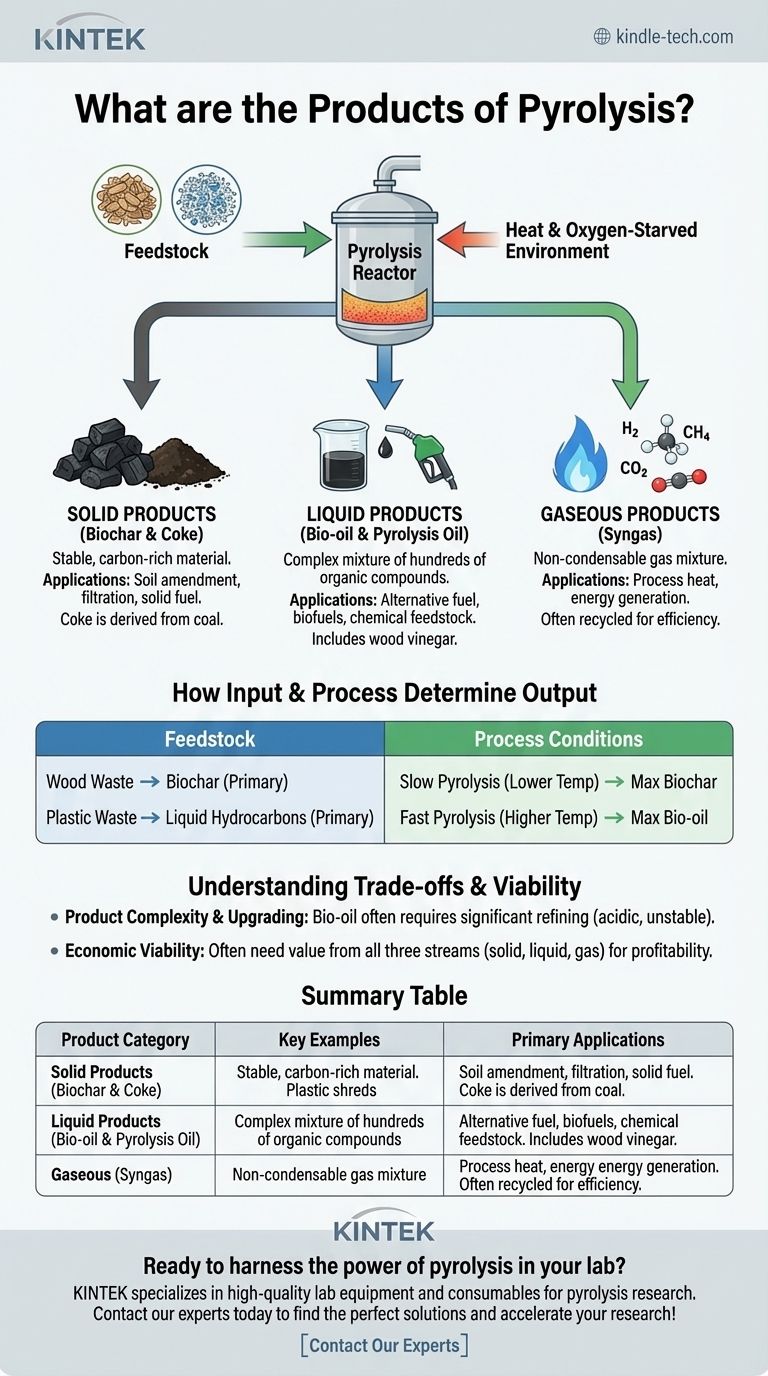
In short, the products of pyrolysis fall into three distinct categories: a carbon-rich solid (biochar or coke), a liquid mixture (bio-oil or pyrolysis oil), and a blend of combustible gases (syngas). The specific yield and composition of these products depend entirely on the material being processed and the conditions under which the pyrolysis takes place.
Pyrolysis is best understood not as a process that creates a single output, but as a thermochemical conversion that transforms a single input, like biomass or plastic, into a portfolio of solid, liquid, and gaseous products, each with its own distinct applications.
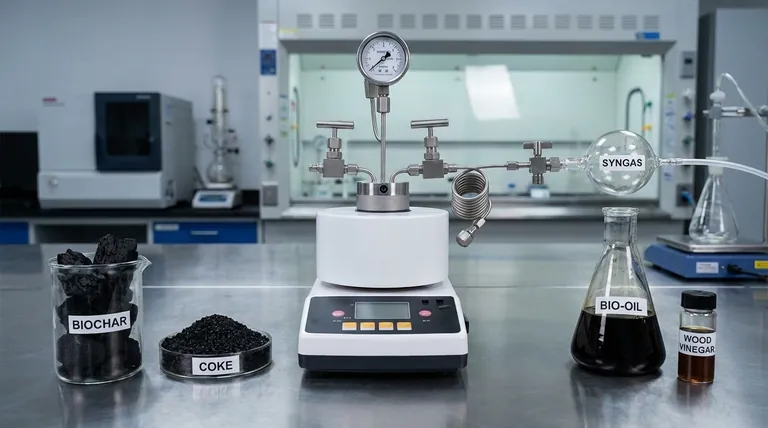

The Three Core Products of Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis deconstructs organic material in an oxygen-starved environment, preventing combustion and instead breaking it down into more basic, valuable components.
Solid Products (Biochar & Coke)
The most common solid product is biochar, a stable, carbon-rich material similar to charcoal. It is the solid residue left after the volatile components have been driven off.
Its primary applications include use as a soil amendment in agriculture to improve fertility, as a sorbent for filtration, or as a solid fuel through briquetting. When derived from coal, this solid is often called coke.
Liquid Products (Bio-oil & Pyrolysis Oil)
After the pyrolysis gas is produced, it is cooled, causing the condensable components to turn into a liquid. This product is generally known as bio-oil or pyrolysis oil.
This dark, viscous liquid is a complex mixture of water, tars, and hundreds of organic compounds. It can be burned as an alternative fuel in boilers and engines, refined into higher-grade biofuels like biodiesel, or serve as a source for valuable industrial chemicals. Byproducts like wood vinegar can also be collected from biomass sources.
Gaseous Products (Syngas)
The non-condensable portion of the output remains as a gas. This is often called synthesis gas, or syngas.
This gas is a mixture of hydrogen (H₂), methane (CH₄), carbon monoxide (CO), and carbon dioxide (CO₂). Its most immediate and common use is to be cycled back to provide heat for the pyrolysis reactor, making the entire process more energy-efficient and self-sustaining.
How Input & Process Determine the Output
You cannot expect to get the same products from different starting materials or process conditions. The output is a direct function of the input and the method.
The Role of Feedstock
The material you start with—the feedstock—is the single most important factor.
Pyrolyzing wood waste will yield biochar, bio-oil, and wood vinegar. In contrast, pyrolyzing plastic waste is specifically targeted to maximize the yield of liquid hydrocarbons that can be used as a fuel.
The Impact of Process Conditions
The parameters of the pyrolysis process itself, such as temperature and heating rate, dictate the proportion of solids, liquids, and gases.
For example, slow pyrolysis at lower temperatures maximizes the production of solid biochar. Conversely, fast pyrolysis uses high temperatures and rapid heating to favor the production of liquid bio-oil.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, pyrolysis is not a magic bullet. Understanding its limitations is key to assessing its viability for any given application.
Product Complexity and Upgrading
The raw liquid product, bio-oil, is not a direct replacement for petroleum crude oil. It is often acidic, corrosive, and unstable, requiring significant upgrading and refining before it can be used as a commercial-grade transportation fuel.
Economic Viability
For a pyrolysis operation to be economically successful, it often needs to find value in all three product streams. Relying solely on the sale of bio-oil while wasting the biochar and syngas is rarely a profitable model. An integrated approach is almost always necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" pyrolysis products are entirely dependent on the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is soil improvement and carbon sequestration: Your goal is to maximize the yield of stable biochar, which is best achieved with slow, lower-temperature pyrolysis.
- If your primary focus is creating alternative liquid fuels: You should optimize for bio-oil production using fast pyrolysis on appropriate feedstocks like plastic or non-food biomass.
- If your primary focus is waste-to-energy and self-sufficiency: You should ensure the system effectively captures and utilizes the syngas to power the operation, reducing external energy costs.
Ultimately, pyrolysis is a versatile technology for converting low-value materials into a range of higher-value products.
Summary Table:
| Product Category | Key Examples | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Solid | Biochar, Coke | Soil amendment, filtration, solid fuel |
| Liquid | Bio-oil, Pyrolysis oil | Alternative fuel, chemical feedstock |
| Gas | Syngas (H₂, CH₄, CO) | Process heat, energy generation |
Ready to harness the power of pyrolysis in your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and analysis. Whether you're developing biochar for soil science, refining bio-oil for fuel applications, or optimizing syngas production, our reliable solutions help you achieve precise and reproducible results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect equipment for your pyrolysis projects and accelerate your research!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable Laboratory High Temperature High Pressure Reactors for Diverse Scientific Applications
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the advantage of using high-pressure hydrothermal reactors to treat biomass waste? Efficient Resource Recovery
- Why use high-pressure reactors for food waste pretreatment? Boost Hydrogen Production Efficiency Today!
- Why are high-precision pressure sensors and temperature control systems critical for hydrothermal reaction equilibrium?
- What is the function of a PTFE-lined hydrothermal autoclave in cys-CDs synthesis? Achieve High-Purity Carbon Dots
- What role does a high-pressure reactor play in the hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) of bio-oil? Drive Deep Fuel Upgrading

















