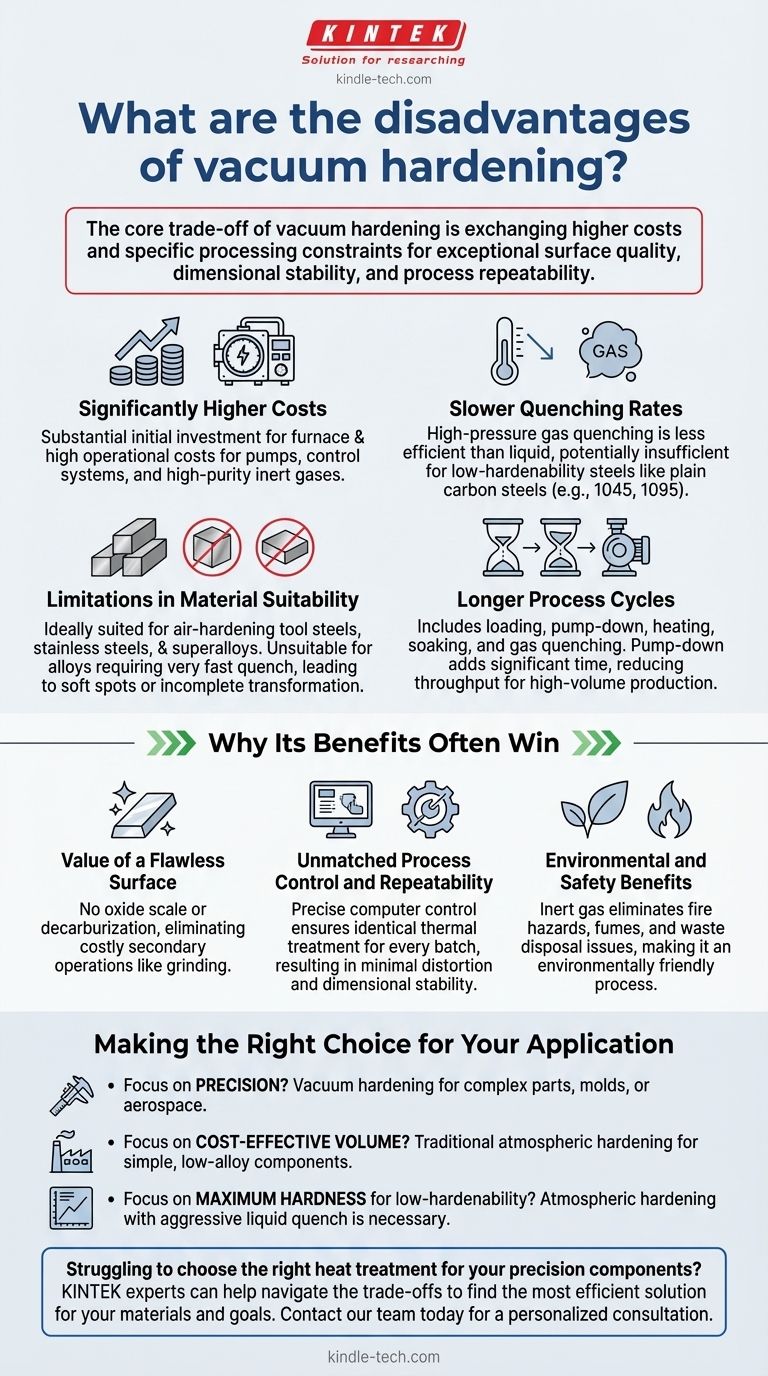
While highly precise, vacuum hardening is not a universal solution. Its primary disadvantages are significantly higher costs, slower cooling rates that limit its use with certain steels, and longer processing cycles that can affect high-volume production throughput.
The core trade-off of vacuum hardening is exchanging higher costs and specific processing constraints for exceptional surface quality, dimensional stability, and process repeatability. Understanding these limitations is key to deciding if the investment is justified for your specific application.

A Closer Look at the Key Disadvantages
Vacuum hardening provides a pristine, controlled environment, but that environment comes with inherent limitations. These drawbacks are not failures of the process, but rather fundamental aspects of its physics and economics.
Significant Cost Investment
The most immediate and significant disadvantage is cost. Both the initial capital expenditure for a vacuum furnace and the operational costs are substantially higher than for traditional atmospheric furnaces.
This is driven by the complexity of the equipment, including powerful vacuum pumps, sophisticated computer control systems, and the need for high-purity inert gases (like nitrogen or argon) for quenching.
Slower Quenching Rates
Vacuum furnaces typically use high-pressure gas quenching to cool parts. While clean and controlled, gas is a much less efficient medium for heat transfer than liquids like oil or water.
This slower cooling rate may be insufficient to achieve the required hardness in materials with low hardenability, such as plain carbon steels (e.g., 1045, 1095). These alloys require an extremely rapid quench to transform correctly, which only an aggressive liquid quench can provide.
Limitations in Material Suitability
Because of the slower quenching, vacuum hardening is ideally suited for air-hardening tool steels (like A2 or D2), stainless steels, and superalloys. These materials are designed to harden with slower cooling rates.
It is generally unsuitable for alloys that demand a very fast quench to achieve their maximum potential hardness. Attempting to vacuum harden these materials can result in soft spots, incomplete transformation, and substandard mechanical properties.
Longer Process Cycles
A vacuum hardening cycle involves multiple stages: loading, pumping down the chamber to create a vacuum, heating, soaking at temperature, and gas quenching.
The pump-down phase adds significant time to the overall process compared to simply placing a part in an atmospheric furnace. This can reduce overall throughput and make it less economical for high-volume, low-margin components.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Its Benefits Often Win
The disadvantages must be weighed against the unique advantages that no other process can offer. For high-value applications, these benefits are often non-negotiable.
The Value of a Flawless Surface
Conventional hardening leaves behind a layer of oxide scale and can deplete carbon from the surface (decarburization), both of which must be removed through costly secondary operations like grinding or sandblasting.
Vacuum hardening produces parts that are clean, bright, and free of surface defects. For precision tooling, molds, or aerospace components, this eliminates post-processing steps and preserves intricate design details.
Unmatched Process Control and Repeatability
Modern vacuum furnaces offer complete, computer-controlled regulation over every stage of the process. This ensures that every part in every batch receives the exact same thermal treatment.
This high degree of control results in minimal distortion and exceptional dimensional stability. For components with tight tolerances, this predictability reduces scrap rates and ensures reliable performance.
Environmental and Safety Benefits
Using inert gas for quenching eliminates the fire hazards, noxious fumes, and waste disposal issues associated with traditional oil quench tanks. Vacuum hardening is an inherently clean and environmentally friendly process, a growing consideration in modern manufacturing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use vacuum hardening hinges entirely on the requirements of the component itself.
- If your primary focus is precision and surface integrity: For complex tool steels, injection molds, or aerospace parts where dimensional accuracy is paramount, vacuum hardening is the definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production: For simple, low-alloy steel components where minor scaling is acceptable, traditional atmospheric hardening is likely more economical.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum hardness on a low-hardenability steel: You will likely require the aggressive cooling of a liquid quench, making atmospheric hardening the necessary technical choice.
By understanding these fundamental trade-offs, you can confidently determine when the precision of vacuum hardening justifies its investment.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| High Cost | Significant capital investment and operational expenses. |
| Slower Quenching | Limits use with low-hardenability steels like 1045 or 1095. |
| Material Limitations | Best for air-hardening steels; unsuitable for alloys needing fast quench. |
| Longer Cycle Times | Reduces throughput, less economical for high-volume production. |
Struggling to choose the right heat treatment for your precision components? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs of processes like vacuum hardening to find the most efficient and cost-effective solution for your specific materials and production goals. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and discover how our expertise can enhance your lab's capabilities and ensure optimal results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries
- How does a vacuum heat treatment work? Achieve Superior Material Properties in a Pristine Environment
- Can I vacuum the inside of my furnace? A Guide to Safe DIY Cleaning vs. Professional Service
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Materials
- What does a vacuum furnace do? Achieve High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Components



















