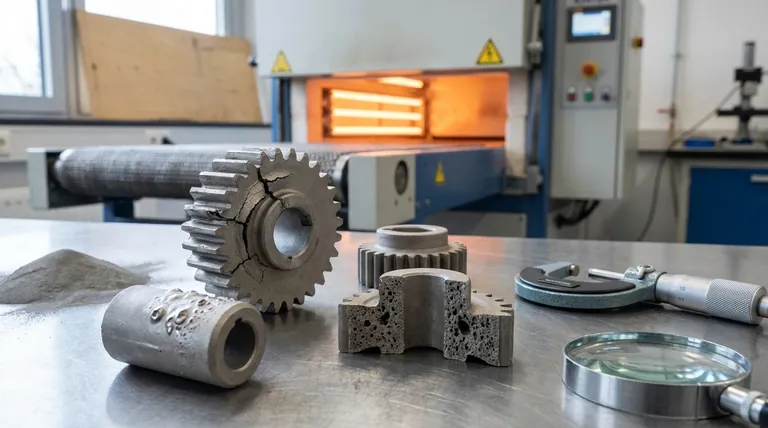
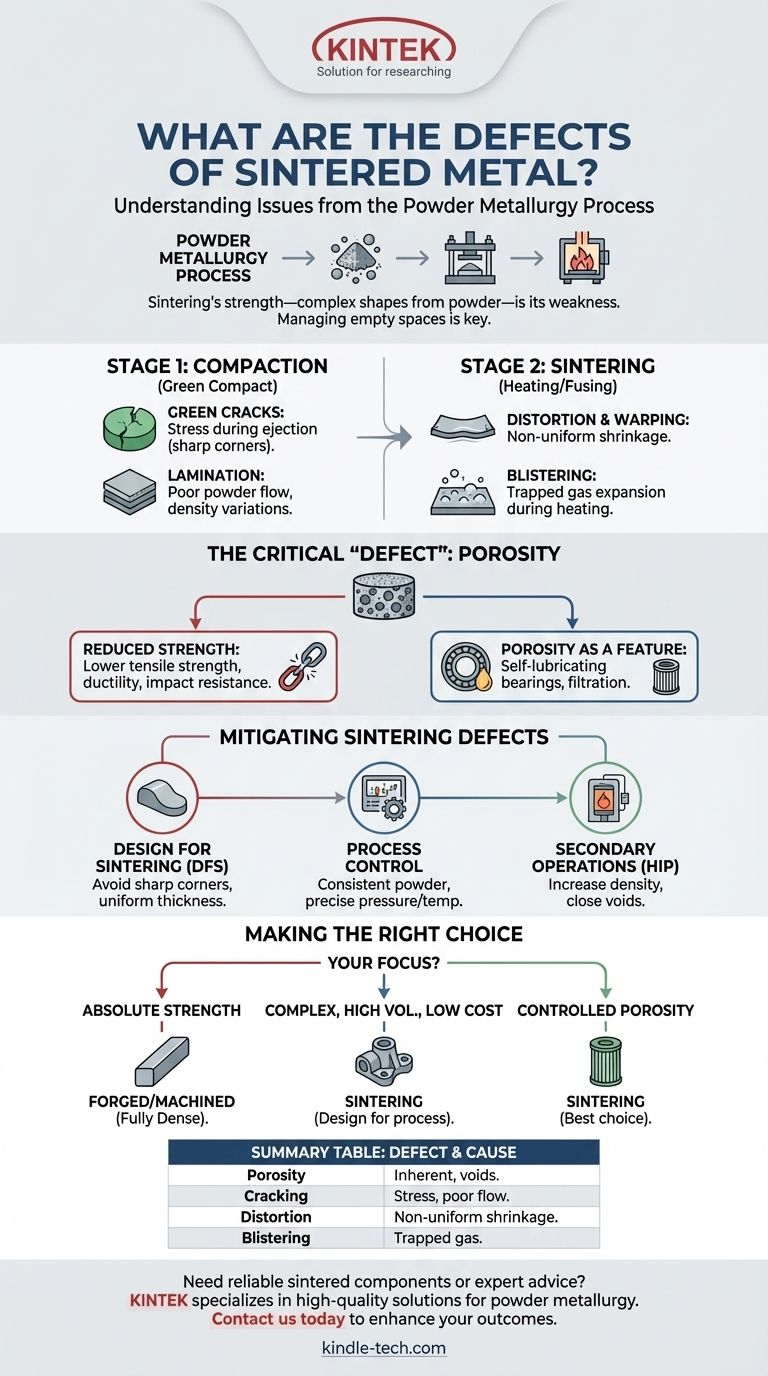
The primary defects in sintered metal are porosity, cracking, and distortion. These issues arise directly from the unique nature of the powder metallurgy process, which involves compacting metal powder and then heating it below its melting point to fuse the particles together, rather than casting a molten liquid.
Sintering's greatest strength—creating complex shapes from powder—is also the source of its inherent weaknesses. The core challenge is managing the empty spaces between the initial powder particles, which can lead to specific, predictable defects if the process is not carefully controlled.
The Powder Metallurgy Process: A Source of Defects
To understand the defects, you must first understand the two-stage process. First, metal powder is pressed into a shape in a die, creating a fragile "green compact." Second, this compact is heated in a controlled atmosphere furnace, where the particles bond and the part gains its strength.
Stage 1: Compaction Defects
Defects at this stage occur before the part is even heated. The most common is the green crack, a fracture in the fragile, unsintered compact.
These cracks are typically caused by stresses introduced during the ejection of the part from the compaction die. Complex geometries with sharp corners or abrupt changes in thickness are particularly vulnerable.
Another compaction defect is lamination, where the part has distinct layers. This is often due to poor powder flow into the die, creating density variations that fail to bond properly.
Stage 2: Sintering Defects
These defects appear during the heating phase as the powder particles fuse. Distortion and warping are significant concerns.
This happens because the part shrinks as the particles bond and the pores between them get smaller. If the initial density of the green compact is not uniform, different sections will shrink at different rates, causing the part to warp.
Blistering is another key defect, appearing as bubbles or bumps on the part's surface. This is caused by gas that gets trapped within the pores of the compact during heating. As the temperature rises, the gas expands faster than it can escape, forcing the material outward.
The Most Critical "Defect": Porosity
The most defining characteristic of a sintered part is its residual porosity. While sometimes a desired feature, for structural applications, it is the primary limitation.
Porosity and Reduced Strength
Because the metal is not melted and cast, microscopic voids always remain between the fused particles. This means a sintered part is almost never 100% dense.
This inherent porosity directly reduces the part's mechanical properties. Compared to a wrought or forged equivalent, a sintered component will generally have lower tensile strength, ductility, and impact resistance.
Porosity as a Feature
Conversely, this porosity can be a significant advantage. It's the basis for self-lubricating bearings, which are impregnated with oil, and for filters, where the interconnected pores allow fluid to pass through.
Mitigating Sintering Defects
Controlling these defects is the central focus of quality powder metallurgy. Success depends on mastering the variables at every stage.
Design for Sintering (DFS)
The most effective strategy is designing the part with the process in mind. This means avoiding sharp internal corners, minimizing extreme variations in wall thickness, and designing features that allow for smooth powder flow and part ejection.
Process Control
Strict control over the raw materials and process is critical. This includes using high-quality metal powder with consistent particle size, ensuring uniform die filling, applying precise compaction pressure, and carefully managing the sintering temperature and atmosphere.
Secondary Operations
For high-performance applications where porosity is unacceptable, secondary operations can be used. Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), for example, applies high pressure and temperature simultaneously to a sintered part, effectively closing the internal voids and increasing density to nearly 100%.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding these potential defects is key to deciding if sintering is the correct manufacturing process for your needs.
- If your primary focus is absolute strength and durability: A forged or machined component from solid bar stock is likely the superior choice, as it will be fully dense.
- If your primary focus is producing a complex shape at high volume and low cost: Sintering is an excellent option, provided the part's design accounts for the process limitations and its mechanical strength requirements are within acceptable limits.
- If your primary focus is controlled porosity for filtration or lubrication: Sintering is not just the best choice; it is often the only choice.
Ultimately, viewing these "defects" as inherent trade-offs in a highly valuable manufacturing process allows for intelligent design and application.
Summary Table:
| Defect Type | Common Causes | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Porosity | Inherent to powder fusion process | Residual voids between particles; reduces strength but enables self-lubrication/filtration |
| Cracking | Stress during ejection, poor powder flow | Fractures in green compact or laminated layers |
| Distortion/Warping | Non-uniform density/shrinkage during sintering | Part warps or changes shape |
| Blistering | Trapped gas expanding during heating | Bubbles or bumps on the surface |
Need reliable sintered metal components or expert advice on mitigating defects? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for powder metallurgy processes. Our expertise ensures you get durable, precision-engineered parts tailored to your laboratory's specific needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your sintering outcomes and deliver the performance you require.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the core function of a high-temperature atmosphere sintering furnace in the fabrication of Ni-Al2O3-TiO2 composites?
- Why is precise temperature control in a sintering furnace critical for NASICON electrolytes? Ensure Material Purity
- How does an atmosphere furnace ensure quality in BN nanotube synthesis? Precision Control for Cup-Stacked Structures
- What are the main components of an industrial furnace? Explore Essential Elements for Precision Heating
- Why Use Ultra-High Vacuum Furnaces for LLZO? Ensure Chemical Stability & Interface Integrity in Solid Electrolytes



















