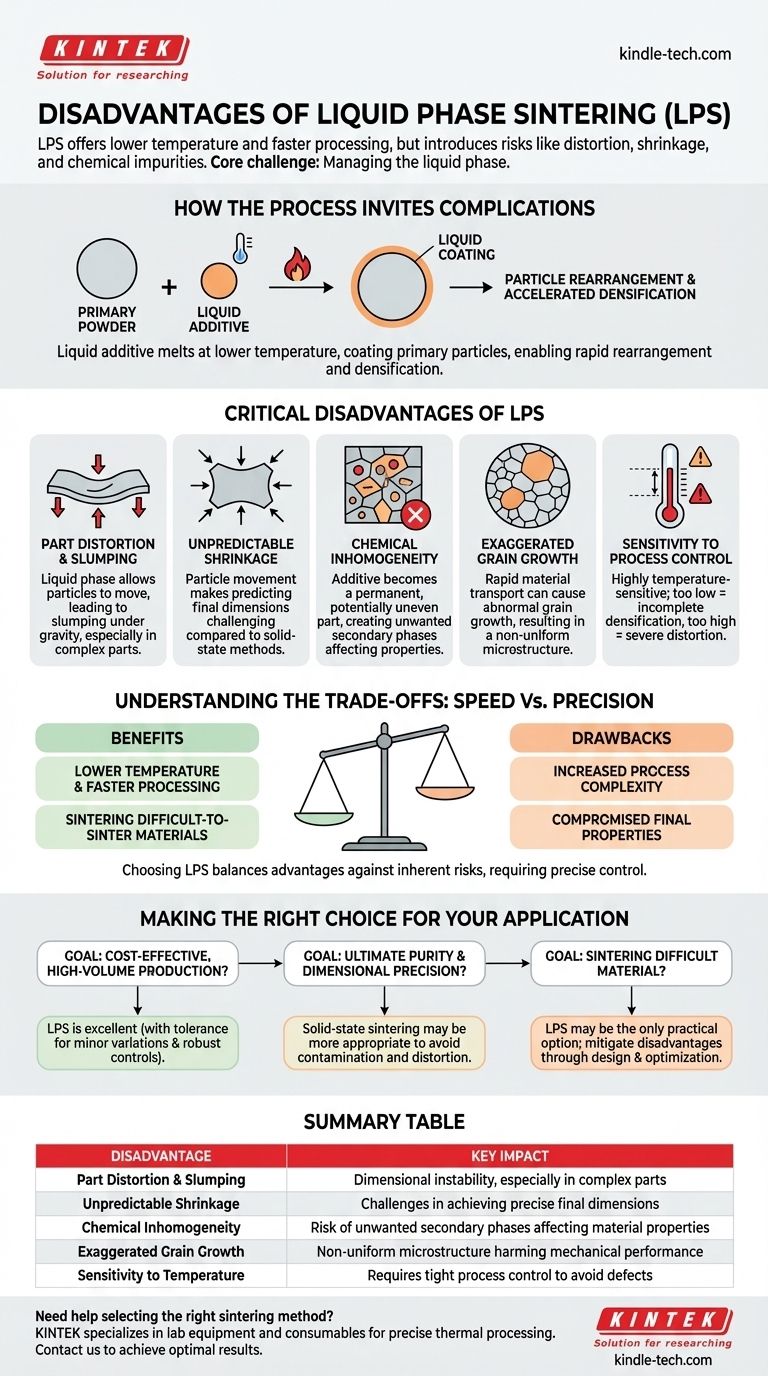
The primary disadvantages of liquid phase sintering are the potential for part distortion, unpredictable shrinkage, and the introduction of chemical impurities from the liquid-forming additive. These issues stem from the very mechanism that makes the process so effective at lowering temperatures and accelerating densification.
The core challenge of liquid phase sintering is managing the liquid phase itself. While it accelerates densification and reduces energy costs, its presence introduces risks of dimensional instability and microstructural defects that are not factors in solid-state methods.
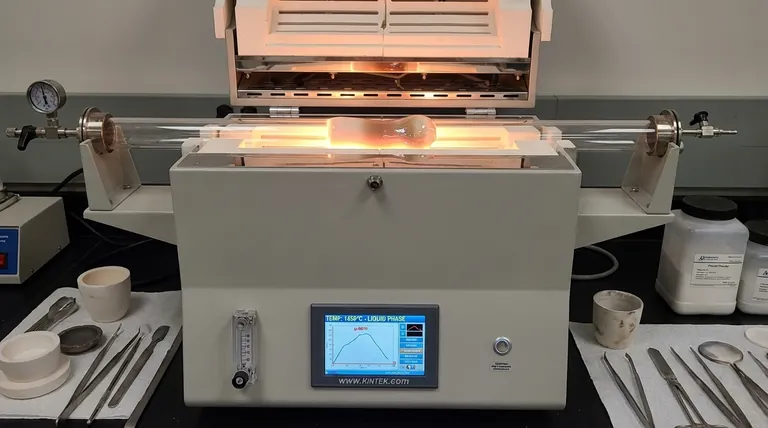

How the Process Invites Complications
To understand the disadvantages, you must first understand the mechanism. Liquid phase sintering (LPS) introduces a secondary material (an additive) that has a lower melting point than the primary powder.
The Role of the Liquid Additive
At the sintering temperature, this additive melts, forming a liquid that coats the solid primary particles. This liquid phase acts as a high-speed transport medium, dramatically accelerating the sintering process.
The Mechanism of Densification
The liquid enables rapid densification through particle rearrangement. Capillary forces from the liquid pull the solid grains together into a more tightly packed arrangement, helping to eliminate pores much faster than solid-state diffusion ever could.
Critical Disadvantages of the Liquid Phase Method
The benefits of lower temperatures and faster processing come with significant risks that require careful management. Each drawback is a direct consequence of introducing a mobile liquid into the system.
Unpredictable Shrinkage and Distortion
The presence of a liquid phase allows particles to move and slide past one another. While this aids densification, it can also lead to slumping or distortion under gravity, especially in larger or complex parts. Predicting the final dimensions can be more challenging compared to solid-state sintering.
Potential for Chemical Inhomogeneity
The additive that forms the liquid phase becomes a permanent part of the final material. If this additive is not perfectly distributed, or if it reacts undesirably with the primary material, it can create unwanted secondary phases in the microstructure. These phases can compromise mechanical properties like strength or corrosion resistance.
Risk of Exaggerated Grain Growth
The liquid provides a rapid path for material transport, which can sometimes lead to exaggerated or abnormal grain growth. A few grains may grow very large at the expense of smaller ones, resulting in a non-uniform microstructure that harms the material's mechanical performance and consistency.
Sensitivity to Process Control
LPS is highly sensitive to temperature. If the temperature is too low, not enough liquid forms, and densification is incomplete. If it's too high, too much liquid forms, leading to severe part distortion, slumping, and potential damage to the furnace. This requires much tighter process control than many solid-state methods.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Speed vs. Precision
Choosing liquid phase sintering is a strategic decision based on balancing its clear advantages against its inherent risks.
Benefit: Lower Temperature and Faster Processing
The most significant advantage is the ability to achieve high density at lower temperatures and in less time. This translates directly to lower energy costs and higher throughput, which is critical for industrial-scale production.
Drawback: Increased Process Complexity
This speed comes at the cost of complexity. The formulation of the powder mix (primary material plus additive) and the thermal cycle must be precisely engineered and controlled to avoid the defects mentioned above.
Benefit: Sintering Difficult-to-Sinter Materials
LPS is often the only viable method for densifying materials with very high melting points or low diffusion rates, such as certain ceramics and refractory metals. The liquid phase provides a densification pathway that would otherwise be impractical.
Drawback: Compromised Final Properties
The additive is not just a temporary processing aid; it remains in the final component. This can alter the material's properties. For example, it might lower the final part's maximum service temperature or affect its thermal or electrical conductivity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use liquid phase sintering must be driven by your end goal.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production: LPS is an excellent choice, provided you can tolerate minor dimensional variations and have robust process controls in place.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity and dimensional precision: A solid-state sintering method may be more appropriate, as it avoids chemical contamination and the risk of liquid-induced distortion.
- If your primary focus is processing a difficult-to-sinter material: LPS may be your only practical option, and the engineering effort should be focused on mitigating its inherent disadvantages through careful material design and process optimization.
Ultimately, understanding these inherent trade-offs is the key to successfully leveraging the power of liquid phase sintering for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Part Distortion & Slumping | Dimensional instability, especially in complex parts |
| Unpredictable Shrinkage | Challenges in achieving precise final dimensions |
| Chemical Inhomogeneity | Risk of unwanted secondary phases affecting material properties |
| Exaggerated Grain Growth | Non-uniform microstructure harming mechanical performance |
| Sensitivity to Temperature | Requires tight process control to avoid defects |
Need help selecting the right sintering method for your materials? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions for precise thermal processing and material synthesis. Whether you're working with high-temperature ceramics or refractory metals, our expertise ensures you achieve optimal results with minimal risk. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's sintering needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control



















