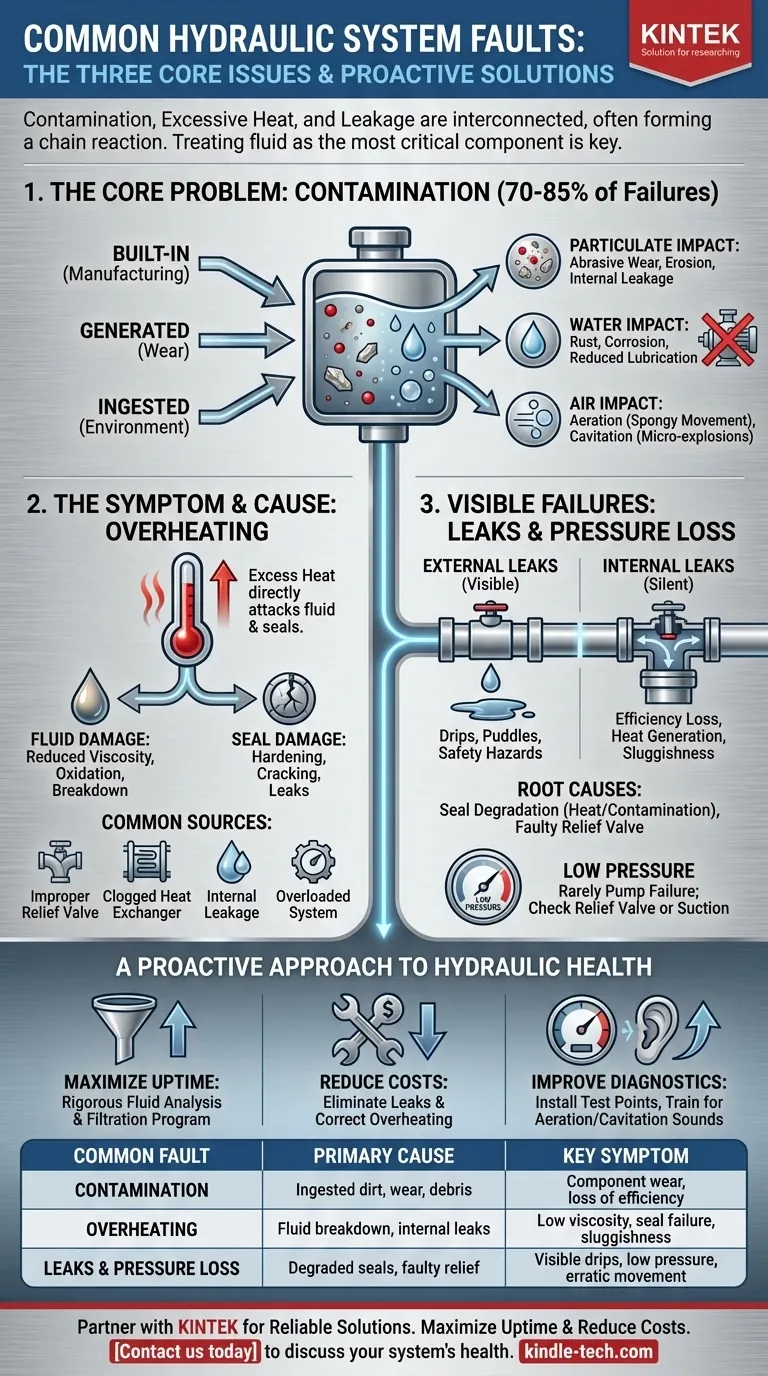
The most common faults in any hydraulic system are almost always linked to three core issues: fluid contamination, excessive heat, and fluid leakage. These problems are not independent; contamination often leads to increased friction and heat, which in turn degrades seals and causes leaks. Understanding this chain reaction is the key to effective troubleshooting and prevention.
The vast majority of hydraulic system failures are not caused by sudden component breakdowns, but by the gradual and preventable degradation of the hydraulic fluid. Treating the fluid as the system's most critical component is the foundation of reliable operation.
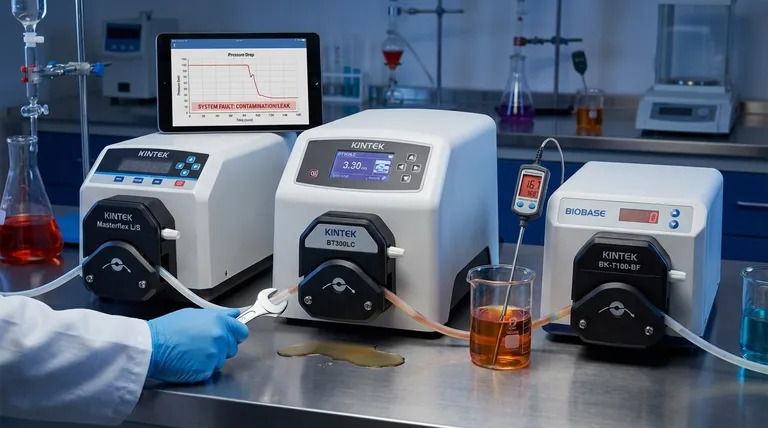

The Core Problem: Contamination
Contamination is the single greatest cause of hydraulic system failure, responsible for an estimated 70-85% of all problems. It is the primary catalyst for wear, component malfunction, and eventual breakdown.
How Contamination Enters a System
Contaminants are not just external dirt. They can be built-in from the manufacturing process, generated internally by component wear, or ingested from the surrounding environment through worn seals or breather caps.
The Impact of Particulate Contamination
Solid particles like metal fragments and silica act as an abrasive lapping compound, grinding away at the tight tolerances inside pumps, valves, and actuators. This erosion widens clearances, causing internal leakage, loss of efficiency, and eventually, component failure.
The Impact of Water and Air
Water contamination promotes rust, corrosion, and reduces the fluid's lubricating properties. Air in the system (aeration) can cause spongy, erratic actuator movement, while the rapid collapse of air bubbles under pressure (cavitation) creates micro-explosions that erode internal components.
The Symptom and The Cause: Overheating
Excessive heat is both a symptom of a system inefficiency and a direct cause of further damage. A system that consistently runs hot is a system that is headed for failure.
Why Excess Heat is Damaging
Heat directly attacks the hydraulic fluid, reducing its viscosity (its thickness and ability to lubricate). This leads to increased metal-to-metal contact. It also hardens and cracks seals, causing leaks, and accelerates the oxidation and breakdown of the fluid itself.
Common Sources of Unwanted Heat
Unwanted heat is generated by any inefficiency in the system. This can be caused by an improperly set pressure relief valve, a clogged or undersized heat exchanger, internal component leakage, or simply forcing the system to work beyond its designed capacity.
Visible Failures: Leaks and Pressure Loss
Leaks and pressure issues are often the most obvious signs of a problem, but they are typically the final symptom of an underlying issue, not the root cause itself.
External vs. Internal Leakage
External leaks are visible drips and puddles, which are wasteful and create safety hazards. Internal leaks, where fluid bypasses a component's seals internally, are more insidious. They don't leave a puddle but silently rob the system of efficiency, generate heat, and lead to sluggish performance.
Root Causes of Leaks and Low Pressure
Leaks are most often caused by seal degradation due to heat or fluid contamination. Low operating pressure is rarely a pump issue; it is more commonly caused by a relief valve set too low, excessive internal leakage, or a restriction in the suction line starving the pump.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Trusting the symptoms without understanding the system can lead to costly and ineffective repairs. Avoiding these common misconceptions is critical for accurate diagnosis.
The "Topping Off" Fallacy
Simply adding new fluid to a reservoir without proper filtration introduces a significant amount of new contamination. New oil is not necessarily clean oil and must be filtered before being added to a system.
Misinterpreting Pressure Readings
A pressure gauge does not measure the pump's output; it measures the resistance to flow. A reading of zero PSI can mean the pump has failed, but it can also mean the fluid is simply circulating back to the tank with no resistance.
Overlooking the Reservoir's Role
The reservoir is more than a storage tank. It is a critical component designed to help cool the fluid, separate air and water, and allow contaminants to settle. A poorly maintained or designed reservoir undermines the entire system's health.
A Proactive Approach to Hydraulic Health
To move from a reactive to a proactive maintenance strategy, you must shift your focus from fixing broken parts to maintaining the health of the hydraulic fluid.
- If your primary focus is maximizing uptime: Implement a rigorous fluid analysis and filtration program to remove contaminants before they can cause wear.
- If your primary focus is reducing operating costs: Prioritize eliminating all leaks and correcting overheating issues, as these are two of the largest sources of wasted energy in a hydraulic system.
- If your primary focus is improving diagnostic speed: Install proper test points (pressure gauges, flow meters) and train personnel to recognize the sounds and symptoms of aeration and cavitation.
By treating the fluid as the heart of the system, you can predict and prevent the vast majority of hydraulic failures.
Summary Table:
| Common Fault | Primary Cause | Key Symptom |
|---|---|---|
| Contamination | Ingested dirt, internal wear, built-in debris | Component wear, loss of efficiency |
| Overheating | Fluid breakdown, internal leakage, undersized cooler | Low viscosity, seal failure, sluggish performance |
| Leaks & Pressure Loss | Degraded seals, faulty relief valves, internal bypass | Visible drips, low pressure, erratic actuator movement |
Don't let hydraulic failure disrupt your operations. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable solutions for laboratory needs. Our expertise can help you implement a proactive maintenance strategy, from fluid analysis to system diagnostics, to maximize uptime and reduce costs. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your hydraulic system's health and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Variable Speed Peristaltic Pump
- Ball Press Mold for Lab
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- XRF Boric Acid Lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the common uses of vacuum pumps in laboratories? Essential for Filtration, Evaporation & Analysis
- What role does a laboratory vacuum pump perform in reactor pretreatment? Ensure High-Purity Heat Storage Results
- How does a laboratory peristaltic pump contribute to the continuous operation of an electrochemical flow cell?
- What is the difference between a vacuum pump and a regular pump? A Guide to Push vs. Pull Mechanics
- What can I use a vacuum pump for? Powering Industrial Processes from Packaging to Automation



















