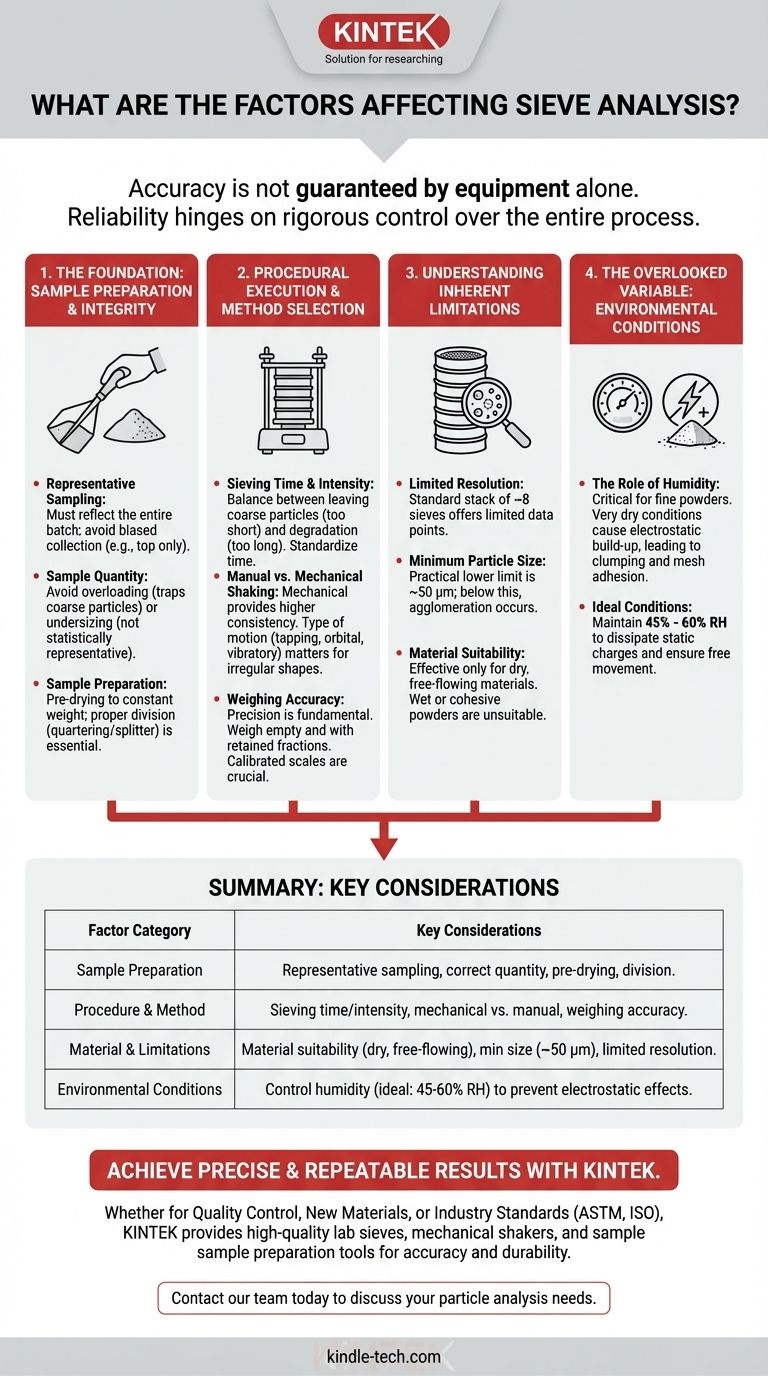
The accuracy of a sieve analysis is not guaranteed by the equipment alone. It is profoundly influenced by a range of factors including the initial sample preparation, the physical properties of the material being tested, the chosen sieving method and duration, and even the ambient environmental conditions of the laboratory.
The reliability of your final particle size distribution data hinges on rigorous control over the entire process—from obtaining a truly representative sample to managing environmental factors. Failing to account for these variables can render your results misleading and unreliable for their intended engineering application.

The Foundation: Sample Preparation and Integrity
The most significant errors in sieve analysis are often introduced before the sieving process even begins. The quality of your results is directly tied to the quality of the sample you start with.
Representative Sampling
The initial sample taken from the bulk material must be truly representative of the entire batch. If the sample is biased (e.g., taken only from the top of a pile), the final analysis will not reflect the true properties of the material, regardless of how carefully the rest of the procedure is followed.
Sample Quantity
The amount of material used is critical. Overloading the sieves prevents particles from having a fair chance to pass through the mesh, leading to an inaccurate over-representation of coarse particles. Conversely, a sample that is too small may not be statistically representative.
Sample Preparation and Conditioning
The material must be prepared correctly according to the chosen standard method. This often includes pre-drying to a constant weight, as the technique is only effective for dry particles. Proper sample division (quartering or using a sample splitter) is essential to reduce a large field sample to a manageable test size without introducing bias.
Procedural Execution and Method Selection
Consistency in the execution of the sieving process is paramount for achieving repeatable and comparable results.
Sieving Time and Intensity
The duration and energy of the shaking action directly impact how many particles pass through each sieve. Insufficient sieving time will leave too many coarse particles, while excessive time may cause particle degradation. A standardized time, often determined during method development, is crucial.
Manual vs. Mechanical Shaking
Mechanical sieve shakers provide a much higher degree of consistency compared to manual shaking. The type of motion (e.g., tapping, orbital, vibratory) can also influence the results, especially for particles with irregular shapes.
Weighing Accuracy
Precision in the weighing steps is fundamental. All sieves must be weighed empty and then re-weighed with their retained fractions. Any errors in these measurements, from an uncalibrated scale or poor technique, will directly translate to errors in the final particle size distribution percentages.
Understanding the Inherent Limitations
Sieve analysis is a powerful tool, but it is essential to recognize its built-in constraints, which affect the resolution and applicability of the data.
Limited Resolution
A standard sieve stack typically consists of a maximum of eight sieves. This means the final particle size distribution curve is based on a limited number of data points, which may not capture fine details in the distribution.
Minimum Particle Size
The practical lower limit for standard sieve analysis is approximately 50 micrometers (µm). Below this size, particles are more likely to agglomerate or be influenced by forces other than gravity, making the results unreliable.
Material Suitability
The method is only effective for dry, free-flowing materials. Wet, sticky, or highly cohesive powders will not pass through the apertures correctly, leading to inaccurate results.
The Overlooked Variable: Environmental Conditions
The physical environment of the testing area can have a surprising impact on the behavior of fine particles.
The Role of Humidity
Ambient humidity is a critical factor, especially for fine powders. Very dry conditions can lead to the build-up of electrostatic charges, causing particles to adhere to each other and to the sieve mesh, preventing them from passing through the apertures.
Ideal Conditions
To mitigate electrostatic effects, the relative humidity in the lab should ideally be maintained between 45% and 60%. This helps dissipate static charges and ensures particles can move freely.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to controlling these factors should align with the purpose of your analysis.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control: Prioritize absolute consistency in sampling technique, sample mass, and sieving time to ensure your results are repeatable day-to-day.
- If your primary focus is analyzing a new material: Invest time in method development, testing different sample sizes and sieving durations to find the optimal parameters for that specific material.
- If your primary focus is meeting an engineering specification: Adhere strictly to the prescribed standard method (e.g., ASTM, ISO), paying special attention to sample preparation and the correct selection of sieve sizes.
Ultimately, a reliable sieve analysis is the result of methodical discipline, not just mechanical action.
Summary Table:
| Factor Category | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Sample Preparation | Representative sampling, correct sample quantity, pre-drying, and sample division |
| Procedure & Method | Sieving time/intensity, mechanical vs. manual shaking, weighing accuracy |
| Material & Limitations | Material suitability (dry, free-flowing), minimum particle size (~50 µm), limited resolution |
| Environmental Conditions | Control humidity (ideal: 45-60% RH) to prevent electrostatic effects |
Achieve precise and repeatable sieve analysis results with KINTEK.
Whether you are focused on routine quality control, developing a method for a new material, or adhering to strict industry standards (ASTM, ISO), the right equipment and consumables are critical. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab sieves, mechanical shakers, and sample preparation tools designed for accuracy and durability.
Let our experts help you select the ideal equipment for your specific materials and applications. Contact our team today to discuss your particle analysis needs and ensure your data is reliable and actionable.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory electromagnetic vibratory sieve shaker used? Optimize Walnut Shell Chemical Pretreatment
- Why is a standardized sieving system necessary for elephant grass research? Ensure Reliable Sample Consistency
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment



















