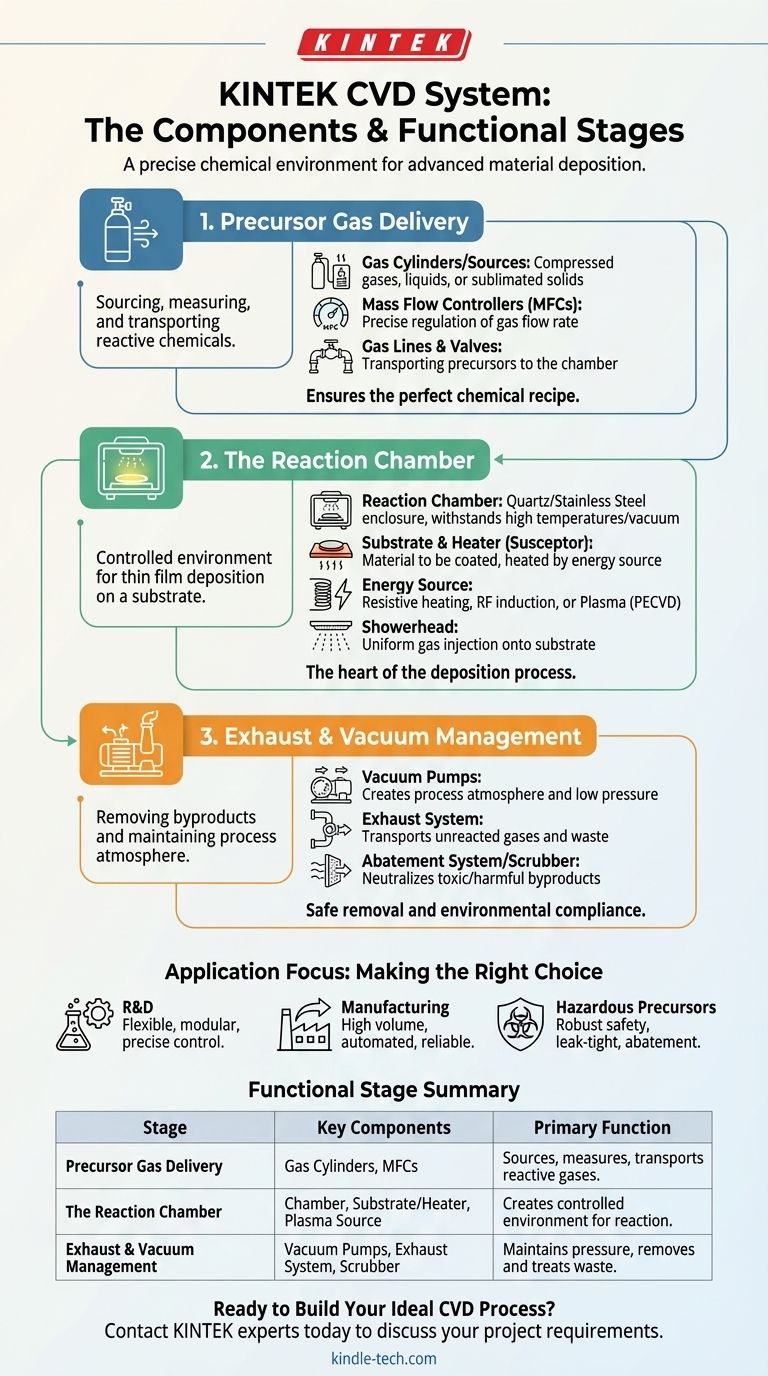
At its core, a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) system is comprised of several key hardware modules working in concert. These generally include a gas delivery system, a reaction chamber where the deposition occurs, an energy source to drive the chemical reaction, a vacuum system to control the environment, and an exhaust system to safely remove byproducts.
To truly understand a CVD system, you must look beyond a simple list of parts. It is more effective to think of it as three integrated functional stages: delivering the reactive gases, facilitating the chemical reaction on a substrate, and managing the resulting waste. The precision with which these three stages are controlled determines the quality of the final material.

The System's Functional Blueprint
A CVD system is not just a collection of components; it is a highly controlled environment designed to execute a precise chemical process. We can break down its operation into three primary functions.
Function 1: Precursor Gas Delivery
This stage is responsible for accurately sourcing, measuring, and transporting the reactive chemicals (precursors) into the reaction chamber.
Sourcing the Reactants
The system begins with sources of precursor gases, which can be stored in cylinders as compressed gases or liquids. Solid precursors can also be used, which are then heated or sublimated into a vapor form.
Ensuring Precise Flow
The most critical components here are Mass Flow Controllers (MFCs). These devices measure and regulate the flow rate of each gas with extreme precision, ensuring the chemical recipe for the thin film is perfectly maintained.
Function 2: The Reaction Chamber
This is the heart of the CVD system, where the environment is controlled to facilitate the deposition of the thin film onto a surface.
The Deposition Environment
The reaction chamber is an enclosure, often made of quartz or stainless steel, that contains the substrate. It is designed to withstand high temperatures and maintain a controlled vacuum or specific pressure.
The Substrate and Heater
The material to be coated, known as the substrate, is placed on a holder called a susceptor. This susceptor is then heated by an energy source (like resistive heating elements or RF induction coils) to the exact temperature required for the chemical reaction to occur on the substrate's surface.
Providing Activation Energy
Beyond thermal energy from heating, some CVD processes use a plasma to energize the precursor gases. This technique, Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD), allows deposition to occur at much lower temperatures, which is crucial for sensitive substrates.
Function 3: Exhaust and Vacuum Management
This stage is responsible for removing unreacted gases and chemical byproducts from the chamber and treating them before release.
Creating the Process Atmosphere
A vacuum system, typically consisting of one or more pumps, is used to remove air and other contaminants from the chamber before the process begins. During deposition, the pumps maintain the specific low pressure required for the reaction.
Removing Volatile Byproducts
The exhaust system transports all gaseous waste away from the reaction chamber. This flow is critical for preventing the buildup of byproducts that could contaminate the film.
Ensuring Safety and Compliance
Before being vented to the atmosphere, the exhaust stream often passes through an abatement system or "scrubber." This unit neutralizes toxic, flammable, or environmentally harmful gases, ensuring safe and compliant operation.
Understanding Integration and Control
Simply having these components is not enough. The true complexity and power of a CVD system lie in how these parts are integrated and controlled in real-time.
The Role of the Central Controller
A sophisticated control system—the brain of the operation—monitors and adjusts all critical parameters. This includes gas flow rates, chamber pressure, and substrate temperature.
The Challenge of Uniformity
Achieving a film of uniform thickness and composition across the entire substrate is a primary engineering challenge. The design of the gas injectors (the "showerhead") and the management of temperature gradients across the susceptor are critical for ensuring uniformity.
Process Recipes
Each unique material requires a specific "recipe" of settings—a timed sequence of gas flows, pressures, and temperatures. The control system executes these recipes with high repeatability, which is essential for manufacturing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal CVD system configuration depends entirely on its intended application.
- If your primary focus is research and development: You need a flexible, modular system with highly precise process controls to explore a wide range of materials and recipes.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing: You need a reliable, automated system optimized for high throughput, repeatability, and low cost-per-substrate, often using batch or cluster tool configurations.
- If your primary focus is working with hazardous precursors: Your primary concern is the robustness of the safety interlocks, exhaust abatement systems, and leak-tightness of the entire apparatus.
Ultimately, a successful CVD process is a result of a well-designed system where every component works in perfect harmony to create a precisely controlled chemical environment.
Summary Table:
| Functional Stage | Key Components | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Precursor Gas Delivery | Gas Cylinders, Mass Flow Controllers (MFCs) | Accurately sources, measures, and transports reactive gases into the chamber. |
| The Reaction Chamber | Chamber, Substrate/Heater (Susceptor), Plasma Source (for PECVD) | Creates a controlled environment for the chemical reaction and thin film deposition. |
| Exhaust & Vacuum Management | Vacuum Pumps, Exhaust System, Abatement Scrubber | Maintains process pressure and safely removes and treats waste byproducts. |
Ready to Build Your Ideal CVD Process?
Whether your goal is advanced R&D or high-volume manufacturing, the precise integration of these components is critical to your success. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing robust and reliable CVD systems tailored to your specific application—from handling hazardous precursors to ensuring perfect film uniformity.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of tungsten filaments in HFCVD? Powering Diamond Film Synthesis with Thermal Excitation
- What are the methods of carbon nanotube purification? Achieve High-Purity CNTs for Your Application
- What are external chemical vapor deposition processes? Understanding CVD Process Design and Control
- What are the new R&D directions for LPCVD equipment? Advanced Stress Control and Multi-functional Systems
- What role do porous substrates play in CDCVD beyond acting as a support? Master the Engine of Membrane Growth
- What is CVD production of graphene? The Industrial Process for High-Quality Graphene Sheets
- What is the difference between chemical vapor deposition and physical vapor deposition? A Guide to Thin Film Coating Technologies
- What is the MOCVD method? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition



















