At its core, the primary disadvantages of sintering are its high energy consumption, significant initial investment costs, and the inherent difficulty in precisely controlling the final material properties. These challenges are compounded by long processing times and potential environmental impacts.
While sintering is a powerful method for creating dense parts from powder, its major drawbacks are rooted in the high capital and energy required, coupled with complex process control challenges that can directly compromise the structural integrity and consistency of the final product.

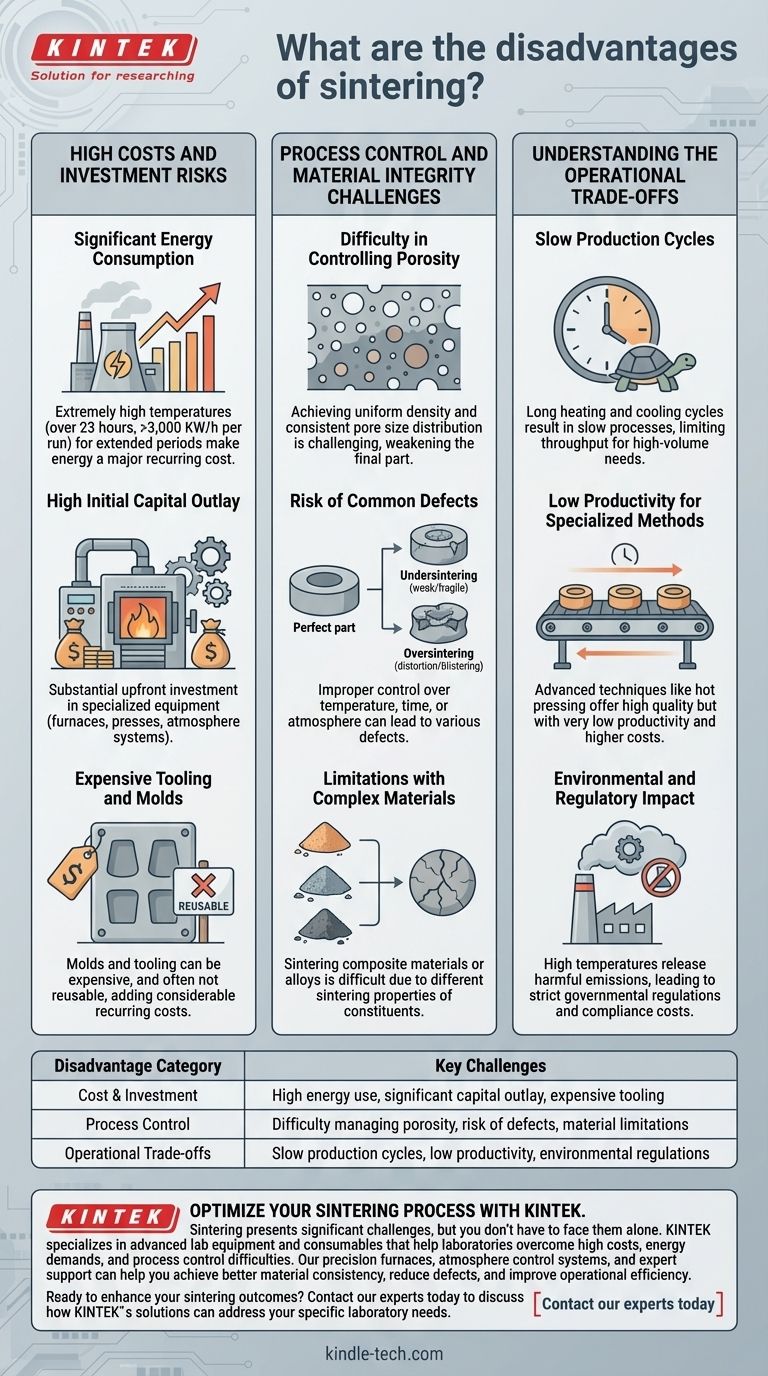
High Costs and Investment Risks
Sintering is not a low-cost manufacturing process. The financial barriers are present in both the initial setup and the ongoing operational expenses, making it a significant commitment.
Significant Energy Consumption
The process relies on maintaining extremely high temperatures for extended periods. A traditional sintering cycle can last over 23 hours and consume more than 3,000 KW/h of power for a single run. This makes energy a major, recurring operational cost.
High Initial Capital Outlay
Establishing a sintering production line requires a substantial upfront investment in specialized equipment like high-temperature furnaces (e.g., pusher, walking-beam), presses, and controlled atmosphere systems. This high barrier to entry poses a significant financial risk, especially if the product line does not succeed commercially.
Expensive Tooling and Molds
The molds and tooling used to form the initial "green" parts can be expensive. In some traditional methods, these molds are not reusable after the high-temperature process, adding a considerable recurring cost to production.
Process Control and Material Integrity Challenges
Achieving a perfect, uniform final part is the goal of sintering, but the process itself introduces several variables that can lead to defects and inconsistencies.
Difficulty in Controlling Porosity
One of the most critical challenges is managing porosity, or the tiny voids left in the material. Achieving a uniform density and a consistent pore size distribution is difficult, and uncontrolled porosity can severely weaken the final part's mechanical strength and performance.
Risk of Common Defects
Improper control over temperature, time, or atmosphere can lead to a range of defects. Undersintering results in a weak, fragile part, while oversintering can cause distortion, blistering, or "sweating" of material phases. Eliminating these defects requires tight process control and expertise.
Limitations with Complex Materials
Sintering composite materials or certain metal alloys can be exceptionally difficult. Different constituent powders may have different sintering temperatures and rates, making it a challenge to create a dense, homogenous final product without compromising the properties of one of the materials.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Beyond the financial and material challenges, sintering presents several operational and regulatory hurdles that must be considered.
Slow Production Cycles
The long heating and cooling cycles mean that sintering is often a slow process. Production times measured in hours or even days can limit throughput and make it less suitable for applications requiring rapid, high-volume manufacturing compared to other methods.
Low Productivity for Specialized Methods
Certain advanced sintering techniques, such as hot pressing, are known for producing very high-quality parts. However, this comes at the cost of very low productivity and even higher costs, restricting their use to specialized, low-volume applications.
Environmental and Regulatory Impact
Heating materials to high temperatures can release harmful emissions, creating an environmental impact. Consequently, sintering facilities are subject to strict governmental regulations, which can affect production rates and add compliance costs for emissions control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the viability of sintering depends entirely on your project's specific priorities and constraints.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, low-volume production: The high initial investment and significant energy costs of sintering likely make it an unsuitable choice.
- If your primary focus is perfect material consistency and strength: Be prepared to invest heavily in advanced process control to overcome the inherent risks of porosity and defects.
- If your primary focus is rapid manufacturing and high throughput: The characteristically long cycle times of traditional sintering will be a major operational bottleneck.
Successful implementation demands a clear understanding of the significant financial, operational, and technical trade-offs inherent in the process.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage Category | Key Challenges |
|---|---|
| Cost & Investment | High energy use, significant capital outlay, expensive tooling |
| Process Control | Difficulty managing porosity, risk of defects, material limitations |
| Operational Trade-offs | Slow production cycles, low productivity, environmental regulations |
Optimize Your Sintering Process with KINTEK
Sintering presents significant challenges, but you don't have to face them alone. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables that help laboratories overcome the high costs, energy demands, and process control difficulties associated with sintering. Our precision furnaces, atmosphere control systems, and expert support can help you achieve better material consistency, reduce defects, and improve operational efficiency.
Ready to enhance your sintering outcomes? Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can address your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- What is the function of a tube furnace? Achieve Precise High-Temperature Processing in a Controlled Atmosphere
- How do I choose a tube furnace? A Guide to Matching Your Process Needs
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material



















