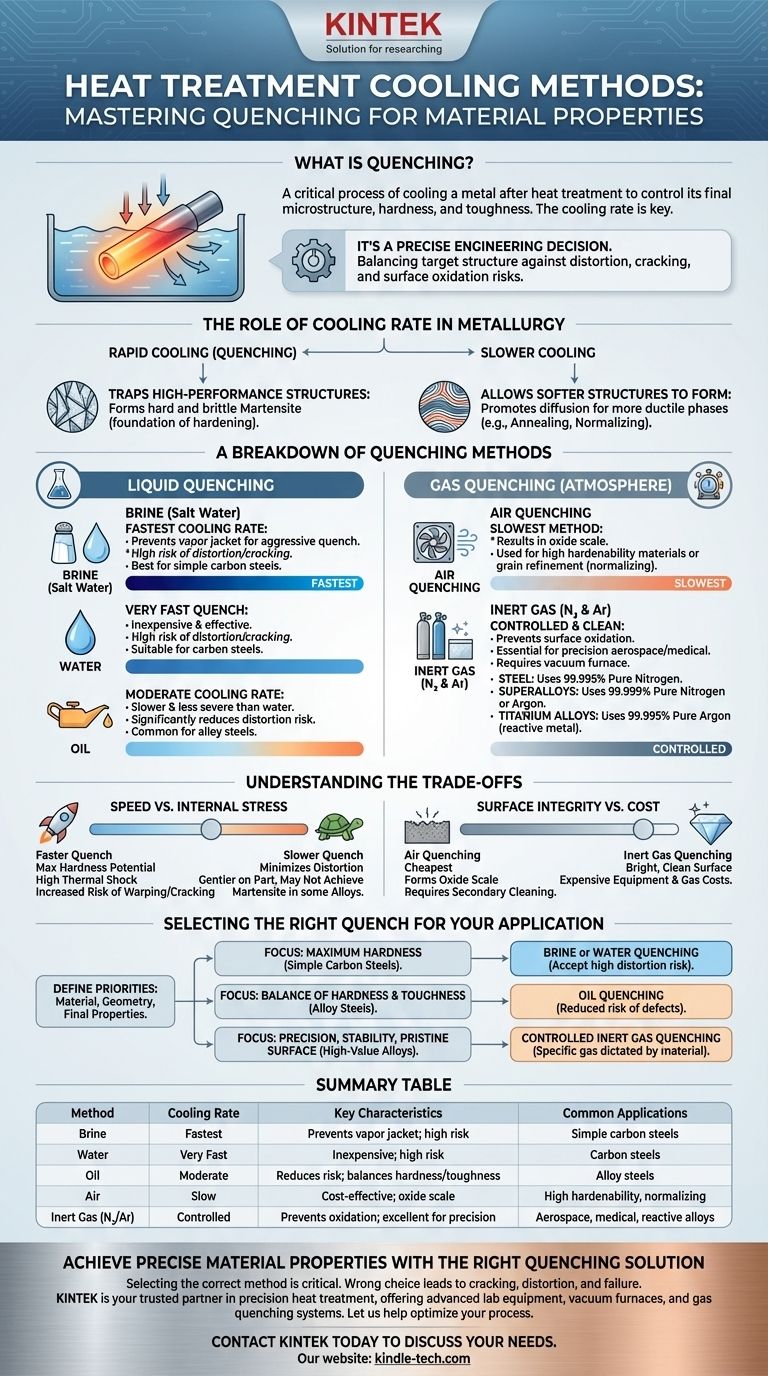
The method of cooling after heat treatment, known as quenching, is a critical step that dictates a metal's final properties. The primary methods involve immersing the heated component in a liquid like brine, water, or oil, or cooling it in a controlled gas atmosphere using air, nitrogen, or argon. The choice of medium determines the cooling rate, which in turn controls the material's microstructure, hardness, and toughness.
The selection of a quenching method is not merely about cooling the part; it is a precise engineering decision. The speed and medium of the quench are chosen to achieve a target metallurgical structure while managing risks like distortion, cracking, and surface oxidation.
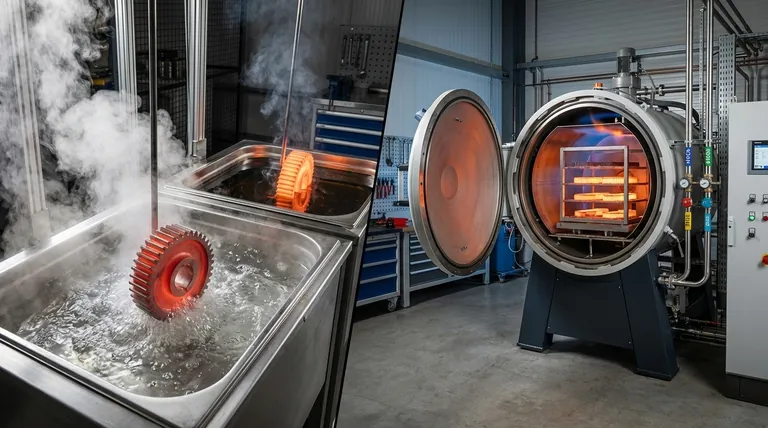

The Role of Cooling Rate in Metallurgy
The entire purpose of quenching is to control the phase transformation of the metal as it cools. By manipulating the cooling rate, you can lock in desirable, non-equilibrium microstructures.
Trapping High-Performance Structures
For materials like steel, heating to a high temperature (austenitizing) dissolves carbon into the iron matrix. Rapid cooling traps this structure, forcing it to transform into martensite, a very hard and brittle phase. This is the foundation of hardening.
Allowing Softer Structures to Form
Slower cooling allows atoms more time to diffuse and form softer, more ductile structures like pearlite or bainite. Processes like annealing or normalizing use slow cooling to soften a material, relieve internal stresses, and refine its grain structure.
A Breakdown of Quenching Methods
Quenching methods are broadly categorized by the medium used. Each offers a different level of cooling severity and control.
Liquid Quenching
This is the most common category, characterized by rapid heat extraction through direct contact with a liquid.
- Brine (Salt Water): Provides the fastest cooling rate. The salt helps disrupt the insulating vapor jacket that can form around the part, ensuring a more uniform and aggressive quench.
- Water: Offers a very fast quench, but is less severe than brine. It is inexpensive and effective but poses a high risk of part distortion and cracking, especially in complex geometries.
- Oil: Slower than water, providing a less severe quench. This significantly reduces the risk of distortion and cracking, making it a common choice for many alloy steels.
Gas Quenching
Also known as atmosphere quenching, this method is used when control, surface integrity, and minimizing distortion are paramount. It is typically performed inside a vacuum furnace.
- Air Quenching: This is the slowest method, often referred to as normalizing for steels. It is used for materials with high hardenability (which harden even with slow cooling) or when the goal is to refine grain structure rather than achieve maximum hardness.
- Inert Gas (Nitrogen & Argon): This is a high-performance method essential for aerospace and medical applications. Cooling with high-purity inert gas prevents surface oxidation entirely. The choice of gas is critical and material-dependent.
- Steel: Typically quenched with 99.995% pure nitrogen.
- Superalloys: Require higher purity, using 99.999% nitrogen or argon.
- Titanium Alloys: These are reactive and require a truly inert gas like 99.995% argon to prevent contamination and embrittlement.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a quenching method involves balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" method; there is only the most appropriate method for a specific material and desired outcome.
Speed vs. Internal Stress
The core trade-off is between achieving desired hardness and maintaining dimensional stability.
- Faster quenches (brine, water) maximize the potential for hardness but introduce significant thermal shock and internal stresses, increasing the risk of warping or cracking.
- Slower quenches (oil, gas) are gentler on the part, minimizing distortion. However, they may not be fast enough to achieve the required martensitic structure in lower-hardenability alloys.
Surface Integrity vs. Cost
The quenching environment directly impacts the surface of the part.
- Air quenching is the cheapest but results in the formation of oxide scale, which often requires a secondary cleaning operation like sandblasting.
- Inert gas quenching delivers a bright, clean surface straight out of the furnace but requires expensive vacuum equipment and the ongoing cost of high-purity gases.
Material Compatibility
The quenching medium must be chemically compatible with the metal alloy being treated. A poor choice can ruin the material. As noted, reactive metals like titanium cannot be exposed to oxygen or even nitrogen at high temperatures and therefore mandate the use of argon.
Selecting the Right Quench for Your Application
Your choice must be driven by the material, the part's geometry, and the final properties you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness in simple carbon steels: Brine or water quenching is effective, but you must accept the high risk of distortion and cracking.
- If your primary focus is a good balance of hardness and toughness in alloy steels: Oil quenching is the most common and practical choice, offering a reduced risk of defects.
- If your primary focus is precision, dimensional stability, and a pristine surface on high-value alloys: Controlled inert gas quenching is the only reliable option, with the specific gas dictated by the material itself.
Ultimately, the quenching process is a deliberate manipulation of metallurgy to produce a component that meets its specific engineering requirements.
Summary Table:
| Quenching Method | Cooling Rate | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brine (Salt Water) | Fastest | Prevents vapor jacket; high risk of distortion/cracking | Simple carbon steels requiring maximum hardness |
| Water | Very Fast | Inexpensive; high risk of distortion/cracking | Carbon steels |
| Oil | Moderate | Reduces risk of distortion; balances hardness and toughness | Alloy steels |
| Air | Slow | Cost-effective; results in oxide scale | Materials with high hardenability, normalizing |
| Inert Gas (N₂/Ar) | Controlled | Prevents oxidation; excellent for precision and surface integrity | Aerospace, medical, reactive alloys (e.g., titanium) |
Achieve Precise Material Properties with the Right Quenching Solution
Selecting the correct quenching method is critical to achieving the desired hardness, toughness, and dimensional stability in your heat-treated components. The wrong choice can lead to cracking, distortion, or failure to meet performance specifications.
KINTEK is your trusted partner in precision heat treatment. We specialize in providing advanced laboratory equipment and consumables, including vacuum furnaces and gas quenching systems, designed for controlled and repeatable results. Whether you are working with standard alloy steels or reactive superalloys, our expertise ensures you have the right technology to optimize your quenching process.
Let us help you enhance your lab's capabilities and ensure material success.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application needs and discover how our solutions can bring reliability and precision to your heat treatment processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 100L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Circulator for Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath Water Bath Cooling
- 80L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Circulator for Water Bath Cooling and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- 30L Chiller Water Bath Cooling Circulator Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- 50L Chiller Water Bath Cooling Circulator Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- 20L Chiller Water Bath Cooling Circulator Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-precision chiller core in natural gas hydrate synthesis? Master Thermal Stability for Lab Success
- What is the importance of a Recirculating Cooling Water System? Protect Your Lab and Master Reaction Control
- Why is a cooling circulation system or chiller necessary for SFE? Prevent Gas Locking and Ensure High-Pressure Flow
- Why is a high-performance cooling circulator necessary in silica membrane desalination? Boost Your Permeate Mass Transfer
- What is the purpose of using a cooling water system after wheat straw pretreatment? Optimize Sugar Yield and Safety



















