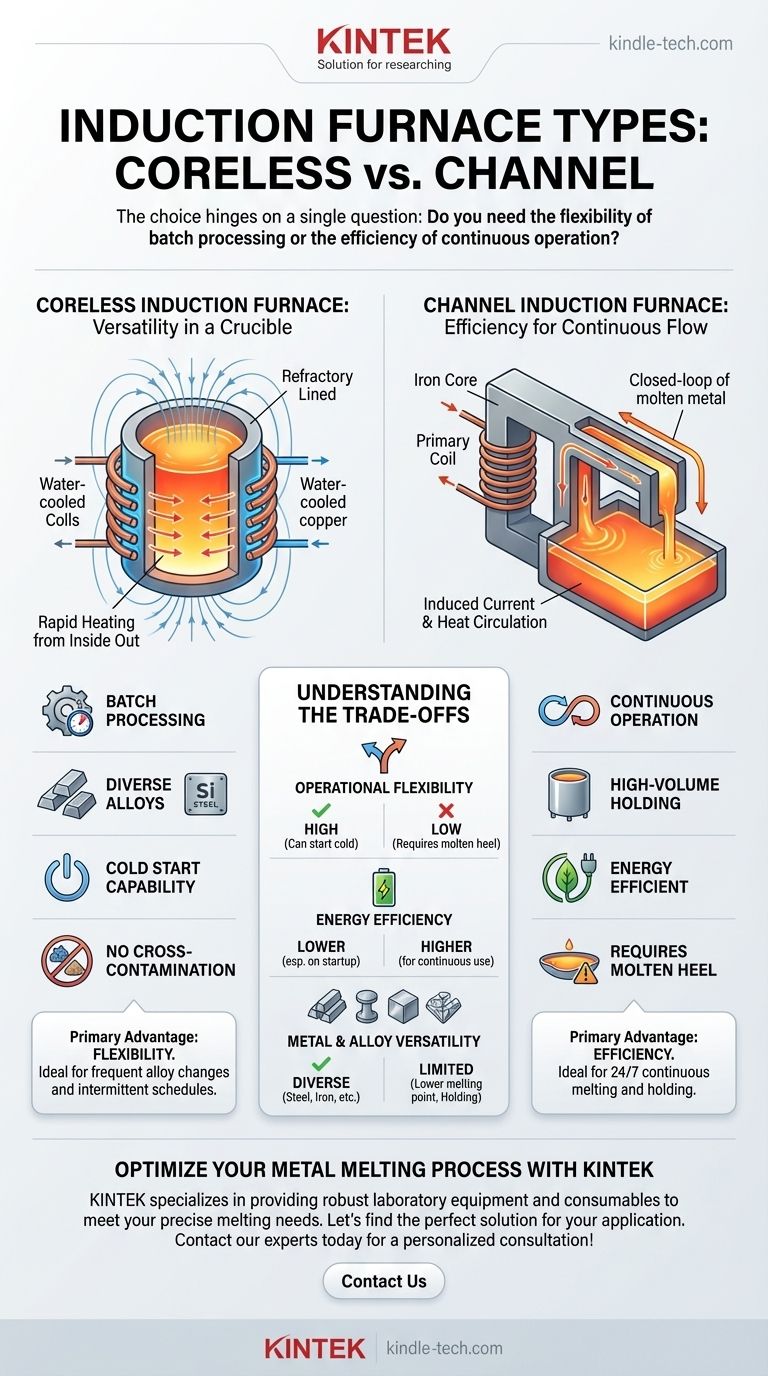
The two primary types of induction furnaces are the coreless furnace and the channel furnace. While both leverage the principle of electromagnetic induction to melt metal, their internal design and operational characteristics are fundamentally different, making each suited for very distinct industrial applications.
The choice between an induction furnace is not about which is "better," but which is correct for the task. Your decision hinges on a single question: do you need the flexibility of batch processing (coreless) or the efficiency of a continuous operation (channel)?
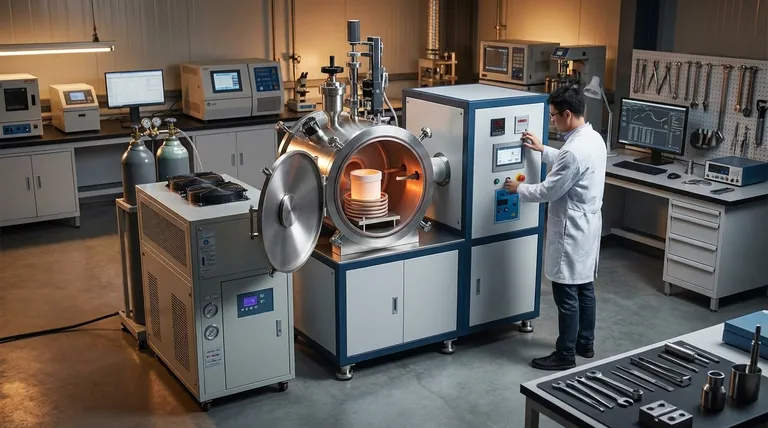

The Coreless Induction Furnace: Versatility in a Crucible
A coreless furnace is the most common and versatile type of induction furnace. It is essentially a refractory-lined crucible surrounded by a powerful, water-cooled copper coil.
How It Works
When alternating current flows through the coil, it generates a powerful magnetic field. This field induces eddy currents directly within the metal charge inside the crucible, causing it to heat up rapidly and melt from the inside out.
Key Applications
The coreless design is ideal for applications requiring frequent changes in alloy composition or intermittent operation. It can be started "cold" without a pool of molten metal, making it perfect for foundries that handle a variety of metals, including steel, iron, and non-ferrous alloys.
Primary Advantage: Flexibility
Because it can be completely emptied between melts, the coreless furnace offers maximum flexibility for producing different alloys without cross-contamination. Its ability to start and stop on demand suits batch-oriented production schedules.
The Channel Induction Furnace: Efficiency for Continuous Flow
A channel furnace operates more like an electrical transformer. It has an iron core with a primary coil, and a closed loop, or "channel," of molten metal acts as the secondary winding.
How It Works
Current flowing through the primary coil induces a much larger current in the molten metal loop. The electrical resistance of the metal in this narrow channel generates intense heat, which then circulates through the main bath of the furnace via convection.
Key Applications
This design is exceptionally energy-efficient for holding large volumes of molten metal at a constant temperature. It is commonly used in high-production foundries for melting low-temperature non-ferrous metals or for holding and superheating cast iron that has been melted in a separate furnace.
Primary Advantage: Efficiency
A key feature—and limitation—of the channel furnace is that it must always maintain a molten "heel" of metal in the channel to complete the electrical circuit. This makes it ideal for continuous, 24/7 operations where its high thermal efficiency provides significant cost savings.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The correct choice depends entirely on your operational model. Neither furnace is universally superior; they are engineered for different purposes.
Operational Flexibility
The coreless furnace is the clear winner. It can be started from cold and shut down completely, offering unparalleled flexibility for varied production schedules and diverse alloy requirements. The channel furnace is rigid, requiring a continuous molten bath to function.
Energy Efficiency
For holding or continuous melting, the channel furnace is significantly more energy-efficient. The coreless furnace consumes more power, particularly during cold startups, but this is the trade-off for its operational flexibility.
Metal and Alloy Versatility
The coreless furnace can melt a wide range of metals with varying melting points, including steel. The channel furnace is typically restricted to lower melting point alloys or serving as a holding unit for metals melted elsewhere.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace type is a critical decision that impacts both productivity and operating costs.
- If your primary focus is operational flexibility and alloy diversity: A coreless furnace is the necessary choice for its ability to handle batch processing and frequent alloy changes.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous melting or holding: A channel furnace offers superior energy efficiency for maintaining large quantities of molten metal at temperature.
- If you need to melt high-temperature alloys like steel: The coreless furnace design is the industry standard for these demanding applications.
By aligning the furnace's inherent design with your production goals, you ensure an efficient and cost-effective melting operation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Coreless Furnace | Channel Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Batch Melting, Alloy Changes | Continuous Melting/Holding |
| Operational Flexibility | High (Can start cold) | Low (Requires molten heel) |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower (esp. on startup) | Higher (for continuous use) |
| Ideal For | Diverse alloys, steel, iron | High-volume non-ferrous, cast iron |
Optimize Your Metal Melting Process with KINTEK
Choosing between a coreless and channel induction furnace is a critical decision that directly impacts your productivity and bottom line. The right equipment ensures maximum efficiency for your specific operational model, whether you require the flexibility of batch processing or the energy savings of continuous melting.
KINTEK specializes in providing robust laboratory equipment and consumables to meet your precise melting needs. Our expertise helps you select the ideal furnace to enhance your lab's capabilities, reduce operating costs, and improve the quality of your results.
Let's find the perfect solution for your application. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity



















