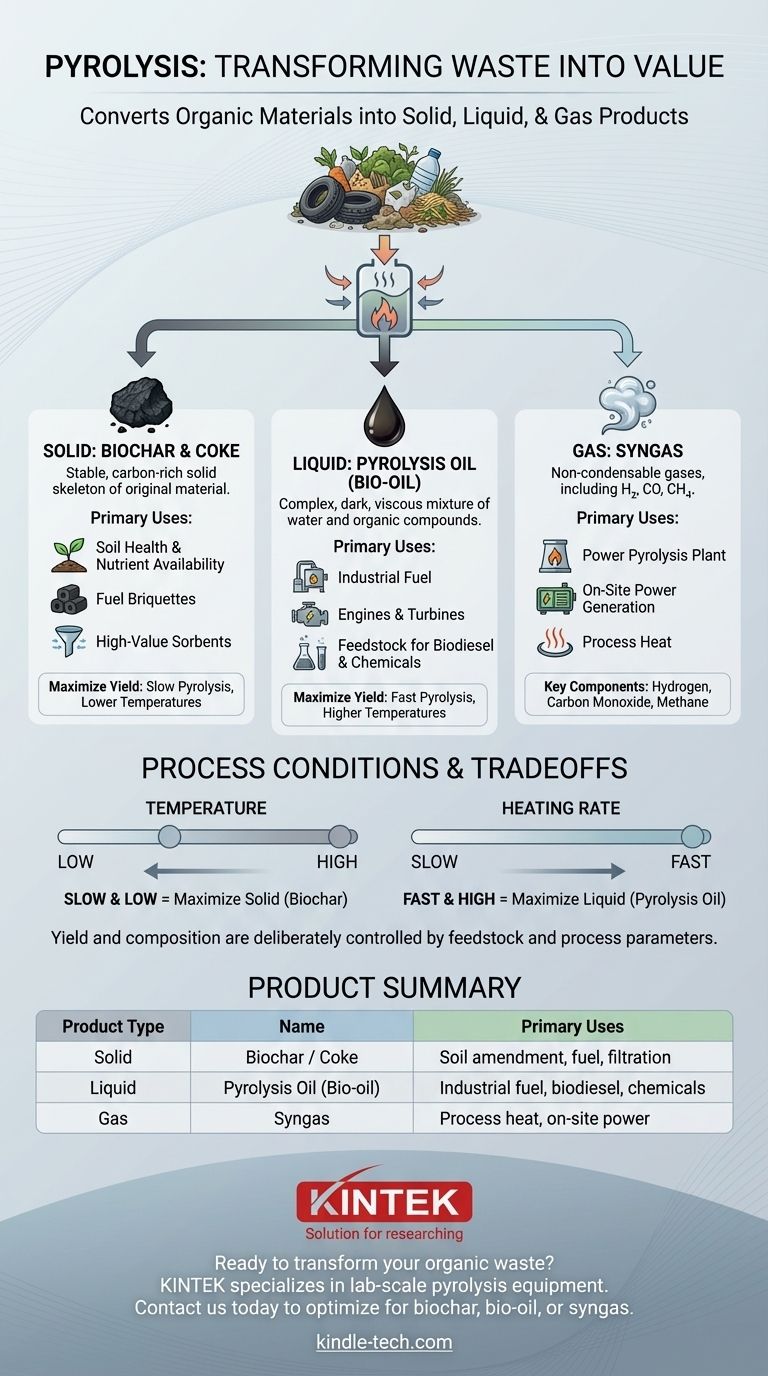
In short, pyrolysis converts organic materials into three distinct product categories: a solid, a liquid, and a gas. The solid is a carbon-rich substance called biochar or coke, the liquid is known as pyrolysis oil (or bio-oil), and the non-condensable gas is referred to as syngas. The specific yield and composition of these products are not fixed; they are deliberately controlled by the raw material used and the process conditions.
The core takeaway is that pyrolysis is not a disposal method but a transformation process. It reclaims value from materials often considered waste by converting them into a versatile portfolio of solid, liquid, and gaseous products, each with its own distinct applications and market.

The Solid Product: Biochar and Coke
What is Biochar?
Biochar (or coke, depending on the feedstock) is the stable, carbon-rich solid that remains after the volatile components of the raw material have been vaporized. It is the solid skeleton of the original organic matter.
Primary Uses and Value
This solid product is highly valuable. As biochar, it is used in agriculture to improve soil health, water retention, and nutrient availability. As a form of carbon, it can also be pressed into briquettes for fuel or used to create high-value sorbents for filtration and cleanup applications.
The Liquid Product: Pyrolysis Oil (Bio-oil)
What is Pyrolysis Oil?
When the hot pyrolysis gas is cooled, a portion of it condenses into a dark, viscous liquid. This is pyrolysis oil, sometimes called bio-oil, wood vinegar, or tar. It is a complex mixture of water, oils, and hundreds of different organic compounds.
Primary Uses and Value
This liquid is a dense and easily transportable energy carrier. It can be used directly as an alternative fuel in industrial boilers, engines, and turbines to generate heat or electricity. With further refining, pyrolysis oil can be upgraded into higher-grade fuels like biodiesel or serve as a feedstock for producing valuable specialty chemicals.
The Gaseous Product: Syngas
What is Syngas?
Syngas (synthesis gas) is the stream of non-condensable gases that do not turn into liquid when cooled. It is a mixture of combustible and non-combustible gases.
Key Components
The primary components of syngas include hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), and methane (CH₄), which are all combustible. It also contains inert gases like carbon dioxide (CO₂) and nitrogen (N₂).
Primary Uses and Value
The most common use for syngas is to power the pyrolysis plant itself. By burning the gas to generate heat for the reactor, the process can become highly energy-efficient and even self-sustaining. Excess gas can be used for on-site power generation.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Process Conditions Matter
The ratio of solid, liquid, and gas produced is not accidental. It is a direct result of the process parameters, allowing operators to target specific outputs.
The Role of Feedstock
The type of raw material—whether it's wood biomass, agricultural waste, plastics, or old tires—fundamentally changes the chemical makeup and relative proportions of the final products. Each feedstock has an optimal conversion pathway.
The Impact of Process Parameters
The two most critical variables are temperature and heating rate. As a general principle, slower pyrolysis processes at lower temperatures tend to maximize the yield of the solid product, biochar. Conversely, fast pyrolysis at higher temperatures is used to maximize the yield of the liquid product, bio-oil.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The value of pyrolysis lies in its flexibility to convert a single feedstock into different products based on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration and soil improvement: You should prioritize a slow pyrolysis process to maximize the production of stable biochar.
- If your primary focus is creating a transportable liquid fuel: You should prioritize a fast pyrolysis process to maximize the yield of pyrolysis oil.
- If your primary focus is energy self-sufficiency or on-site power: You should design your system to efficiently capture and combust the syngas to power the operation.
Ultimately, pyrolysis is a powerful tool that allows us to see waste not as an endpoint, but as a valuable raw material for a new generation of energy and products.
Summary Table:
| Product Type | Name | Primary Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Solid | Biochar / Coke | Soil amendment, fuel briquettes, filtration sorbents |
| Liquid | Pyrolysis Oil (Bio-oil) | Industrial fuel, feedstock for biodiesel & chemicals |
| Gas | Syngas | Process heat, on-site power generation |
Ready to transform your organic waste streams into valuable products? KINTEK specializes in lab-scale pyrolysis equipment and consumables, helping you optimize for biochar, bio-oil, or syngas production. Our experts can help you select the right system to meet your specific research and development goals. Contact our team today to discuss your project and discover the value we can bring to your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable Laboratory High Temperature High Pressure Reactors for Diverse Scientific Applications
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Wall Mounted Water Distillation Unit
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-pressure reactor play in the hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) of bio-oil? Drive Deep Fuel Upgrading
- Why are high-strength alloy tube reactors critical for HHIP? Ensuring Safety and Purity in High-Pressure Environments
- What is the function of a PTFE-lined hydrothermal autoclave in cys-CDs synthesis? Achieve High-Purity Carbon Dots
- Why are high-precision pressure sensors and temperature control systems critical for hydrothermal reaction equilibrium?
- What role does a PTFE-lined stainless steel autoclave play in the synthesis of BiOBr precursor nanosheets?



















