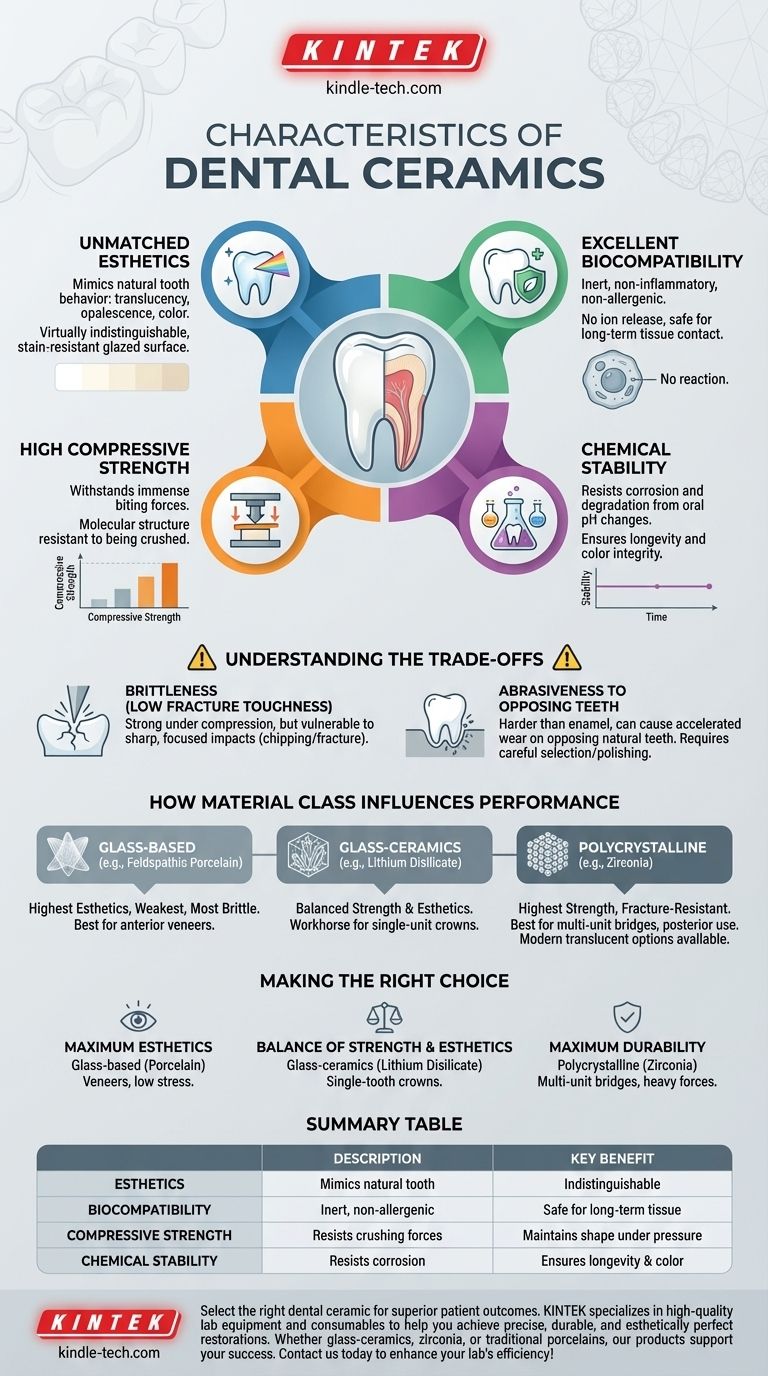
In essence, dental ceramics are defined by four primary characteristics: superior esthetics, high biocompatibility, excellent chemical stability, and significant compressive strength. These properties make them ideal for restoring the form and function of natural teeth in applications ranging from crowns and bridges to veneers and composite fillers.
The core value of dental ceramics lies in their unique ability to mimic natural tooth appearance while providing impressive durability. However, this strength is paired with an inherent brittleness, making the choice of a specific ceramic a critical decision based on the clinical demands of the restoration.
The Four Pillars of Dental Ceramics
The selection of ceramics in dentistry is not arbitrary; it is a deliberate choice based on a powerful combination of material properties that are difficult to find in any other single material class.
Unmatched Esthetics
Ceramics possess an optical behavior—including translucency, opalescence, and color—that can be manipulated to precisely match that of natural tooth enamel and dentin.
This allows for restorations that are virtually indistinguishable from the surrounding teeth. Furthermore, their glazed surface is highly resistant to staining from coffee, tea, or other foods.
Excellent Biocompatibility
Dental ceramics are highly biocompatible, meaning they are inert and do not provoke an inflammatory or allergic response from the body's tissues.
Unlike some metal alloys, they do not release ions into the oral environment, making them a safe and predictable choice for long-term contact with gingival tissue.
High Compressive Strength and Hardness
Ceramics excel at withstanding compressive forces, such as those exerted during chewing. Their molecular structure is highly resistant to being crushed.
This hardness ensures the restoration maintains its shape and function under the immense pressures of the human bite.
Chemical Stability and Inertness
The oral cavity is a harsh environment, subject to constant changes in pH from food, drinks, and bacterial activity.
Ceramics are chemically inert and do not corrode or degrade in this environment. This stability ensures the restoration's longevity, integrity, and color over many years.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Brittleness and Abrasiveness
No material is perfect. The primary limitations of dental ceramics are a direct consequence of their strength and hardness, and understanding these trade-offs is fundamental to clinical success.
The Brittleness Factor (Low Fracture Toughness)
While exceptionally strong under compression, ceramics are brittle. They have low resistance to fracture propagation when subjected to tensile or shear stress, such as from a sharp, focused impact.
This means a ceramic crown can perform flawlessly for years under normal chewing but may chip or fracture if it encounters a hard object unexpectedly. Material selection is key, as modern ceramics like zirconia have significantly higher fracture toughness than older feldspathic porcelains.
Abrasiveness to Opposing Teeth
The very hardness that makes ceramics durable can also be a liability. Some types of ceramic are harder than natural tooth enamel.
If a ceramic crown opposes a natural tooth, it can cause accelerated wear on the natural tooth over time. This requires careful material selection and proper polishing of the final restoration to minimize abrasive potential.
How Material Class Influences Performance
The term "dental ceramic" encompasses a wide range of materials, each with a different balance of strength and esthetics.
Glass-Based Ceramics (e.g., Feldspathic Porcelain)
These are the most traditional ceramics and offer the highest level of esthetics and translucency.
However, they are also the weakest and most brittle. Their use is typically reserved for low-stress applications where appearance is paramount, such as anterior veneers.
Glass-Ceramics (e.g., Lithium Disilicate)
This class represents a powerful compromise, reinforcing a glass matrix with crystalline fillers to dramatically increase strength while retaining excellent esthetics.
Materials like lithium disilicate have become the workhorse for single-unit crowns in both anterior and posterior regions due to their balanced blend of beauty and durability.
Polycrystalline Ceramics (e.g., Zirconia)
These materials contain no glass phase and consist of tightly packed crystalline structures, making them the strongest and most fracture-resistant ceramics available.
Historically, their opacity limited their use to posterior bridges or as substructures. However, modern translucent zirconias offer significantly improved esthetics, expanding their application to full-contour crowns even in visible areas.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal ceramic is always the one that best meets the specific functional and esthetic demands of the clinical situation.
- If your primary focus is maximum esthetics: Glass-based ceramics (porcelain) are the ideal choice for applications like veneers where biting forces are minimal.
- If your primary focus is a balance of strength and esthetics: Glass-ceramics like lithium disilicate provide a reliable and beautiful solution for most single-tooth crowns.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability: High-strength polycrystalline ceramics like zirconia are unmatched for multi-unit bridges and patients with heavy biting forces.
Understanding these fundamental characteristics empowers you to select materials that deliver predictable, durable, and esthetically superior results.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Esthetics | Mimics natural tooth translucency and color | Virtually indistinguishable from natural teeth |
| Biocompatibility | Inert and non-allergenic | Safe for long-term tissue contact |
| Compressive Strength | Resists crushing forces from chewing | Maintains shape and function under pressure |
| Chemical Stability | Resists corrosion in the oral environment | Ensures longevity and color stability |
Select the right dental ceramic for superior patient outcomes. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for dental laboratories, helping you achieve precise, durable, and esthetically perfect restorations. Whether you're working with glass-ceramics, zirconia, or traditional porcelains, our products support your success. Contact us today to learn how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hollow Cleaning Basket and Rack Carrier
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are high-precision vacuum sintering furnaces preferred over traditional methods for biofunctional dental ceramics?
- What is sintering dentistry? The Key to Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- Why are ceramics used in implants? Unlock Superior Biocompatibility and Durability for Medical Devices
- What is the structure and properties of dental ceramics? Mastering the Science Behind Durable, Aesthetic Restorations
- What is a burnout furnace used for in dentistry? Create Perfect Dental Crowns & Bridges
- What is the sintering temperature of yttria stabilized zirconia? Master the Thermal Cycle for Superior Results
- How do you fix a broken ceramic tooth? Get Professional Repair & Restoration Solutions
- What is the difference between dental ceramic and dental porcelain? Choosing the Right Material for Your Restoration












