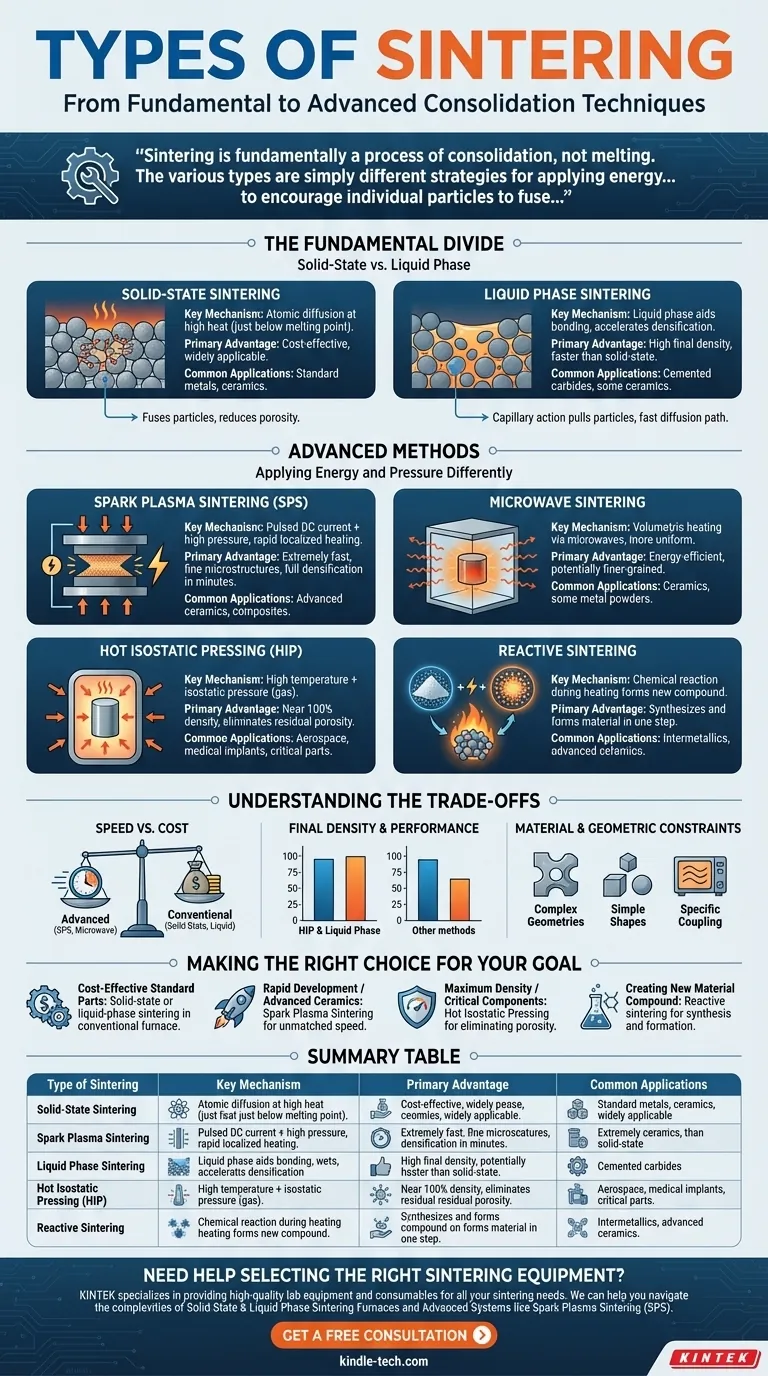
The primary types of sintering are Solid-State, Liquid Phase, Reactive, Microwave, Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS), and Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP). These methods differ fundamentally in how they apply energy and pressure to bond powdered materials into a solid mass without fully melting them, each offering distinct advantages in speed, final density, and material compatibility.
Sintering is fundamentally a process of consolidation, not melting. The various types are simply different strategies for applying energy—whether thermal, electrical, or chemical—to encourage individual particles to fuse, reduce porosity, and form a dense, functional component.
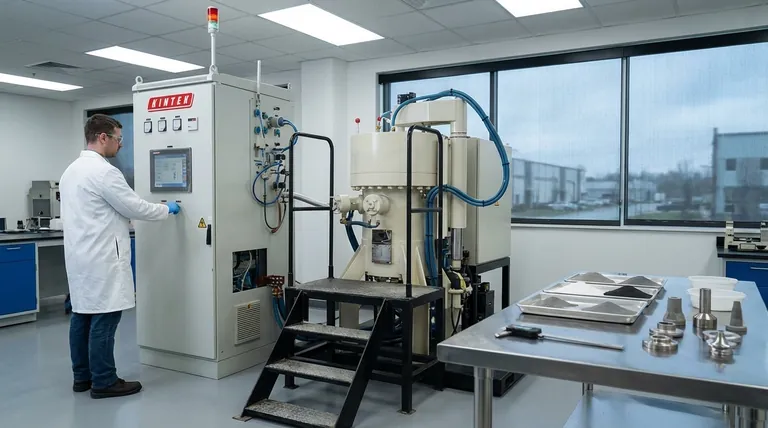

The Fundamental Divide: Solid-State vs. Liquid Phase
The most traditional and foundational classification of sintering depends on whether the entire process occurs in the solid state or if a small amount of liquid is strategically introduced to aid bonding.
Solid-State Sintering
In solid-state sintering, a compacted powder is heated to a temperature just below its melting point.
At this elevated temperature, atoms gain enough energy to diffuse across the boundaries of adjacent particles, gradually fusing them together and reducing the empty space, or porosity, between them.
This is a common, cost-effective method used for a wide range of metals and ceramics.
Liquid Phase Sintering
Liquid phase sintering involves a powder mixture where at least one component has a lower melting point than the others.
During heating, this component melts, creating a liquid that wets the solid particles. This liquid phase accelerates densification by pulling the solid particles together through capillary action and providing a fast path for atomic diffusion.
This method is highly effective for achieving very high densities and is often faster than solid-state sintering.
Advanced Methods: Applying Energy and Pressure Differently
Modern manufacturing and material science demands have led to the development of more advanced sintering techniques that offer greater speed, control, and performance.
Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS)
SPS, also known as Field-Assisted Sintering Technology (FAST), simultaneously applies high mechanical pressure and a pulsed DC electrical current to the powder.
The current generates rapid, localized heating at the particle contact points, dramatically accelerating the diffusion and bonding process. This allows for full densification in minutes rather than hours.
Microwave Sintering
This technique uses microwave radiation to heat the material. Unlike conventional furnaces that heat from the outside in, microwaves heat the material volumetrically.
This internal heating is often more uniform and significantly faster, leading to energy savings and potentially finer-grained microstructures in the final part.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
HIP subjects a component to both elevated temperature and high, uniform pressure from all directions, typically applied by a high-pressure inert gas.
This process is exceptionally effective at closing and eliminating any residual internal porosity, making it ideal for producing critical, high-performance parts with nearly 100% density.
Reactive Sintering
In reactive sintering, the initial powders are chosen so that they undergo a chemical reaction during the heating cycle.
This exothermic reaction can contribute to the heating process itself and results in the formation of a new, desired chemical compound. It is a method for both forming a part and synthesizing a new material simultaneously.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sintering method involves balancing process capabilities with material requirements and economic factors. No single method is universally superior.
Speed vs. Cost
Conventional furnace-based methods like solid-state and liquid-phase sintering are generally slower but rely on less complex and less expensive equipment.
Advanced methods like Spark Plasma Sintering and Microwave Sintering offer dramatic reductions in processing time but require a significant capital investment in specialized machinery.
Final Density and Performance
For applications where mechanical strength and reliability are paramount, achieving the highest possible density is critical.
Hot Isostatic Pressing and Liquid Phase Sintering are specifically designed to minimize or eliminate porosity, yielding components with superior mechanical properties.
Material and Geometric Constraints
The chosen method must be compatible with the material being processed. Microwave sintering, for example, works best with materials that couple well with microwave energy.
Furthermore, complex geometries or large parts may be better suited to conventional furnace methods or HIP, whereas SPS is often limited to simpler shapes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific application and material will dictate the most appropriate sintering technique.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of standard parts: Solid-state or liquid-phase sintering in a conventional furnace is the established and reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is rapid development or processing advanced ceramics: Spark Plasma Sintering offers unmatched speed for densifying novel or difficult-to-sinter materials.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density for critical components: Hot Isostatic Pressing is the definitive method for eliminating residual porosity and maximizing mechanical integrity.
- If your primary focus is creating a new material compound during fabrication: Reactive sintering provides a unique pathway to synthesize and form a component in a single process.
Ultimately, selecting the right sintering method is about matching the process to your material's needs and your final application's demands.
Summary Table:
| Type of Sintering | Key Mechanism | Primary Advantage | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid-State Sintering | Atomic diffusion at high heat | Cost-effective, widely applicable | Standard metals, ceramics |
| Liquid Phase Sintering | Liquid phase aids bonding | High final density, faster | Cemented carbides, some ceramics |
| Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) | Pulsed DC current + pressure | Extremely fast, fine microstructures | Advanced ceramics, composites |
| Microwave Sintering | Volumetric heating via microwaves | Energy-efficient, uniform heating | Ceramics, some metal powders |
| Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) | High temp + isostatic pressure | Near 100% density, eliminates porosity | Aerospace, medical implants |
| Reactive Sintering | Chemical reaction during heating | Synthesizes and forms material in one step | Intermetallics, advanced ceramics |
Need Help Selecting the Right Sintering Equipment?
Choosing the optimal sintering process is critical for achieving the desired material properties, whether you prioritize speed, final density, or cost-effectiveness. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your sintering needs.
We can help you navigate the complexities of:
- Solid-State & Liquid Phase Sintering Furnaces for reliable, cost-effective production.
- Advanced Systems like Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) for rapid R&D and processing of advanced materials.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and material goals. Let us help you find the perfect solution to enhance your lab's capabilities and achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace play for nanocopper? Achieve Maximum Densification Today
- How does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace facilitate TiBw/TA15 synthesis? Achieve 100% Dense Titanium Composites
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics
- How does a vacuum environment system contribute to the hot pressing sintering of B4C-CeB6? Unlock Peak Ceramic Density
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics



















