natural part of the process but must be precisely calculated and accounted for in the initial design of the 'green' compact and tooling. Uncontrolled shrinkage can lead to parts that are out of tolerance.
Process Sensitivity
The final properties of a sintered part are highly sensitive to variables like particle size, heating rate, sintering time, temperature, and atmosphere. Achieving consistent results requires tight control over the entire manufacturing chain, from powder production to the final heat treatment cycle.
When to Consider Sintering for Your Project
Choosing the right manufacturing process depends entirely on your material and design goals. Sintering is the optimal choice in several key scenarios.
- If your primary focus is working with high-temperature metals like tungsten or ceramics: Sintering is often the only practical and cost-effective manufacturing method available.
- If your primary focus is producing complex, net-shape metal parts in high volumes: Powder metallurgy using sintering offers excellent dimensional control, material utilization, and reduces the need for secondary machining.
- If your primary focus is creating custom prototypes with intricate geometry: Additive manufacturing techniques like Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and binder jetting rely on sintering to turn digital designs into functional parts.
By understanding its principles, you can leverage sintering to create high-performance components that are otherwise difficult or impossible to manufacture.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Core Process | Thermal treatment below melting point to bond powder particles. |
| Primary Outcome | Increased density, strength, and improved material properties. |
| Key Advantage | Enables fabrication of complex, net-shape parts from hard-to-melt materials. |
| Main Limitation | Requires precise control to manage inherent shrinkage and porosity. |
| Ideal For | High-temperature metals (tungsten), ceramics, and complex geometries. |
Ready to leverage sintering for your high-performance components?
KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables that power advanced sintering processes. Whether you are developing new materials in R&D or optimizing production in manufacturing, our expertise and products support the precise temperature control and atmospheric conditions critical for success.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve stronger, denser, and more complex parts.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process



















