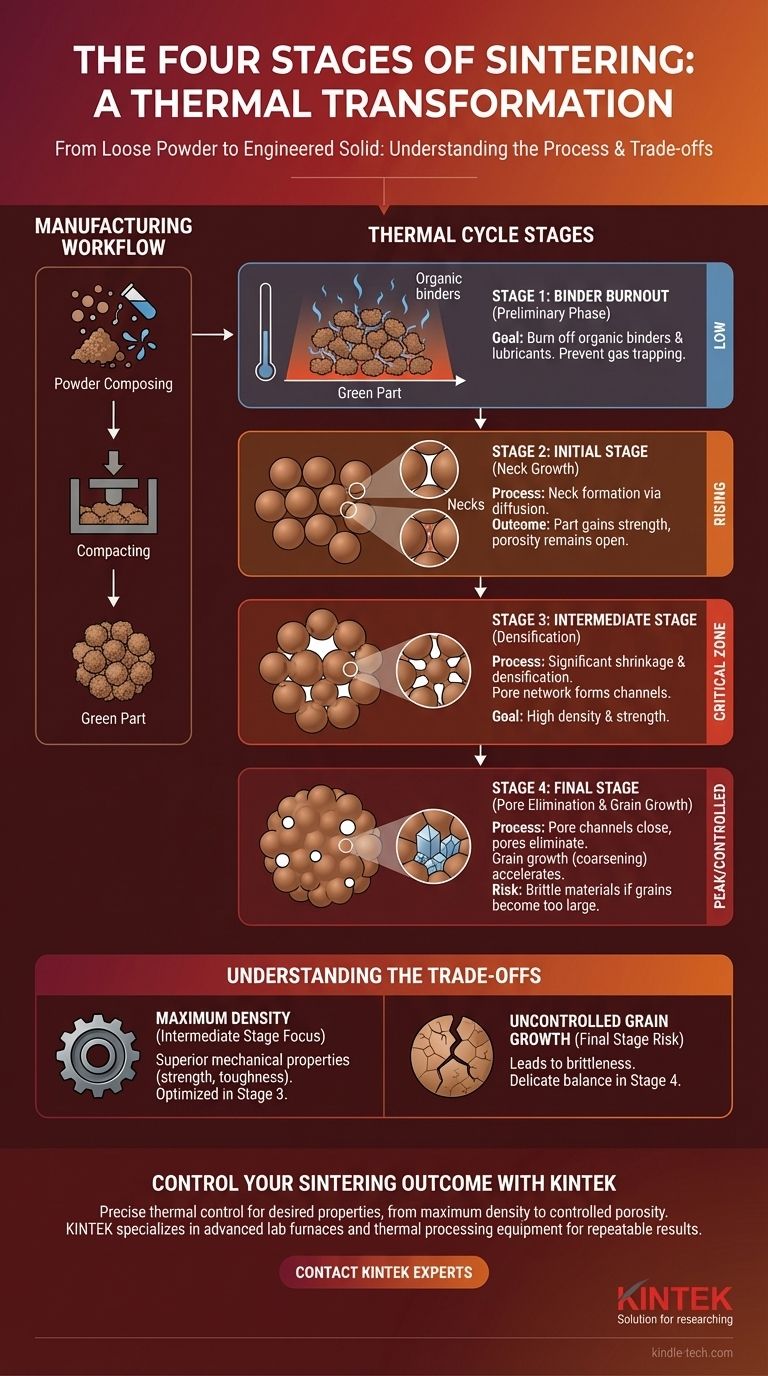
The four stages of sintering describe the physical transformation a compacted powder undergoes as it is heated to bond together into a solid mass. While often preceded by manufacturing steps like powder mixing and pressing, the core thermal process of sintering is best understood as: a preliminary binder burnout phase, an initial stage of particle necking, an intermediate stage of densification, and a final stage characterized by grain growth.
Sintering is not a single event but a carefully controlled thermal process. Understanding its distinct stages—from initial particle bonding to final grain coarsening—is essential for controlling the final properties, such as density, porosity, and strength, of a manufactured part.

The Sintering Process vs. The Sintering Stages
To understand sintering correctly, it is critical to distinguish between the overall manufacturing workflow and the specific thermal stages that occur inside the furnace.
The Manufacturing Workflow
Before sintering can begin, a part must be prepared. This general process includes composing the powder (mixing it with binders or other agents), compacting the powder into a desired shape using a mold and pressure, and creating what is known as a "green part" or "green body." This green part is fragile and has not yet undergone thermal bonding.
The Thermal Cycle Stages
The term "sintering stages" refers specifically to what happens to the green part when it is subjected to a controlled heating and cooling cycle. The driving force behind this transformation is the reduction of surface energy, as individual particles fuse to minimize their exposed surface area.
A Detailed Look at the Four Key Stages
The thermal cycle is designed to progressively transform the loose powder compact into a dense, solid object. Each stage has a distinct physical mechanism and objective.
Stage 1: Binder Burnout (The Preliminary Step)
Before true sintering begins, the green part is heated at a relatively low temperature. The primary goal of this phase is to burn off the organic binders and lubricants that were added to aid the compacting process.
This must be done slowly and carefully to prevent the rapid formation of gas from trapping inside the part, which could cause cracks or defects.
Stage 2: Initial Stage (Neck Growth)
As the temperature rises, the actual sintering begins. At the points where individual powder particles touch, atoms begin to diffuse across the boundaries.
This diffusion creates small bridges, or "necks," between the particles. During this stage, the part gains significant strength, but its overall density does not increase substantially. The pore structure remains open and interconnected.
Stage 3: Intermediate Stage (Densification)
This is the most critical stage for achieving a dense final product. The necks between particles grow larger, and the particle centers draw closer together.
This process causes the pores within the material to shrink, forming a network of interconnected channels. The part undergoes significant shrinkage and densification, which is often the primary goal of the sintering process.
Stage 4: Final Stage (Pore Elimination & Grain Growth)
In the final stage, the interconnected pore channels close off, leaving behind isolated, spherical pores. The primary mechanism shifts from densification to the elimination of these last few pores.
Simultaneously, a process called grain growth (or coarsening) accelerates. The smaller crystal grains within the material are consumed by larger ones, reducing the total grain boundary area. This stage requires careful control to achieve full density without excessive grain growth.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The success of sintering depends on navigating the inherent trade-offs between its competing mechanisms, primarily densification and grain growth.
The Goal: Maximum Density
For most structural applications, the objective is to achieve the highest possible density. A dense part has fewer internal voids, leading to superior mechanical properties like strength and toughness. This is primarily achieved during the intermediate stage.
The Risk: Uncontrolled Grain Growth
While densification is desirable, allowing the process to continue for too long or at too high a temperature can lead to excessive grain growth. Overly large grains can make some materials, particularly ceramics, brittle and prone to fracture. The final stage of sintering is a delicate balance between removing the last remnants of porosity and preventing this detrimental coarsening.
Controlling Sintering for Your Desired Outcome
The key to effective manufacturing is to control the sintering profile (temperature and time) to achieve the microstructure that best suits your application.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and density: Your goal is to optimize the intermediate stage and carefully manage the final stage to close pores without causing excessive grain growth.
- If your primary focus is creating a porous material (e.g., a filter): You would intentionally stop the process during the initial stage, ensuring strong necks have formed for structural integrity while maintaining an open, interconnected pore network.
- If your primary focus is repeatable, cost-effective production: Understanding these stages is crucial for diagnosing production flaws. For example, warping might indicate non-uniform heating, while low density could point to insufficient time or temperature to complete the intermediate stage.
By mastering these stages, you move from simply heating a material to precisely engineering its final form and function.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Primary Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Binder Burnout | Removal of organic binders | Prepares green part for sintering |
| 2. Initial Stage | Neck formation between particles | Part gains strength, open porosity |
| 3. Intermediate Stage | Significant densification & shrinkage | High density and strength achieved |
| 4. Final Stage | Pore elimination & grain growth | Final microstructure control |
Master the sintering process for your lab's materials.
Understanding the four stages of sintering is key to achieving the exact material properties—density, porosity, and strength—required for your specific application. Whether you need maximum densification for structural integrity or a controlled porous network for filtration, precise thermal control is essential.
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab furnaces and thermal processing equipment, providing the reliable, consistent heat treatment solutions that laboratories depend on for repeatable results. Our expertise in sintering technology can help you optimize your process from binder burnout to final grain growth.
Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss how KINTEK's lab equipment can enhance your sintering outcomes and improve your material performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when selecting the size of an ultra-low freezer? A Guide to Maximizing Efficiency and Capacity
- What is the temperature at the bottom of the blast furnace? Unlocking the Heart of Iron Production
- Can you heat treat cast aluminum? Strengthening Specific Alloys for Demanding Applications
- Why do we use sputter coating? For Superior Thin Film Uniformity and Adhesion
- Why KBr pellets are used as a reference in IR spectroscopy? Achieve Clear, Interference-Free Analysis
- Why is a laboratory oven essential in the catalyst impregnation workflow? Secure Your Material's Structural Integrity
- Which of the following are methods used to deposit thin films? A Guide to PVD, CVD & More
- Is cold plasma pyrolysis expensive? Unlocking High-Value Resources from Waste



















