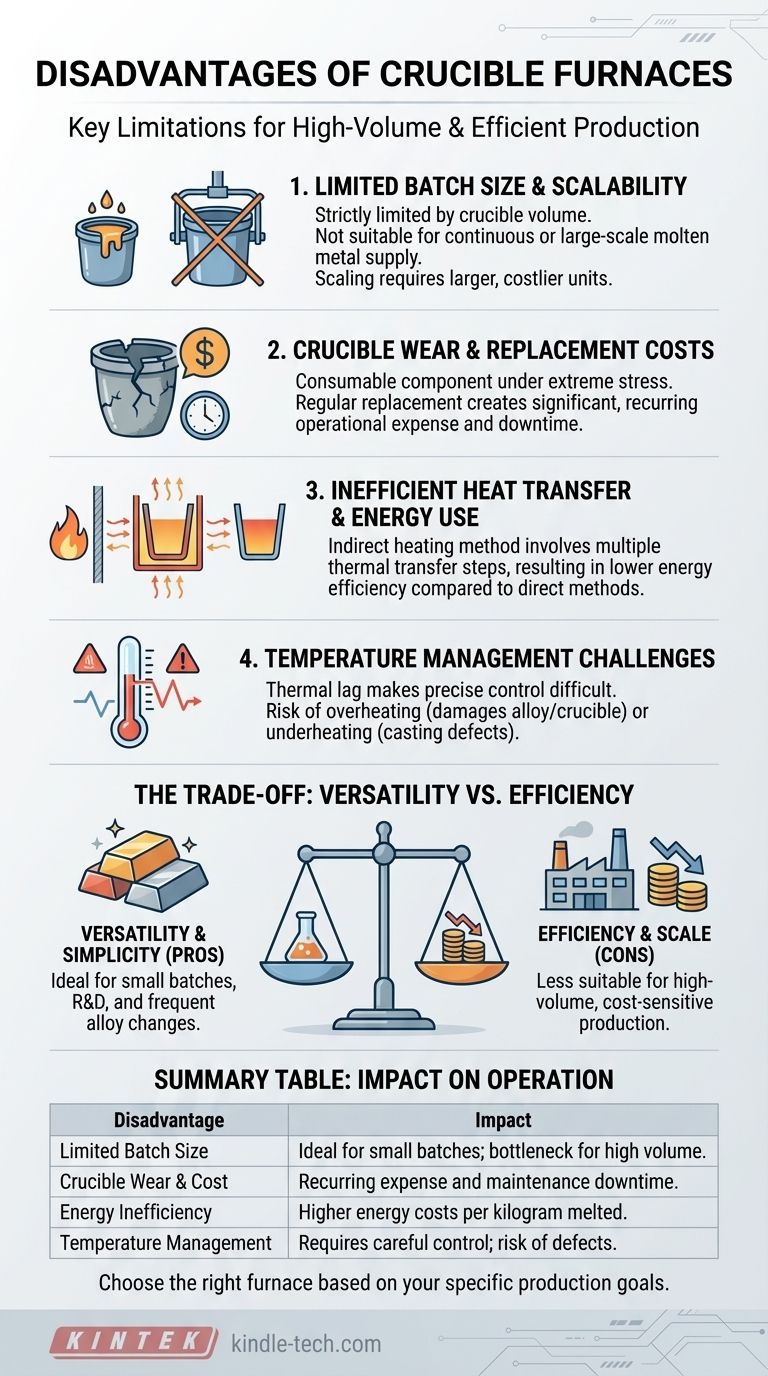
The primary disadvantages of a crucible furnace are its limited capacity for large-scale melting, the ongoing operational cost and downtime associated with crucible wear, and its relatively low energy efficiency compared to other furnace types. These factors make it ideal for versatility and small batches but less suitable for high-volume, continuous production environments.
While valued for its simplicity and flexibility, the crucible furnace's core design introduces inherent trade-offs. Its indirect heating method and reliance on a consumable crucible create limitations in scale, efficiency, and long-term operational cost that must be carefully evaluated against your specific goals.

The Fundamental Limitations of Crucible Furnaces
A crucible furnace operates by heating a container (the crucible) which then transfers that heat to the material inside. This simple, ancient design is effective but carries several distinct disadvantages.
Limited Batch Size and Scalability
Crucible furnaces are fundamentally batch-operation devices. The amount of metal you can melt at one time is strictly limited by the volume of the crucible.
While this is perfect for laboratories, artisan workshops, or small foundries, it becomes a significant bottleneck for any operation requiring a large or continuous supply of molten metal. Scaling up production is not as simple as running the furnace longer; it requires purchasing larger, more expensive furnaces and crucibles.
Crucible Wear and Replacement Costs
The crucible is a consumable component, not a permanent part of the furnace. Made from materials like graphite or silicon carbide, it is subjected to extreme thermal stress and chemical attack from molten metal.
This degradation means crucibles must be replaced regularly. This introduces a significant and recurring operational cost. Furthermore, a failing crucible can be catastrophic, leading to lost metal, furnace damage, and serious safety hazards. This constant need for inspection and replacement adds to the furnace's total cost of ownership.
Inefficient Heat Transfer and Energy Use
A crucible furnace uses indirect heating. The energy source (gas or electric) heats the furnace chamber, which then heats the outside of the crucible, which in turn heats the metal inside.
Each step in this thermal transfer process involves energy loss. This makes crucible furnaces less energy-efficient than direct-heating methods like induction furnaces, where the energy is induced directly within the metal itself. For high-volume operations, this inefficiency translates directly to higher energy bills.
The Need for Careful Temperature Management
The references note the need for careful temperature control, but the consequences are critical. Overheating the melt can burn off valuable alloying elements, alter the metal's properties, and drastically reduce the crucible's lifespan.
Conversely, underheating can result in a failed pour or casting defects. While modern control systems help, the furnace's thermal lag from indirect heating can make precise, rapid temperature adjustments challenging, placing a higher burden on the operator.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Versatility vs. Efficiency
The disadvantages of a crucible furnace do not exist in a vacuum. They are the direct trade-off for its primary advantages: simplicity and versatility.
The Value of Simplicity and Flexibility
The key strength of a crucible furnace is its ability to melt a wide range of different alloys without significant cross-contamination. Changing from melting aluminum to bronze can be as simple as swapping crucibles.
This makes them exceptionally valuable for jobbing foundries, research and development labs, and artists who need to switch between materials frequently. Their lower initial purchase price and simpler operation also make them accessible for smaller-scale users.
When Disadvantages Become Dealbreakers
The limitations become critical when your operational priorities shift from flexibility to efficiency and volume.
For a production foundry melting tons of iron per day, the small batch size, higher energy cost per kilogram, and constant crucible replacement would be operationally and financially unsustainable. In these scenarios, the higher upfront cost of an induction or arc furnace is easily justified by its superior efficiency and throughput.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a furnace requires aligning the equipment's characteristics with your operational needs. The disadvantages of a crucible furnace are only "disadvantages" if they conflict with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is flexibility, small batches, or prototyping: The versatility of a crucible furnace outweighs its inefficiencies, making it an excellent and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and energy efficiency: The limitations in scale and the operational costs of crucible wear make other furnace types, like induction, a more logical long-term investment.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial capital cost for a startup or hobby: A crucible furnace provides the most accessible entry point into metal melting, with the understanding that operational costs will be higher per unit of metal melted.
Ultimately, understanding these trade-offs empowers you to choose the right tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Impact on Operation |
|---|---|
| Limited Batch Size | Not suitable for high-volume, continuous production; ideal for small batches. |
| Crucible Wear & Cost | Regular replacement of the consumable crucible adds recurring operational expense. |
| Energy Inefficiency | Indirect heating leads to higher energy costs per kilogram of metal melted. |
| Temperature Management | Requires careful control to avoid damaging the metal or crucible, adding complexity. |
Choosing the right furnace is critical for your lab's efficiency and budget. The disadvantages of a crucible furnace highlight the importance of matching equipment to your specific production goals, whether for small-batch versatility or high-volume throughput.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you analyze your metal melting requirements—from batch size and material flexibility to energy costs—to determine if a crucible furnace is the right solution or if an alternative like an induction furnace would better serve your long-term objectives.
Optimize your lab's melting process and control costs. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and discover the right furnace solution for your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the basic construction and temperature control mechanism of a laboratory tube furnace? Master Precision Heating for Your Lab
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis



















