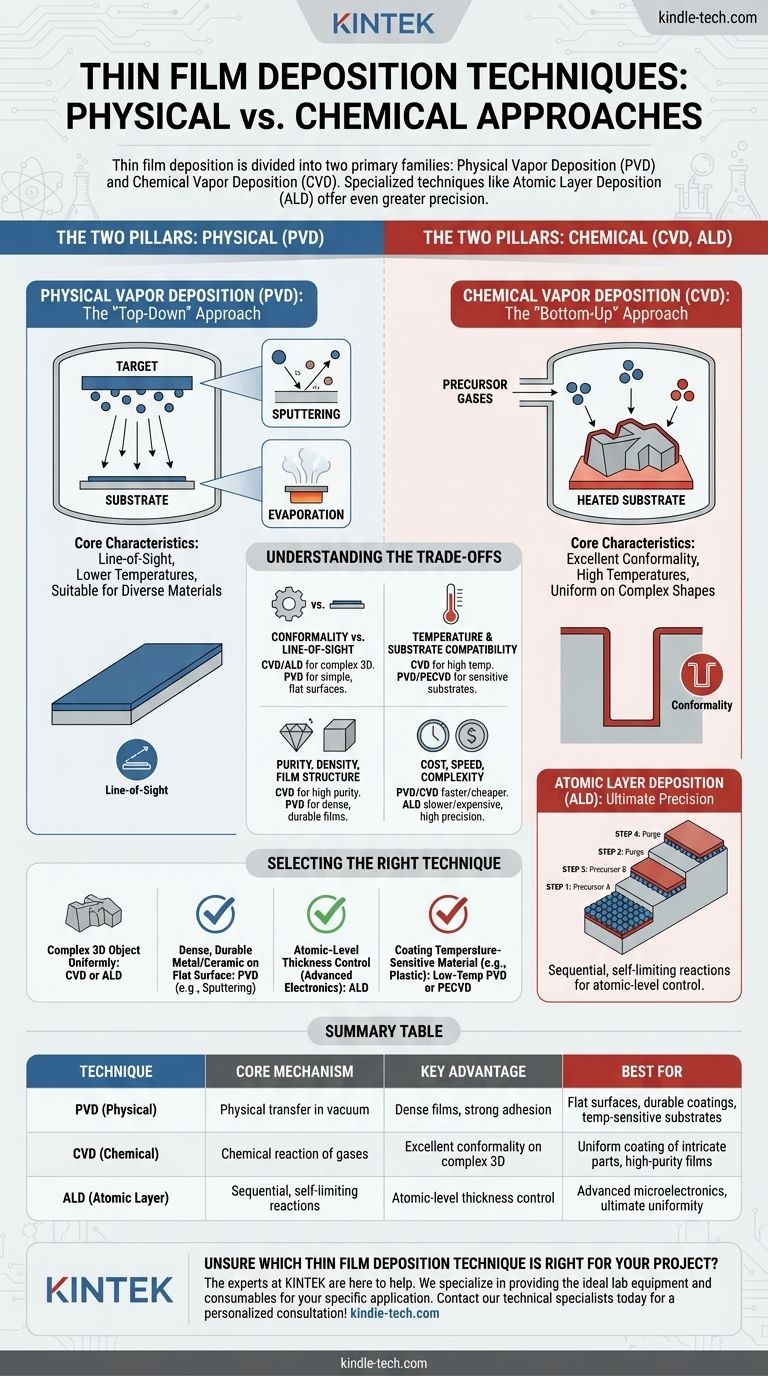
At its core, thin film deposition is divided into two primary families: Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). PVD physically transfers a solid material onto a substrate within a vacuum, often by sputtering or evaporation. In contrast, CVD uses chemical reactions between precursor gases on a heated surface to grow the film from the bottom up. Specialized techniques like Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) offer even greater precision by building the film one atomic layer at a time.
The fundamental difference between deposition techniques is not just the equipment, but the mechanism itself. Your choice between a physical (PVD) or chemical (CVD, ALD) process hinges on your need for uniform coverage on complex shapes, the temperature sensitivity of your substrate, and the required purity and density of the final film.
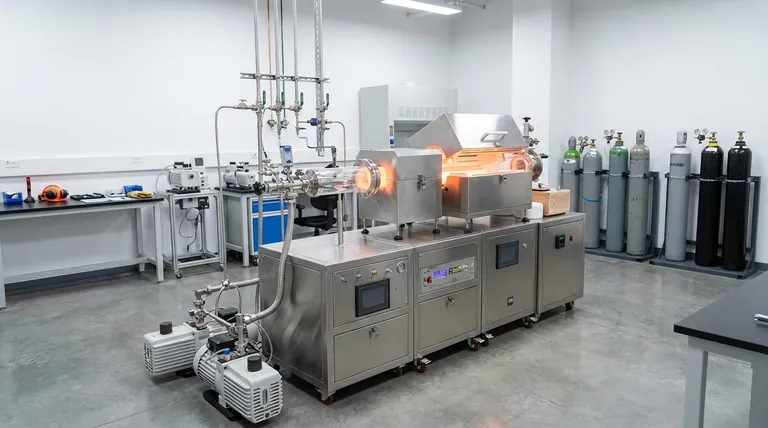

The Two Pillars: Physical vs. Chemical Methods
Understanding the foundational difference between physical and chemical deposition is the first step in making an informed decision. These are not just different techniques; they are entirely different approaches to building a material layer.
A physical process (PVD) takes a solid block of the desired material, turns it into a vapor, and lets it condense onto your part. A chemical process (CVD) starts with reactive gases and uses them as building blocks to construct the film directly on the surface through a chemical reaction.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): The "Top-Down" Approach
PVD encompasses a set of vacuum deposition methods that use physical means to produce a vapor of material, which then deposits on the object to be coated.
How PVD Works
In a high-vacuum chamber, a solid source material, known as the "target," is converted into a vapor. This vapor then travels in a straight line and condenses on the cooler substrate, forming a thin film.
Key Technique: Sputtering
In sputtering, the target is bombarded with high-energy ions (usually an inert gas like argon). This bombardment acts like a microscopic sandblaster, knocking atoms off the target, which then travel and deposit onto the substrate.
Key Technique: Evaporation
This method involves heating the source material in the vacuum chamber until it evaporates or sublimes. The resulting vapor rises, travels to the substrate, and condenses back into a solid state, creating the film.
Core Characteristics of PVD
PVD is fundamentally a "line-of-sight" process, meaning it coats surfaces that are directly exposed to the source. It is often performed at lower temperatures than traditional CVD, making it suitable for a wider range of substrate materials.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): The "Bottom-Up" Approach
CVD builds films through a chemical process rather than a physical one. This distinction gives it a unique and powerful set of capabilities.
How CVD Works
Volatile precursor gases are introduced into a reaction chamber containing a heated substrate. These gases react or decompose on the hot surface, leaving behind the desired solid material as a thin film.
Core Characteristics of CVD
The most significant advantage of CVD is its excellent conformality. Because the precursor gases can flow around complex shapes before reacting, CVD can deposit a perfectly uniform film on intricate 3D structures.
Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD): Ultimate Precision
ALD is a sophisticated subtype of CVD that breaks the chemical reaction into two separate, self-limiting half-reactions. This allows for the deposition of a film one single atomic layer at a time, providing unparalleled control over thickness and uniformity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single deposition technique is universally superior. The optimal choice is always a matter of balancing competing factors based on the application's specific requirements.
Conformality vs. Line-of-Sight
If you need to coat the inside of a narrow trench or a complex mechanical part, the conformal nature of CVD and ALD is essential. For coating a simple, flat surface like a lens or wafer, the line-of-sight nature of PVD is often sufficient and more economical.
Temperature and Substrate Compatibility
Traditional CVD often requires very high temperatures (several hundred degrees Celsius) to drive the chemical reactions. This can damage sensitive substrates like polymers or certain electronics. PVD and specialized low-temperature CVD variants (like PECVD) are better suited for these applications.
Purity, Density, and Film Structure
CVD can produce exceptionally pure films because the precursor gases can be refined to a very high degree. PVD processes, particularly sputtering, often result in denser films with strong adhesion, which is ideal for durable protective coatings.
Cost, Speed, and Complexity
Generally, PVD and simple CVD systems are faster and less expensive for many applications. ALD, while offering incredible precision, is a much slower and more expensive process, reserved for high-value applications like advanced microelectronics.
Selecting the Right Technique for Your Application
Your final decision should be driven by the most critical property of your desired film.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex 3D object uniformly: CVD or ALD are the superior choices due to their non-line-of-sight, conformal nature.
- If your primary focus is depositing a dense, durable metal or ceramic film on a flat surface: PVD methods like sputtering are often the most effective and economical solution.
- If your primary focus is atomic-level thickness control for advanced electronics: ALD is the only technique that provides the necessary layer-by-layer precision.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive material like plastic: A low-temperature PVD process or Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is the most suitable path.
By matching the core mechanism of the deposition technique to your end goal, you can ensure the performance and quality required for your project.
Summary Table:
| Technique | Core Mechanism | Key Advantage | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVD (Physical) | Physical transfer in vacuum | Dense films, strong adhesion | Flat surfaces, durable coatings, temperature-sensitive substrates |
| CVD (Chemical) | Chemical reaction of gases | Excellent conformality on complex 3D shapes | Uniform coating of intricate parts, high-purity films |
| ALD (Atomic Layer) | Sequential, self-limiting reactions | Atomic-level thickness control | Advanced microelectronics, ultimate uniformity |
Unsure which thin film deposition technique is right for your project? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing the ideal lab equipment and consumables for your specific application, whether you require the conformal coating of CVD, the precision of ALD, or the durability of PVD. Let us help you achieve the perfect film properties for your research or production needs.
Contact our technical specialists today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- Do CVD diamonds pass diamond tester? Yes, they are real diamonds.
- Why argon gas is used in CVD? Ensure High-Purity, Uniform Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between RTA and RTP? Mastering Semiconductor Thermal Processing
- What is the difference between CVD and sputter coating? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is Organometallic Chemical Vapour Deposition (MOCVD) used for? Leading LED and GaN Semiconductor Growth
- What are the different types of chemical vapour deposition process? A Guide to CVD Methods for Your Lab
- How do Mass Flow Controllers (MFCs) influence LDIP properties during CVD? Achieve Precise Isotropic Carbon Synthesis
- What is the process of graphene transfer? From CVD Growth to Your Final Application



















