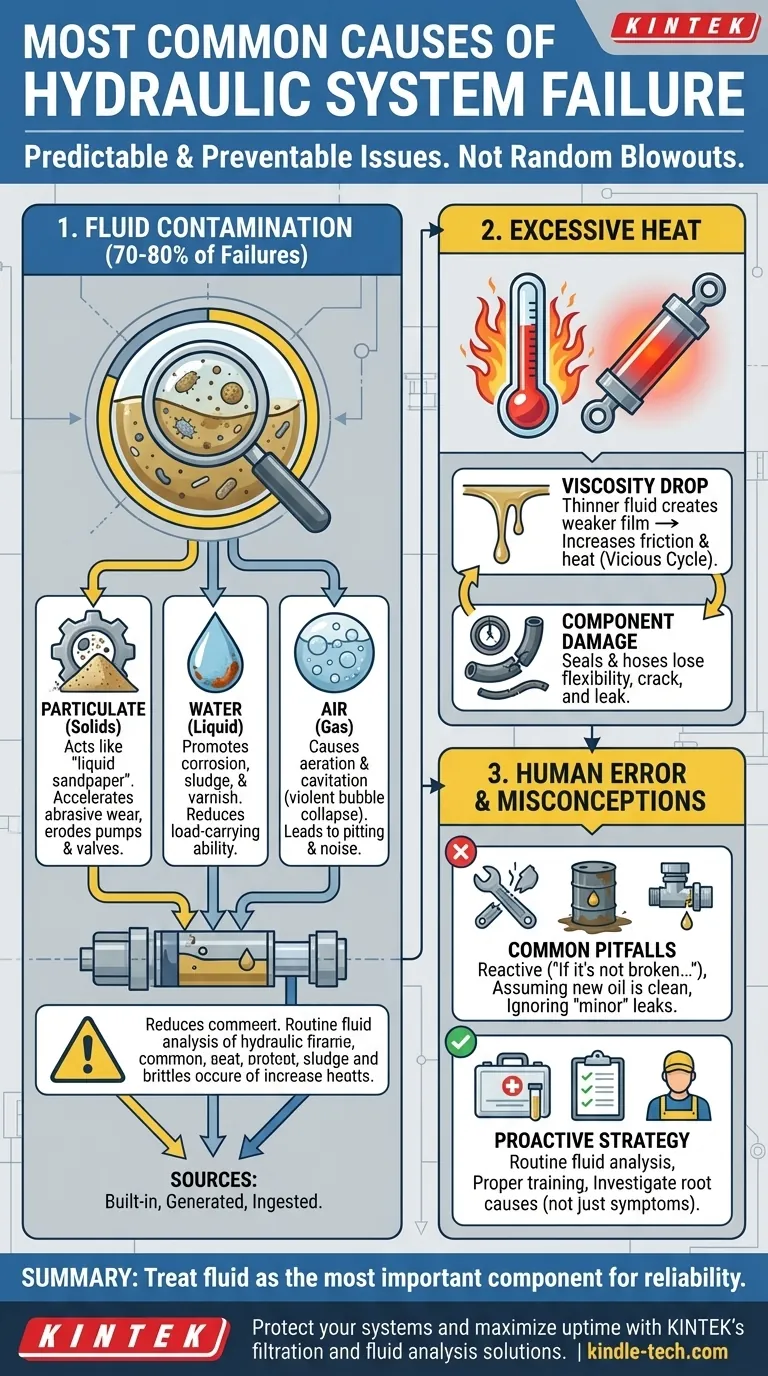
To put it directly, the vast majority of hydraulic system failures are not caused by dramatic component blowouts, but by three persistent and preventable issues. The most dominant cause, by a significant margin, is fluid contamination, followed by problems arising from excessive heat, and finally, human error in operation and maintenance.
The core takeaway is that hydraulic failures are rarely sudden or random. They are the predictable result of neglecting three pillars of system health: fluid cleanliness, temperature control, and proper procedure. Mastering these is the key to shifting from reactive repairs to proactive reliability.

The Dominant Culprit: Contamination
Contamination is responsible for an estimated 70-80% of all hydraulic system failures. It is the single greatest enemy of system reliability and must be the primary focus of any maintenance strategy.
How Contamination Enters a System
Contaminants are not just outside dirt. They can be built-in from the manufacturing process, generated internally as components wear, or ingested from the surrounding environment through worn seals or breathers.
The Impact of Particulate Contamination
Solid particles, like dirt, sand, and metal flakes, act like liquid sandpaper inside your system. They accelerate abrasive wear, eroding the tight tolerances inside pumps, motors, and valves, leading to internal leakage, loss of efficiency, and eventual seizure.
The Silent Threat of Water Contamination
Water does not compress and has poor lubricating properties. Its presence promotes corrosion, reduces the fluid's ability to carry loads, and can lead to the formation of sludge and varnish that clog system pathways.
The Problem with Air Contamination
Air can exist as dissolved bubbles (aeration) or vapor pockets (cavitation). Both are destructive, causing spongy actuator response, loud operation, fluid degradation through oxidation, and severe pitting damage to components as vapor bubbles violently collapse.
The Silent Killer: Excessive Heat
After contamination, excessive operating temperature is the next most common cause of failure. Heat attacks the hydraulic fluid itself, along with the seals and hoses that contain it.
What Causes Overheating?
Heat is a byproduct of inefficiency. Every time pressure drops without performing useful work (like flow across a relief valve or through an undersized line), the lost energy is converted directly into heat. Poor system design and blocked heat exchangers are common root causes.
The Vicious Cycle of Heat and Viscosity
Hydraulic fluid viscosity (its thickness) drops as temperature rises. Thinner fluid provides a weaker lubricating film, which increases metal-to-metal contact and friction. This friction, in turn, generates even more heat, creating a destructive feedback loop.
How Heat Degrades Seals and Hoses
High temperatures cause seals and hoses to lose their flexibility, becoming hard and brittle. This leads to cracking and an inability to properly seal, resulting in both internal and external leaks that can drain a system or introduce more contaminants.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Misconceptions
Effective hydraulic maintenance requires moving beyond common but flawed assumptions. Understanding these pitfalls is critical for building a truly reliable system.
The "If it's not broken, don't fix it" Mentality
This reactive approach is the most expensive maintenance strategy. Waiting for a component to fail ignores the underlying root cause—like contamination—which will simply destroy the replacement part as well, leading to recurring downtime.
The Misconception of "Clean" New Oil
Never assume new oil from a drum is clean enough for your system. It often contains particulate levels far higher than what is acceptable for modern high-pressure hydraulics. All new fluid should be filtered before being added to a system.
Overlooking Minor Leaks
A small, weeping leak is not a minor issue; it is a major warning sign. It indicates a seal has failed, and just as fluid can get out, dirt and moisture can get in, directly compromising the entire system.
A Proactive Strategy for System Reliability
Your goal should be to control the conditions that lead to failure, not just react to the failures themselves. The following approach will help you prioritize your actions based on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing uptime: Implement a routine fluid analysis program to identify contamination and fluid degradation before they cause damage.
- If your primary focus is reducing long-term cost: Invest in proper training for technicians and operators on clean handling procedures and correct system operation.
- If you are diagnosing a recurring failure: Look past the broken part and investigate the fluid's condition and the system's operating temperature to find the true root cause.
Ultimately, achieving hydraulic system reliability comes from treating the fluid as the most important component in the entire system.
Summary Table:
| Common Cause | Estimated Contribution to Failures | Primary Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid Contamination | 70-80% | Accelerated abrasive wear, corrosion, component damage |
| Excessive Heat | Significant secondary cause | Fluid degradation, seal failure, viscosity breakdown |
| Human Error | Contributes to both above causes | Improper maintenance, ignoring warning signs |
Protect your hydraulic systems and maximize uptime with KINTEK.
Hydraulic failures are predictable and preventable. KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables that keep your operations running smoothly, including filtration systems and fluid analysis tools crucial for proactive hydraulic maintenance.
Let us help you implement a reliability-focused strategy. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory or industrial needs and discover how our solutions can reduce downtime and long-term costs for your business.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Lab Heat Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press for XRF KBR FTIR Lab Applications
- Hydraulic Diaphragm Lab Filter Press for Laboratory Filtration
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press contribute to the characterization of Pt/Pd alloy samples? | KINTEK Solutions
- What technical value does a four-column hydraulic press provide? Optimize Your Composite Powder Fabrication Today
- How do you do a KBr pellet procedure? A Step-by-Step Guide for High-Quality FTIR Analysis
- Where are hydraulic presses used? Powering Industries from Automotive to Aerospace
- How do I choose a hydraulic press? Match Tonnage, Size & Features to Your Needs
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- What is the alternative to KBr in IR spectroscopy? Explore Faster, Easier Sample Prep Methods
- How do you explain XRF results? A Guide to Interpreting Elemental Analysis Data











