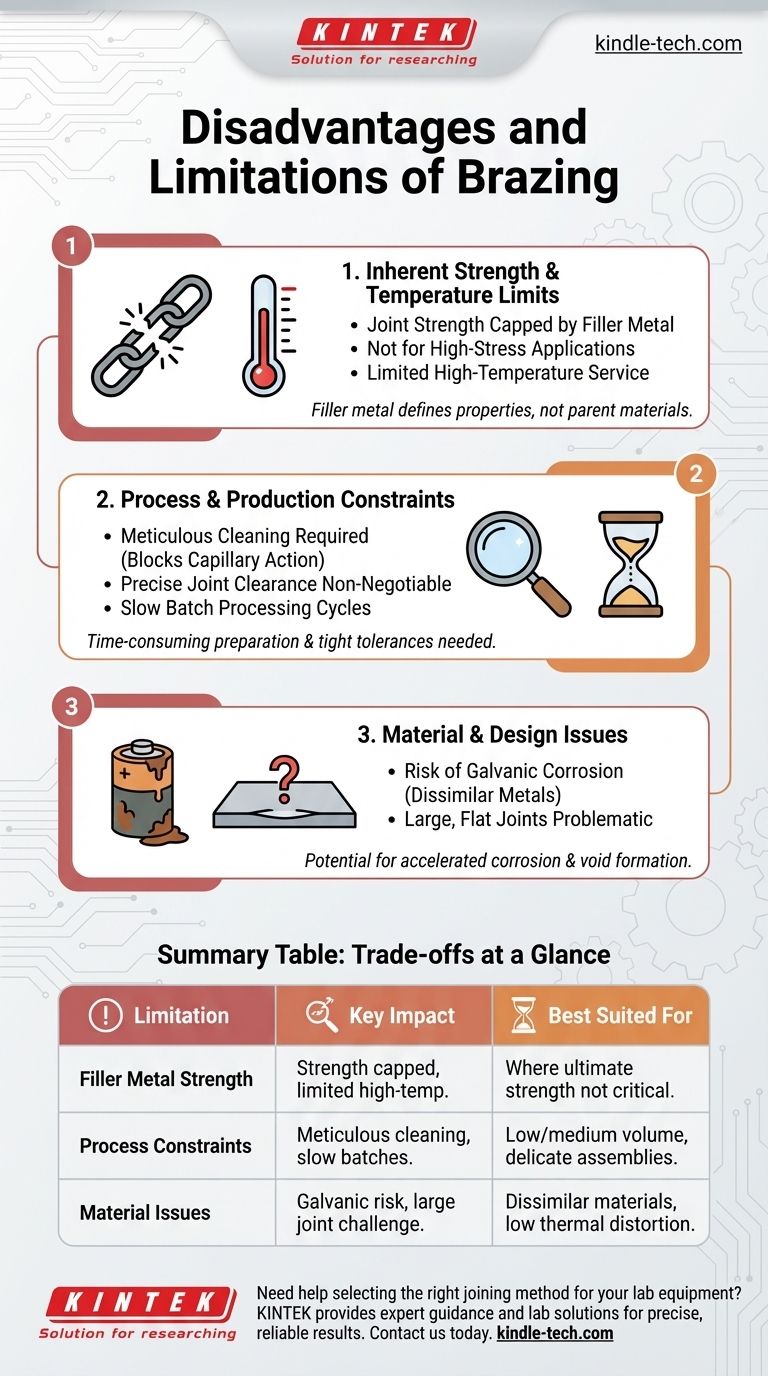
While an excellent joining method, brazing is not universally applicable. Its primary disadvantages stem from the inherent strength limitations of the filler metal, the meticulous preparation required for a successful bond, and process constraints that can make it unsuitable for certain high-volume production environments.
The core limitation of brazing is that the final joint's properties—its strength and temperature resistance—are defined by the filler metal, not the stronger parent materials. This, combined with its sensitivity to surface cleanliness and joint design, creates a specific set of operational trade-offs.

Limitation 1: Inherent Strength and Temperature Resistance
The most fundamental limitation of a brazed joint is that it can only be as strong as the filler metal used to create it.
The Filler Metal Ceiling
Unlike welding, which fuses the parent materials, brazing uses a separate, lower-melting-point alloy to act as the adhesive. This means the tensile strength of the joint is capped by the strength of this filler metal, which is almost always lower than that of the base metals being joined.
Not Suited for High-Stress Applications
Because the filler is the weak link, brazing is generally not the preferred method for applications subjected to extremely high loads or stresses where the full strength of the parent material must be maintained.
Limited High-Temperature Service
The service temperature of a brazed component is restricted by the melting point of the filler alloy. If the component operates at a temperature that approaches the filler's melting point, the joint will lose integrity and fail.
Limitation 2: Process and Production Constraints
The brazing process itself imposes strict requirements that can impact production speed and complexity.
The Critical Need for Cleanliness
Brazing relies on capillary action to draw the molten filler metal into the joint. This action can be completely blocked by contaminants like oils, grease, and oxides. Therefore, parts must be scrupulously cleaned before brazing, adding a mandatory and time-consuming step to the manufacturing process.
Precise Joint Clearance is Non-Negotiable
For capillary action to work effectively, the gap between the two parts being joined must be precise and consistent. A gap that is too wide will prevent the filler from being drawn in, while a gap that is too narrow can restrict its flow. This requires tight manufacturing tolerances.
Slow Batch Processing Cycles
As noted in furnace and vacuum brazing, the process is often performed in batches. The cycle of loading parts, creating a vacuum or controlled atmosphere, heating, cooling, and unloading is inherently slow, making it less suitable for maintaining the pace of high-volume, continuous production lines.
Limitation 3: Potential Material and Design Issues
Beyond strength and process, there are material considerations to keep in mind.
Risk of Galvanic Corrosion
When joining dissimilar metals, the combination of two different parent materials and a third filler metal can create a galvanic cell in the presence of an electrolyte (like moisture). This can lead to accelerated corrosion at the joint, compromising its long-term durability.
Large, Flat Joints Can Be Problematic
Achieving a void-free joint over a very large surface area can be difficult. It's challenging to ensure the flux or atmosphere works perfectly across the entire area and that the filler metal flows evenly into every part of the joint.
Understanding the Trade-offs
It is crucial to view these limitations not as failures, but as inherent trade-offs for brazing's unique advantages.
Lower Heat for Less Distortion
The lower process temperatures used in brazing (compared to welding) are a significant advantage. This minimizes thermal distortion and residual stress, making it ideal for joining delicate, thin-walled, or complex assemblies that would be damaged by high heat.
Joining Dissimilar Materials
Brazing is one of the best methods for joining radically different materials, such as copper to steel or ceramics to metals. The limitations of the filler metal are the price paid for this unique capability.
Creating Clean, Leak-Proof Joints
The meticulous cleaning and precise gaps required by the process result in extremely high-quality, neat, and often hermetically sealed joints with little need for post-processing finishing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the "disadvantages" of brazing are only disadvantages if they conflict with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength and high-temperature performance: You should likely consider a welding process that fuses the base metals.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, high-volume production: An automated welding process or mechanical fastening may be more suitable than slower batch brazing cycles.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials or complex assemblies with minimal thermal distortion: The process requirements and strength limitations of brazing are acceptable trade-offs for achieving your goal.
Choosing the right joining method requires understanding not just its strengths, but also its inherent limitations and how they align with the demands of your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Key Impact | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|
| Filler Metal Strength | Joint strength capped by filler, not base metals. Limited high-temp use. | Applications where ultimate strength is not critical. |
| Process Constraints | Requires meticulous cleaning, precise joint gaps, and slow batch cycles. | Low-to-medium volume production; complex or delicate assemblies. |
| Material Issues | Risk of galvanic corrosion with dissimilar metals; challenging for large, flat joints. | Joining dissimilar materials where thermal distortion must be minimized. |
Need help selecting the right joining method for your lab equipment?
Brazing offers unique benefits for delicate assemblies and dissimilar materials, but understanding its limitations is key to a successful application. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables to support your specific joining and fabrication needs.
Let our experts guide you to the optimal solution for your project.
Contact us today to discuss how we can help you achieve precise, reliable results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Plate
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- What are some applications of brazing? Join Dissimilar Metals with Strong, Leak-Proof Bonds
- Which element made stainless steel difficult to brazed? It's Chromium's Oxide Layer
- Why would you braze instead of weld? Preserve Material Integrity and Join Dissimilar Metals
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing














