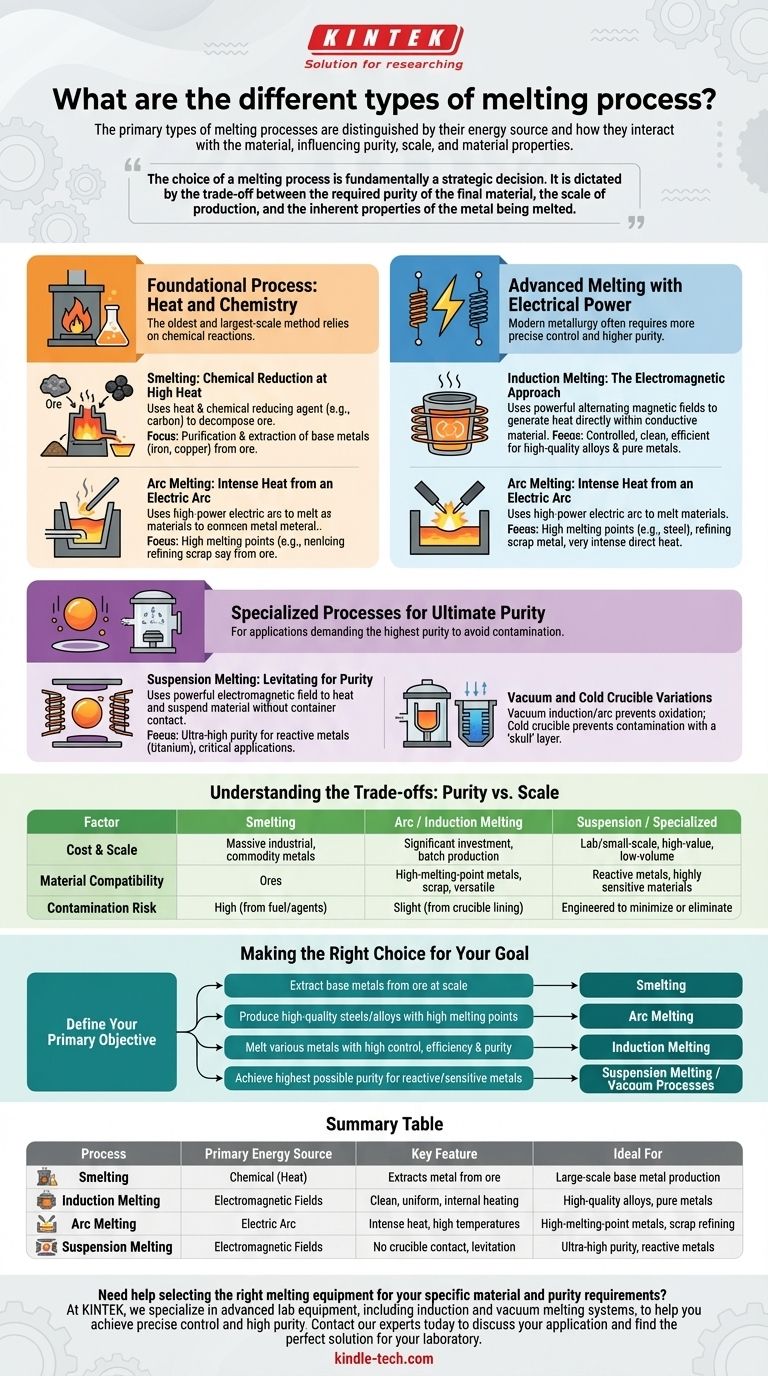
The primary types of melting processes are distinguished by their energy source and how they interact with the material. The main industrial methods include smelting, which uses chemical reduction; arc melting, which uses an intense electric arc; and induction melting, which uses electromagnetic fields. For applications demanding the highest purity, specialized techniques like suspension melting are employed to avoid contamination entirely.
The choice of a melting process is fundamentally a strategic decision. It is dictated by the trade-off between the required purity of the final material, the scale of production, and the inherent properties of the metal being melted.

Foundational Process: Heat and Chemistry
The oldest and largest-scale method relies on chemical reactions to not only melt but also extract metal from its raw, impure state.
Smelting: Chemical Reduction at High Heat
Smelting is a form of extractive metallurgy. It uses heat and a chemical reducing agent, like carbon, to decompose an ore, driving off other elements as gases or slag and leaving the molten metal behind.
This process is not just about melting; it's about purification and extraction. It is the foundational process for producing base metals like iron, copper, and tin from their naturally occurring ores.
Advanced Melting with Electrical Power
Modern metallurgy often requires more precise control and higher purity than smelting can offer. These methods rely on electrical energy to generate clean, contained heat.
Induction Melting: The Electromagnetic Approach
Induction melting uses powerful alternating magnetic fields to generate heat directly within the conductive material. Coils surrounding a crucible create a magnetic field, which induces swirling electrical currents (eddy currents) in the metal charge.
The resistance of the metal to these currents generates intense, uniform heat from the inside out. This method is highly controlled, clean, and efficient, making it ideal for producing high-quality alloys and pure metals.
Arc Melting: Intense Heat from an Electric Arc
An Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) uses a high-power electric arc to melt materials. A massive electrical current jumps across a gap between electrodes and the metal charge, creating an arc with a temperature of thousands of degrees.
This intense, direct heat is highly effective for melting metals with very high melting points, such as steel, and for refining scrap metal into new, high-quality products.
Specialized Processes for Ultimate Purity
For aerospace, electronics, or medical applications, even trace impurities are unacceptable. These processes are designed to eliminate the primary source of contamination: contact with a crucible.
Suspension Melting: Levitating for Purity
Suspension melting, often called levitation melting, uses a powerful electromagnetic field to both heat and suspend the material. The metal floats within a vacuum or inert atmosphere as it melts, never touching a container wall.
This complete lack of contact ensures ultra-high purity, making it essential for processing highly reactive metals like titanium or for creating materials where any contamination would be catastrophic.
Vacuum and Cold Crucible Variations
To further enhance purity, induction and arc melting can be performed inside a vacuum chamber. Vacuum induction melting prevents oxidation and helps pull dissolved gases like oxygen and hydrogen out of the molten metal.
A cold crucible design is another method to prevent contamination. The crucible is made of water-cooled copper segments, which causes a thin, solid layer of the material being melted—a "skull"—to form against the wall, containing the rest of the liquid metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Purity vs. Scale
No single melting process is universally superior. The optimal choice depends on balancing cost, the material being processed, and the final quality requirements.
Cost and Production Scale
Smelting is a massive industrial operation suited for commodity metals. Arc and induction furnaces represent a significant capital investment but offer flexibility for batch production. Suspension melting is a laboratory or small-scale process, reserved for low-volume, high-value materials.
Material Compatibility
Smelting is designed specifically for ores. Arc melting excels with high-melting-point metals and scrap recycling. Induction melting is highly versatile for most conductive metals and alloys. Suspension and vacuum processes are necessary for reactive metals that would otherwise be contaminated.
Contamination Risk
The risk of contamination is a critical differentiator. Smelting introduces elements from the fuel and fluxing agents. Standard arc and induction melting risk slight contamination from the crucible lining. Suspension and cold-crucible methods are engineered specifically to minimize or eliminate this risk.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a process begins with defining your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is extracting base metals from ore at scale: Smelting is the established industrial process.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality steels or alloys with high melting points: Arc melting provides the necessary intense heat and refining capability.
- If your primary focus is melting various metals with high control, efficiency, and purity: Induction melting offers the best all-around performance.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible purity for reactive or sensitive metals: Suspension melting or specialized vacuum processes are required to eliminate contamination.
Understanding these fundamental differences allows you to select a process that aligns perfectly with your material, purity requirements, and operational scale.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Energy Source | Key Feature | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smelting | Chemical (Heat) | Extracts metal from ore | Large-scale production of base metals (e.g., iron, copper) |
| Induction Melting | Electromagnetic Fields | Clean, uniform, internal heating | High-quality alloys, pure metals, versatile applications |
| Arc Melting | Electric Arc | Intense heat, high temperatures | High-melting-point metals (e.g., steel), scrap metal refining |
| Suspension Melting | Electromagnetic Fields | No crucible contact, levitation | Ultra-high purity, reactive metals (e.g., titanium), sensitive applications |
Need help selecting the right melting equipment for your specific material and purity requirements? The choice of melting process is critical to your success. At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment, including induction and vacuum melting systems, to help you achieve precise control and high purity for your materials. Whether you're developing new alloys or refining high-value metals, our expertise ensures you get the performance you need. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and find the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys



















