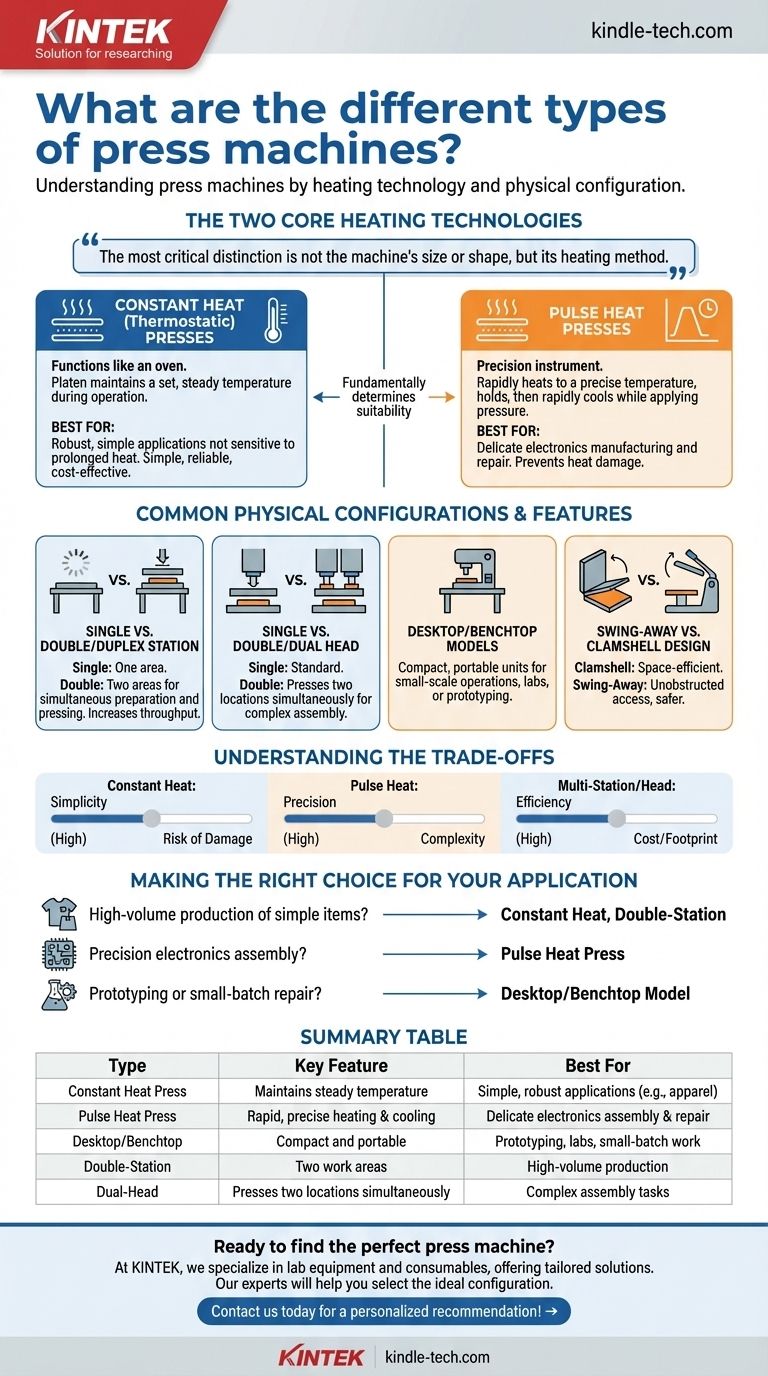
When selecting a press machine, the terminology can be confusing, but the types are best understood by breaking them down into two key categories: their heating technology and their physical configuration. The primary types include constant temperature (thermostatic) presses, which maintain a steady heat, and pulse heat presses, which offer precision control. These technologies are then built into various forms, such as compact desktop models or high-throughput double-station machines.
The most critical distinction is not the machine's size or shape, but its heating method. Your choice between constant and pulse heat technology will fundamentally determine the machine's suitability for either robust, simple applications or delicate, precision-focused work.

The Two Core Heating Technologies
The engine of any heat press is how it delivers thermal energy. This is the single most important factor that dictates its use case.
Constant Heat (Thermostatic) Presses
A constant heat press, also known as a thermostatic press, functions like an oven. The heating element, or platen, is brought to a set temperature and remains there during operation.
This method is ideal for materials and processes that are not sensitive to prolonged heat exposure. It is simple, reliable, and cost-effective.
Pulse Heat Presses
A pulse heat press is a precision instrument. It keeps the heating element (called a thermode or indenter) at a cool or ambient temperature until the moment of operation.
When activated, it rapidly heats to a precise temperature, holds it for a specific duration, and then rapidly cools down while still applying pressure. This process is crucial for preventing heat damage to sensitive components, making it essential for electronics manufacturing and repair.
Common Physical Configurations & Features
Beyond the heating method, the physical design of the press is tailored for specific workflows, scales of production, and application complexities.
Single vs. Double/Duplex Station
This refers to the machine's workflow layout. A single-station press has one area to load, press, and unload a part.
A double-station (or duplex) press has two work areas. This allows an operator to prepare one part for pressing while the other is currently in a press cycle, significantly increasing throughput for production environments.
Single vs. Double/Dual Head
The "head" or "indenter" is the part of the machine that delivers the heat and pressure. Most machines are single-head.
A double-head or dual-indenter machine can press two separate locations on a single workpiece simultaneously. This is common in complex electronics assembly where multiple connections must be bonded at once.
Desktop/Benchtop Models
This categorization is based purely on size and portability. Desktop or benchtop presses are compact units designed to fit in a smaller workshop, laboratory, or repair facility. They offer full functionality but for smaller-scale operations.
Swing-Away vs. Clamshell Design
This describes how the top heat platen opens. A clamshell design opens on a hinge like a mouth, which is space-efficient.
A swing-away design allows the top platen to be moved completely to the side. This provides unobstructed access to the work area, reducing the risk of accidental contact with the hot surface and making it easier to position items precisely.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right machine requires acknowledging the inherent compromises in each design.
Constant Heat: Simplicity vs. Risk
The primary benefit of a constant heat press is its simplicity and lower cost. However, the continuous heat exposure presents a risk of damage to delicate substrates or electronic components.
Pulse Heat: Precision vs. Complexity
Pulse heat technology offers unparalleled precision and safety for sensitive applications. This control comes at the cost of increased machine complexity, a higher price point, and potentially slower individual cycle times due to the heating/cooling process.
Multi-Station/Head: Efficiency vs. Cost
Adding stations or heads directly boosts productivity and the ability to handle complex jobs. This increased capability requires a larger initial investment, more maintenance, and a larger physical footprint.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided entirely by the demands of your specific task.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of simple items (e.g., apparel, promotional goods): A constant heat, double-station press will maximize your throughput and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is precision electronics assembly (e.g., soldering flex cables, bonding fine wires): A pulse heat press is non-negotiable for its control and ability to prevent component damage.
- If your primary focus is prototyping or small-batch repair work: A desktop or benchtop model provides the necessary functionality without the large footprint or high cost of a production-scale machine.
Understanding these core distinctions between heating methods and configurations allows you to select a tool perfectly matched to your specific task.
Summary Table:
| Type | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Constant Heat Press | Maintains steady temperature | Simple, robust applications (e.g., apparel, promotional goods) |
| Pulse Heat Press | Rapid, precise heating and cooling | Delicate electronics assembly and repair |
| Desktop/Benchtop | Compact and portable | Prototyping, labs, and small-batch work |
| Double-Station | Two work areas for loading/unloading | High-volume production environments |
| Dual-Head | Presses two locations simultaneously | Complex assembly tasks |
Ready to find the perfect press machine for your lab or production line?
At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables, offering a range of press machines tailored to your specific needs—whether you require the precision of pulse heat technology for sensitive electronics or the high-throughput capability of a double-station press. Our experts will help you select the ideal configuration to enhance efficiency, ensure quality, and protect your materials.
Contact us today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- Can you use a heat press for transfers? The Definitive Tool for Professional Results
- How does a high-pressure heating press enhance fluoroplastic-carbon nanotube composites? Boost Strength by 20%
- What are the advantages of using a hot press for Li7P2S8I0.5Cl0.5? Boost Conductivity with Precision Densification
- What is the role of a hydraulic press with heating plates in copper welding tests? Analyze Stress & Thermal Cycles
- How does a hydraulic hot press contribute to the fabrication of all-solid-state battery cells? Enhance Ion Transport
- What is the difference between hot press and compression molding? Shape vs. Material Performance
- Why must electric heating elements be wrapped around the pellet forming die? Boost Oat Straw Pellet Quality
- What happens when you compress hot metal? A Guide to Plastic Deformation & Recrystallization



















