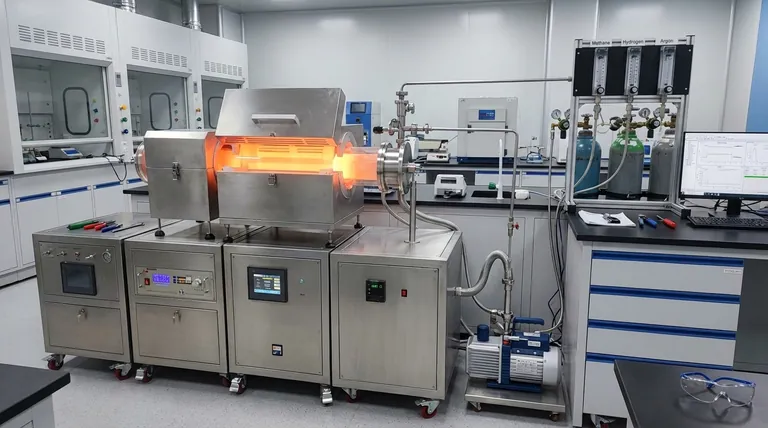
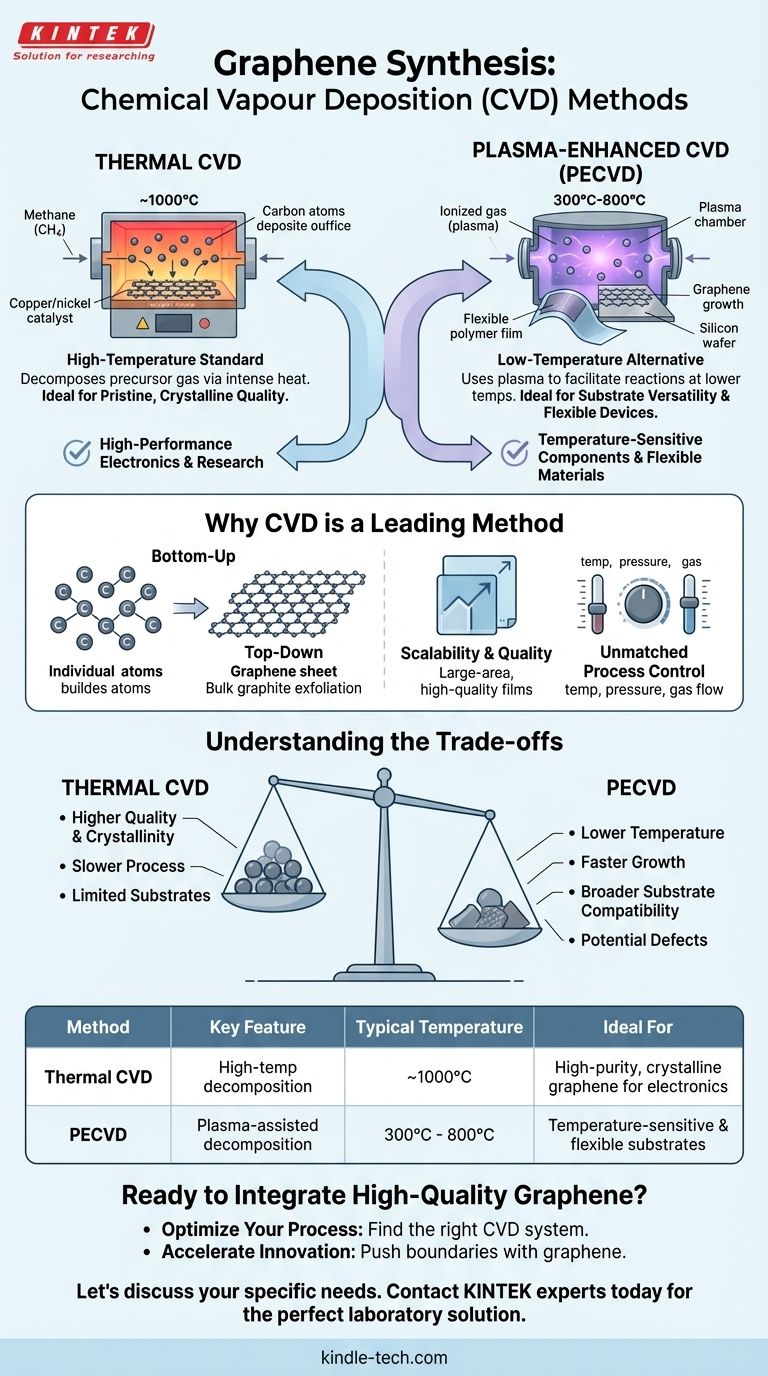
For producing high-quality graphene, the two primary methods of chemical vapor deposition (CVD) are Thermal CVD and Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD). Thermal CVD leverages extremely high temperatures to decompose a carbon-containing gas, allowing carbon atoms to arrange themselves into a graphene lattice on a catalyst surface. In contrast, PECVD uses plasma to break down the precursor gas, enabling the process to occur at significantly lower temperatures.
The choice between Thermal CVD and Plasma-Enhanced CVD is a strategic decision that balances the need for pristine, crystalline quality against the demands for lower-temperature processing and substrate versatility.

Why CVD is a Leading Method for Graphene Production
Chemical Vapor Deposition is not just one method among many; it has become the gold standard for producing the kind of graphene required for advanced applications. This is due to its fundamental "bottom-up" approach.
The "Bottom-Up" Advantage
Unlike "top-down" methods like exfoliation, which start with a bulk material (graphite) and break it down, CVD builds graphene atom by atom. This constructive approach provides an unparalleled degree of control over the final product.
Scalability and Quality
CVD has emerged as the most reliable technique for synthesizing large-area, high-quality single or few-layer graphene films. This scalability is critical for moving graphene from laboratory curiosities to commercially viable products in electronics and materials science.
Unmatched Process Control
By carefully adjusting deposition parameters like temperature, pressure, and gas flow, CVD allows for precise control over the graphene's final characteristics. This includes its chemical composition, crystal structure, layer number, and grain size.
Deconstructing the Core CVD Methods
While both Thermal and Plasma-Enhanced CVD fall under the same family, their operating principles lead to different strengths and applications.
Thermal CVD: The High-Temperature Standard
Thermal CVD is the most established method for producing exceptionally pure graphene. The process involves introducing a hydrocarbon gas, such as methane, into a furnace heated to around 1000°C.
At this high temperature, the gas molecules decompose, and carbon atoms deposit onto a catalytic metal substrate, typically a copper or nickel foil. These atoms then self-assemble into the hexagonal lattice structure of graphene. The result is a highly crystalline film with minimal defects.
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD): The Low-Temperature Alternative
PECVD achieves the same goal—decomposing a precursor gas—but without relying solely on intense heat. Instead, it uses an electromagnetic field to create a plasma, an ionized gas that contains highly reactive species.
These reactive species facilitate the necessary chemical reactions at much lower temperatures, often between 300°C and 800°C. This opens the door to depositing graphene on a wider array of materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The decision to use one method over the other is governed by a clear set of engineering trade-offs.
Quality vs. Temperature
The primary trade-off is between crystal quality and processing temperature. Thermal CVD's slow, high-temperature process generally yields higher-quality, more ordered graphene with larger crystal domains and fewer defects.
PECVD, while efficient, can sometimes introduce more structural defects due to the energetic plasma environment and faster growth rates.
Substrate Compatibility
This is the most significant advantage of PECVD. The extreme heat of Thermal CVD limits its use to substrates that can withstand temperatures of ~1000°C.
PECVD’s lower operating temperature makes it compatible with a much broader range of substrates, including those that are temperature-sensitive, such as certain silicon wafers, polymers, and flexible plastics.
Process Complexity
While Thermal CVD requires a high-temperature furnace, PECVD systems are inherently more complex due to the need for plasma generation and control equipment. However, the lower energy consumption of PECVD can be a significant advantage in large-scale industrial settings.
Selecting the Right Method for Your Application
Your final choice depends entirely on the requirements of your end product.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research or high-performance electronics: Thermal CVD is the standard choice for producing the most pristine, defect-free graphene layers required for optimal electronic properties.
- If your primary focus is integration with temperature-sensitive components: Plasma-Enhanced CVD is the necessary choice, as it allows for direct graphene growth on materials that would be destroyed by thermal processes.
- If your primary focus is developing flexible devices or composite materials: PECVD provides the crucial ability to deposit graphene directly onto polymer films and other flexible substrates.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental trade-off between crystalline perfection and processing flexibility is the key to mastering graphene synthesis.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Feature | Typical Temperature | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal CVD | High-temperature gas decomposition | ~1000°C | High-purity, crystalline graphene for electronics |
| Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) | Plasma-assisted decomposition | 300°C - 800°C | Temperature-sensitive & flexible substrates |
Ready to integrate high-quality graphene into your research or product development?
The choice of CVD method is critical to your project's success. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and expert support needed for advanced materials synthesis.
- Optimize Your Process: Get the right CVD system for your specific application, whether you require the ultimate purity of Thermal CVD or the versatility of PECVD.
- Accelerate Innovation: From fundamental research to flexible electronics, our solutions help you push the boundaries of what's possible with graphene.
Let's discuss your specific needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs



















