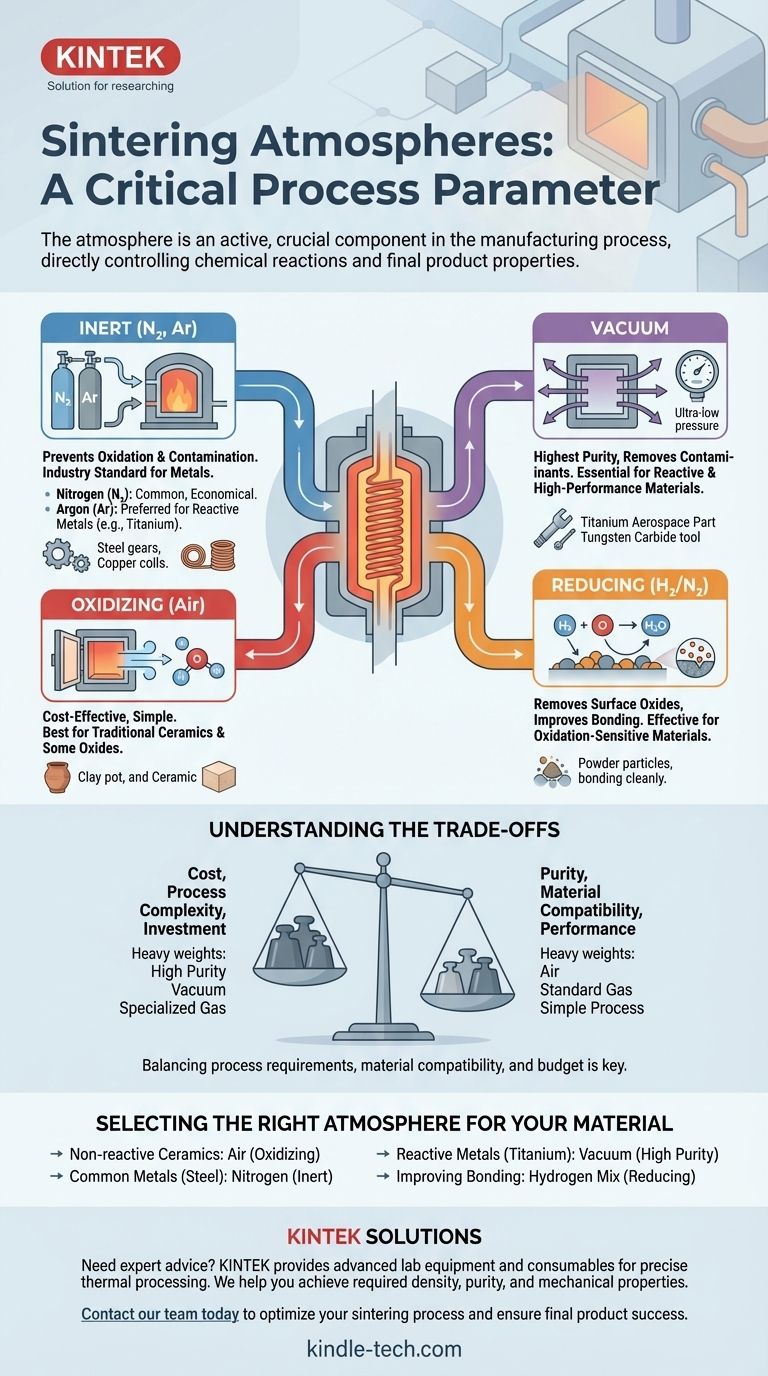
The atmosphere inside a sintering furnace is a critical, active component in the manufacturing process, not a passive background condition. The primary types of sintering atmospheres are oxidizing (like air), inert (such as nitrogen and argon), or a vacuum. The choice of atmosphere is dictated entirely by the material being processed and the desired chemical and physical properties of the final product.
Choosing a sintering atmosphere is a critical process parameter that directly controls chemical reactions. The right atmosphere prevents unwanted effects like oxidation and ensures the final component achieves its required density, purity, and mechanical properties.

The Purpose of a Controlled Atmosphere
The atmosphere's role is to create the ideal chemical environment for particles to bond effectively. This environment can be designed to be either non-reactive or intentionally reactive, depending on the material.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
For most metals and certain advanced ceramics, the primary goal is to prevent a reaction with oxygen. Heating these materials in air would cause them to form undesirable oxides, compromising their structural integrity and performance.
An inert atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) or a vacuum displaces the oxygen, creating a clean environment where particles can diffuse and bond without contamination.
Removing Binders and Impurities
Many powder metallurgy processes use a polymer "binder" to hold the green part's shape before sintering. During the initial heating stages, a controlled gas flow helps to effectively burn off and carry away these binders, preventing residual carbon from being trapped in the final part.
A Breakdown of Common Sintering Atmospheres
Each type of atmosphere offers a distinct set of benefits and is suited for specific materials and applications.
Oxidizing Atmospheres (Air)
This is the simplest and most cost-effective option, as it uses ambient air. It is primarily used for sintering traditional ceramics, such as clays and some oxides, where the formation of an oxide layer is either acceptable or beneficial to the final properties.
Inert Atmospheres (Nitrogen & Argon)
Inert atmospheres are the workhorse for preventing unwanted chemical reactions. They are essential for sintering most metals, including steels, copper alloys, and other non-reactive materials.
Nitrogen (N₂) is the most common and economical choice. Argon (Ar) is heavier and more purely inert than nitrogen, making it the preferred choice for materials that can react with nitrogen at high temperatures (like titanium).
Vacuum
A vacuum environment provides the highest level of purity by removing nearly all gas molecules from the furnace chamber. This is essential for highly reactive or high-performance materials where even trace amounts of gas could cause contamination.
Materials like titanium, tungsten, and certain stainless steels are often sintered in a vacuum to achieve maximum density and purity.
Reducing Atmospheres (e.g., Hydrogen)
A reducing atmosphere is an active environment designed to remove oxygen. Typically composed of a hydrogen (H₂) and nitrogen mix, it chemically reacts with and strips away surface oxides present on the powder particles.
This is highly effective for improving the bonding and density of materials that are sensitive to even slight oxidation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The selection of an atmosphere is a balance between process requirements, material compatibility, and cost.
Cost vs. Purity
There is a direct correlation between the purity of the atmosphere and its cost. Air is essentially free, while high-purity argon and the equipment required for a high vacuum represent a significant investment in both capital and operational expense.
Material Compatibility
The atmosphere must be chemically compatible with the material being sintered. Using a nitrogen atmosphere to sinter titanium, for example, would be a critical error, as it would form brittle titanium nitrides and ruin the component.
Process Complexity
An air furnace is simple to operate. In contrast, vacuum furnaces require robust seals, powerful pumps, and longer cycle times to pump down the chamber, adding significant operational complexity.
Selecting the Right Atmosphere for Your Material
Your choice should be guided by the chemical nature of your material and the performance requirements of the end product.
- If your primary focus is processing non-reactive ceramics or simple oxides: An air atmosphere is the most practical and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation in common metals like steel: An inert atmosphere of nitrogen is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest purity for reactive metals like titanium: A high-vacuum environment is non-negotiable to avoid contamination.
- If your primary focus is removing surface oxides to improve bonding: A reducing atmosphere containing hydrogen is the most effective choice.
Ultimately, the sintering atmosphere is a deliberate engineering choice that dictates the chemical and physical success of your final component.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Key Characteristics | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidizing (Air) | Cost-effective, simple | Traditional ceramics, some oxides |
| Inert (N₂, Ar) | Prevents oxidation, industry standard | Steels, copper alloys |
| Vacuum | Highest purity, removes contaminants | Titanium, tungsten, stainless steels |
| Reducing (H₂/N₂) | Removes surface oxides, improves bonding | Oxidation-sensitive materials |
Need expert advice on selecting the perfect sintering atmosphere for your materials?
KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise thermal processing. Our experts can help you choose the right furnace and atmosphere to achieve the required density, purity, and mechanical properties for your components.
Contact our team today to optimize your sintering process and ensure the success of your final product.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of nitrogen in annealing process? Creating a Controlled, Protective Atmosphere
- What are the functions of nitrogen (N2) in controlled furnace atmospheres? Achieve Superior Heat Treatment Results
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety



















