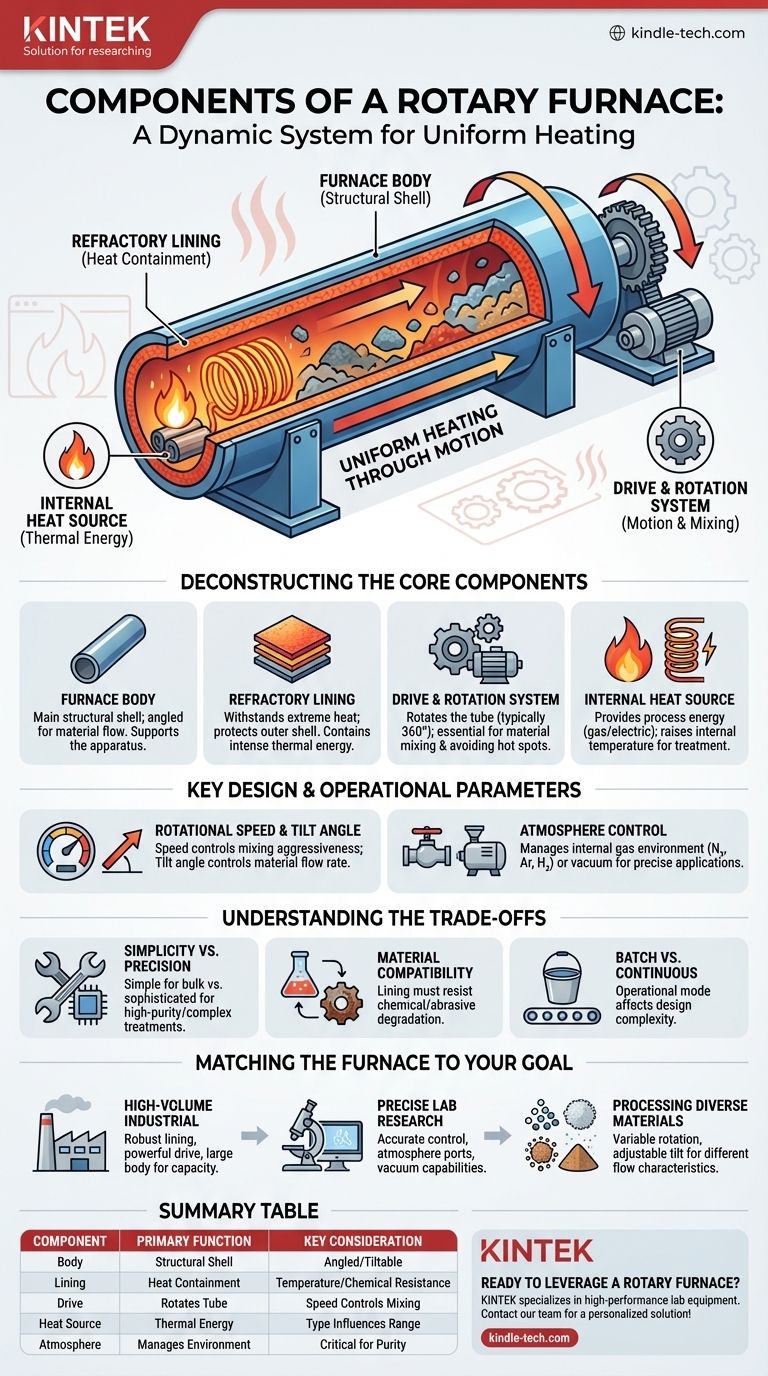
At its core, a rotary furnace is a dynamic system designed for uniform heating through motion. Its primary components are the main furnace body, an internal refractory lining to contain heat, a drive gear or rotation system, and an internal heat source to provide the necessary thermal energy.
The key insight is that a rotary furnace is not a static oven. It is an integrated system where the mechanical components (body, drive) and thermal components (lining, heat source) work together to actively mix materials, ensuring every particle is heated evenly and efficiently.

Deconstructing the Core Components
Understanding how a rotary furnace operates begins with its fundamental parts. Each component serves a distinct purpose in the overall process of controlled, uniform heating.
The Furnace Body and Structure
The furnace body is the main external shell, typically a metal barrel or tube. This structure provides the foundational support for the entire apparatus and is often designed to be installed at an angle to facilitate material movement. In many designs, especially for laboratory use, the entire body can be tilted.
The Refractory Lining
Inside the metal body is a crucial layer of refractory material. This lining is engineered to withstand extreme temperatures, protecting the outer metal shell from thermal stress and damage. It is the primary element responsible for containing the intense heat required for smelting or heat treatment.
The Drive and Rotation System
This is the mechanism that gives the rotary furnace its name. A drive gear and motor system cause the furnace tube to rotate, typically 360°. This constant motion is essential for tumbling and mixing the materials inside, preventing hot spots and ensuring a consistent temperature throughout the batch.
The Internal Heat Source
The heat source provides the energy for the process. While the specific type can vary (e.g., gas burners, electric elements), its function is to raise the internal temperature to the desired level for smelting or treating materials like powders, granules, and solids.
Key Design and Operational Parameters
Beyond the physical parts, several design variables dictate the furnace's performance and suitability for specific applications.
Rotational Speed and Tilt Angle
The speed of rotation directly influences how aggressively the material is mixed. The tilt angle of the furnace body controls the rate at which material moves from the charging end to the discharge end in continuous or semi-continuous processes.
Tube and Lining Dimensions
The diameter, length, and thickness of the furnace tube are critical design factors. These dimensions determine the furnace's capacity (the amount of material it can process) and its thermal efficiency and durability.
Atmosphere Control Systems
For precise applications, especially in laboratory settings, furnaces are equipped with ports to control the internal atmosphere. This allows for the introduction of specific gases like nitrogen, argon, or hydrogen to create an inert or reactive environment. An external vacuum pump can also be used to operate under vacuum conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While effective, the design of a rotary furnace presents specific operational considerations that must be managed.
Simplicity vs. Precision
The basic operation of charging and smelting can often be handled by relatively unskilled workers, making it robust for bulk processing. However, achieving high-purity results or complex heat treatments requires precise control over temperature, rotation speed, and atmosphere, which demands more sophisticated systems and skilled oversight.
Material Compatibility
The material used for the furnace tube and lining must be compatible with the substances being processed. Aggressive chemical reactions or abrasive materials can degrade the refractory lining over time, necessitating maintenance and replacement.
Batch vs. Continuous Processing
A key consideration is the operational mode. Simple batch processing involves charging, heating for a set time (e.g., 4-6 hours), and tapping. Continuous systems require more complex designs to manage the constant flow of material through the angled, rotating tube.
Matching the Furnace to Your Goal
Selecting or operating a rotary furnace effectively means aligning its components and capabilities with your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is high-volume industrial smelting: Prioritize a robust, thick refractory lining, a powerful and reliable drive system, and a large furnace body to maximize batch capacity.
- If your primary focus is precise laboratory research: Emphasize accurate computer control systems for temperature and rotation, along with integrated ports for gas introduction and vacuum capabilities.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse materials: Look for a design with variable rotation speed and an adjustable tilt angle to accommodate the different flow characteristics of powders, granules, or solids.
Ultimately, understanding how each component contributes to the furnace's function allows you to leverage its unique advantages for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace Body | Main structural shell and support | Often angled for material flow; can be tiltable |
| Refractory Lining | Contains extreme heat, protects shell | Material must withstand process temperatures and chemicals |
| Drive/Rotation System | Rotates the furnace tube for mixing | Speed controls mixing aggressiveness |
| Heat Source | Provides thermal energy (gas/electric) | Type influences temperature range and control |
| Atmosphere Control | Manages internal gas environment (e.g., N₂, Ar) | Critical for precise lab applications and purity |
Ready to leverage a rotary furnace for your lab's unique needs? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including rotary furnaces tailored for research and material processing. Whether you need precise temperature control, atmosphere management, or a robust system for diverse materials, our experts can help you select the perfect configuration. Contact our team today to discuss your application and get a personalized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the equipment for pyrolysis laboratory? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Research
- How does precision temperature control impact TiAl alloy sintering? Master Microstructure Development
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What is the meaning of rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding



















