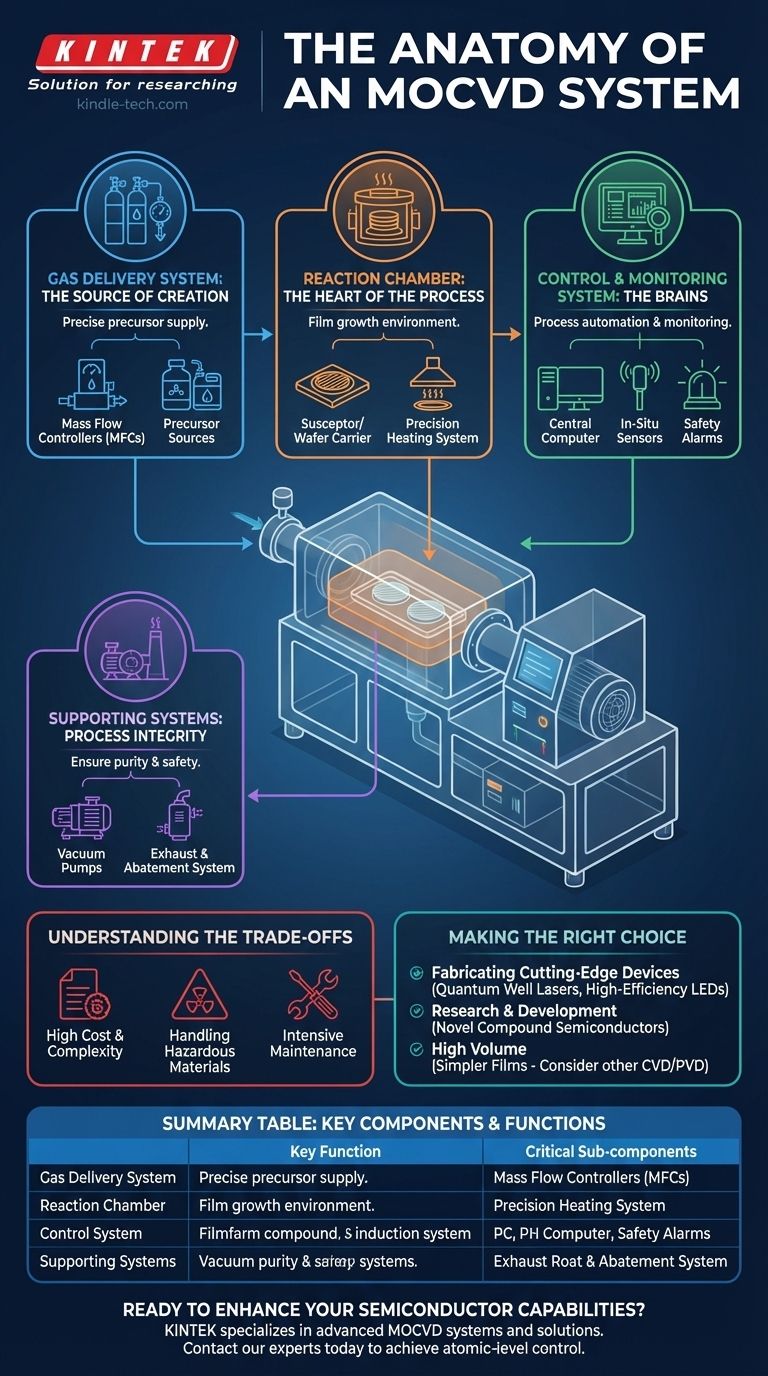
At its core, a Metal-Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition (MOCVD) system is an advanced apparatus designed for growing high-purity crystalline thin films. Its primary components include a gas delivery system to supply precursor chemicals, a reaction chamber where the film growth occurs, a precision heating system for the substrate, a vacuum system to maintain purity, and a sophisticated electronic control system to manage the entire process.
An MOCVD system is best understood not as a single machine, but as an integrated environment. Each component works in concert to achieve the ultimate goal: precise, atomic-level control over the deposition of complex materials, enabling the fabrication of high-performance semiconductor devices.

The Gas Delivery System: The Source of Creation
The gas delivery system is responsible for supplying the chemical "ingredients" for the thin film in a highly controlled manner. Its precision is fundamental to the quality of the final product.
Precursor Sources and Gas Lines
The system begins with sources of metal-organic compounds and hydrides, which are the precursor materials. These are stored in specialized containers and delivered through a network of stainless steel tubes.
Mass Flow Controllers (MFCs)
MFCs are the critical components for metering the exact amount of each gas into the system. They ensure the chemical recipe is followed with extreme accuracy, which directly dictates the film's composition and properties.
The Reaction Chamber: The Heart of the Process
The reaction chamber, or reactor, is the controlled environment where the substrate is heated and exposed to the precursor gases, causing the desired thin film to deposit onto its surface.
The Chamber and Wafer Carrier
The chamber itself is designed to maintain a stable temperature and pressure. Inside, a wafer carrier, often called a susceptor, holds the substrate wafers that will be coated.
The Precision Heating System
An energy source, typically induction heating or lamps, heats the susceptor to the precise temperatures required for the chemical reactions to occur. Accurate temperature control is essential for achieving the desired crystal structure in the film.
The Control and Monitoring System: The Brains of the Operation
Modern MOCVD equipment relies on a sophisticated control system to automate, monitor, and ensure the safety of the entire deposition process.
Process Automation
A central computer controls all aspects of the process, including valve switching, gas flow rates from the MFCs, and temperature settings. This allows for repeatable, complex recipes to be executed flawlessly.
In-Situ Monitoring
Advanced systems include real-time feedback tools. These sensors can measure parameters like film thickness, wafer temperature, and even material stress during the growth process, allowing for on-the-fly adjustments.
Safety and Alarm Systems
Given the hazardous nature of the precursor gases, integrated safety and alarm systems are mandatory. They monitor for leaks or process deviations and can trigger automatic shutdowns to ensure operator safety.
Supporting Systems: Ensuring Process Integrity
Several other crucial systems work in the background to create the ideal conditions for deposition and to handle the byproducts safely.
The Vacuum System
A vacuum pumping system is used to purge the reaction chamber of any contaminants or air before the process begins. This ensures the extreme purity required for high-quality semiconductor materials.
The Exhaust and Abatement System
After the reaction, unused precursor gases and chemical byproducts must be safely removed. An exhaust system, often called a scrubbing or abatement system, treats these hazardous gases to render them harmless before they are released.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Complexity vs. Capability
While MOCVD offers unparalleled control over material growth, its sophistication comes with inherent challenges that must be understood.
High Cost and Complexity
MOCVD systems are intricate and expensive to purchase and operate. The precision components, such as MFCs and in-situ monitoring tools, contribute significantly to the overall cost.
Handling of Hazardous Materials
The metal-organic precursors used in MOCVD are often toxic, pyrophoric (ignite spontaneously in air), and corrosive. This necessitates stringent safety protocols, specialized facilities, and a robust exhaust abatement system.
Intensive Maintenance
The complexity of the system and the reactive nature of the chemicals mean that MOCVD tools require regular, specialized maintenance to ensure consistent performance and prevent component failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting MOCVD is a decision driven by the need for the highest quality materials. The system's components are all geared towards achieving this singular purpose.
- If your primary focus is fabricating cutting-edge devices like quantum well lasers or high-efficiency LEDs: The atomic-level precision of a fully-featured MOCVD system is essential and non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is research and development of novel compound semiconductors: The system's precise control over gas flows and temperature provides the process window needed to explore new material properties.
- If your primary focus is depositing simpler, less sensitive films in high volume: A less complex deposition method, such as a different type of CVD or a physical vapor deposition (PVD) technique, may be a more cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, the intricate assembly of an MOCVD system provides the power to engineer materials at the atomic scale, forming the foundation for next-generation electronic and optoelectronic technology.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function | Critical Sub-components |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Delivery System | Precise precursor supply | Mass Flow Controllers (MFCs), precursor sources |
| Reaction Chamber | Film growth environment | Susceptor/wafer carrier, heating system |
| Control System | Process automation & monitoring | Central computer, in-situ sensors, safety alarms |
| Supporting Systems | Process integrity & safety | Vacuum pumps, exhaust/abatement system |
Ready to enhance your semiconductor research or production capabilities? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise thin-film deposition. Our expertise in MOCVD systems and semiconductor manufacturing solutions can help you achieve atomic-level control for your most demanding applications. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs with reliable, high-performance equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is the process of thin film deposition? A Guide to PVD, CVD, and Coating Techniques
- Is graphene production bad for the environment? The Truth About Manufacturing Methods
- What is physical vapor deposition on plastic? Upgrade Plastic Parts with Durable, Functional Coatings
- What are the applications of vapor deposition? Unlock Precision Coatings for Electronics, Automotive, and Medical Devices
- What is the sputtering process of surface treatment? Achieve Atomic-Level Coating Precision
- What is one manner for depositing extremely controlled thin films? Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) for Nanometer Precision
- What is atomic layer deposition of a gas? Achieve Perfectly Uniform Thin Films with Atomic Precision
- What is the size of a CVD diamond? From Micron-Thin Coatings to Multi-Carat Gems



















