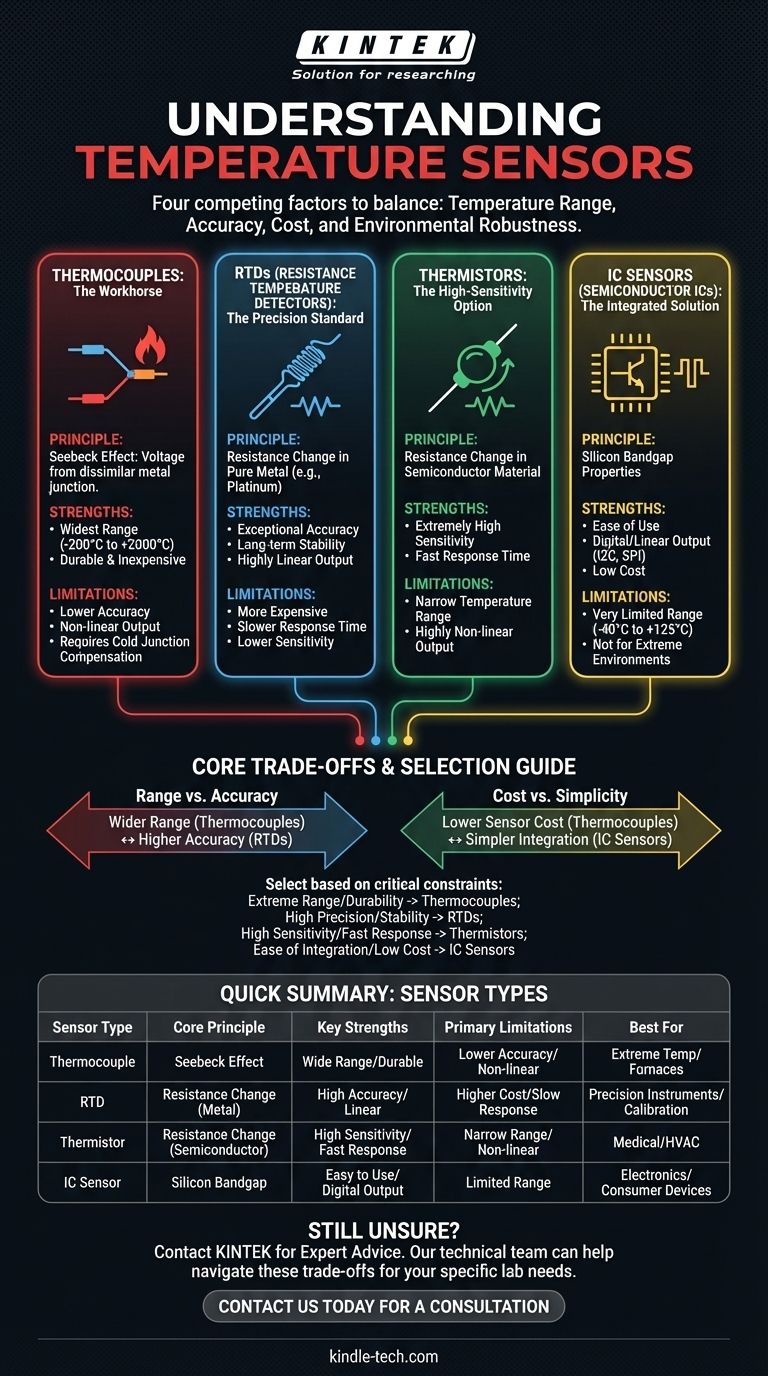
When selecting a temperature sensor, the choice primarily comes down to four distinct technologies. These are thermocouples, Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs), thermistors, and semiconductor-based ICs. Each operates on a different physical principle and is engineered for specific applications, costs, and environments.
The central challenge is not finding the "best" sensor, but understanding the inherent trade-offs. Your final decision will always be a balance between four competing factors: temperature range, accuracy, cost, and environmental robustness.

The Workhorse: Thermocouples
Core Principle: The Seebeck Effect
A thermocouple is formed when two wires made of dissimilar metals are joined at one end. This junction generates a small, predictable voltage that changes with temperature—a phenomenon known as the Seebeck effect.
Key Strengths
Thermocouples have the widest operating temperature range of any common sensor, capable of measuring from cryogenic levels (-200°C) to over 2000°C. They are also very durable and inexpensive.
Primary Limitations
Their primary weakness is lower accuracy compared to other types. The voltage output is also non-linear and requires signal conditioning and a reference, known as cold junction compensation, to produce an accurate reading.
The Precision Standard: Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs)
Core Principle: Resistance Change in Pure Metal
An RTD leverages the fact that the electrical resistance of a pure metal, most commonly platinum, changes in a highly predictable and linear way with temperature. The sensor measures this change in resistance.
Key Strengths
RTDs are known for their exceptional accuracy and long-term stability. Their output is the most linear of all analog temperature sensors, making them a standard for laboratory and calibration work.
Primary Limitations
This precision comes at a cost, making RTDs more expensive than thermocouples or thermistors. They also have a slower response time and lower sensitivity to small temperature changes.
The High-Sensitivity Option: Thermistors
Core Principle: Resistance Change in a Semiconductor
A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance is highly dependent on temperature. Unlike RTDs made of pure metal, thermistors are constructed from a semiconductor material (like a ceramic or polymer).
Key Strengths
Thermistors offer extremely high sensitivity, meaning their resistance changes significantly for even a small change in temperature. This allows for very precise readings over a limited range, and they have a fast response time.
Primary Limitations
Their useful temperature range is narrow. More importantly, their resistance-temperature relationship is highly non-linear, often requiring a lookup table or complex formula to convert resistance into an accurate temperature reading.
The Integrated Solution: Semiconductor IC Sensors
Core Principle: Silicon Bandgap Properties
These are modern, silicon-based integrated circuits (ICs) that exploit the predictable voltage-temperature characteristics of a transistor's p-n junction. They package the sensor and signal conditioning circuitry into a single chip.
Key Strengths
Their main advantage is ease of use. They often provide a calibrated, linear output (voltage or current) or even a direct digital output (e.g., I2C, SPI), which simplifies circuit design immensely. They are also very low cost.
Primary Limitations
IC sensors have a very limited temperature range, typically constrained to commercial or industrial bands (e.g., -40°C to 125°C). They are not suited for the extreme temperatures or harsh industrial environments where thermocouples excel.
Understanding the Core Trade-offs
Range vs. Accuracy
There is a direct trade-off between a sensor's operating range and its precision. Thermocouples offer a massive range but sacrifice accuracy. RTDs provide the highest accuracy but in a more moderate range.
Cost vs. Simplicity
The sensor element itself might be cheap (like a thermocouple), but the required external circuitry for signal conditioning can add complexity and cost. In contrast, an IC sensor may cost slightly more but simplifies the overall design.
Sensitivity vs. Linearity
Thermistors provide the highest sensitivity to temperature changes but are the most non-linear. RTDs and IC sensors are prized for their linearity but are less sensitive than thermistors.
Selecting the Right Sensor for Your Application
Choosing the correct sensor requires clearly defining your project's most critical constraint.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature range and durability: Thermocouples are the standard for industrial furnaces, engines, and cryogenics.
- If your primary focus is high precision and long-term stability: RTDs are the correct choice for scientific instruments, calibration standards, and critical process monitoring.
- If your primary focus is high sensitivity and fast response in a narrow range: NTC thermistors excel in medical devices, HVAC systems, and appliance temperature control.
- If your primary focus is ease of integration and low cost for electronics: Semiconductor IC sensors are ideal for on-board thermal management of circuit boards and consumer devices.
Understanding these fundamental differences empowers you to select the optimal sensor based on your project's specific engineering requirements.
Summary Table:
| Sensor Type | Core Principle | Key Strengths | Primary Limitations | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermocouple | Seebeck Effect (voltage) | Wide range (-200°C to +2000°C), durable, inexpensive | Lower accuracy, requires cold junction compensation | Extreme temperatures, industrial furnaces |
| RTD | Resistance change in pure metal (e.g., Platinum) | High accuracy, excellent stability, linear output | Higher cost, slower response time | Precision instruments, calibration, process control |
| Thermistor | Resistance change in semiconductor | Very high sensitivity, fast response | Narrow range, highly non-linear output | Medical devices, HVAC, appliance control |
| IC Sensor | Silicon bandgap properties | Easy to use (digital/linear output), low cost | Limited range (-40°C to +125°C) | On-board electronics, consumer devices |
Still Unsure Which Temperature Sensor is Right for Your Lab Equipment?
Selecting the correct sensor is critical for the accuracy and reliability of your experiments and processes. The experts at KINTEK specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, backed by deep technical knowledge.
We can help you navigate these trade-offs to find the perfect solution for your specific laboratory needs, ensuring precise temperature control and long-term stability.
Contact our technical team today for a personalized consultation and elevate your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Bomb Type Probe for Steelmaking Production Process
- Oxygen Probe to Measure Temperature and Active Oxygen Content in Molten Steel
- Shaking Incubators for Diverse Laboratory Applications
- Square Bidirectional Pressure Mold for Lab Use
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
People Also Ask
- Will stainless steel work as a crucible? The Surprising Dangers of Using the Wrong Material
- What is the most accurate temperature sensor? Why RTDs Lead in Precision and Stability
- What is a thermistor on a heat press? The Key to Consistent, Professional Transfers
- Why are glassy carbon crucibles selected for high-temperature molten salt corrosion? Achieve Unmatched Data Accuracy
- Can you melt steel in a graphite crucible? Understand the critical risks of carbon contamination.
















