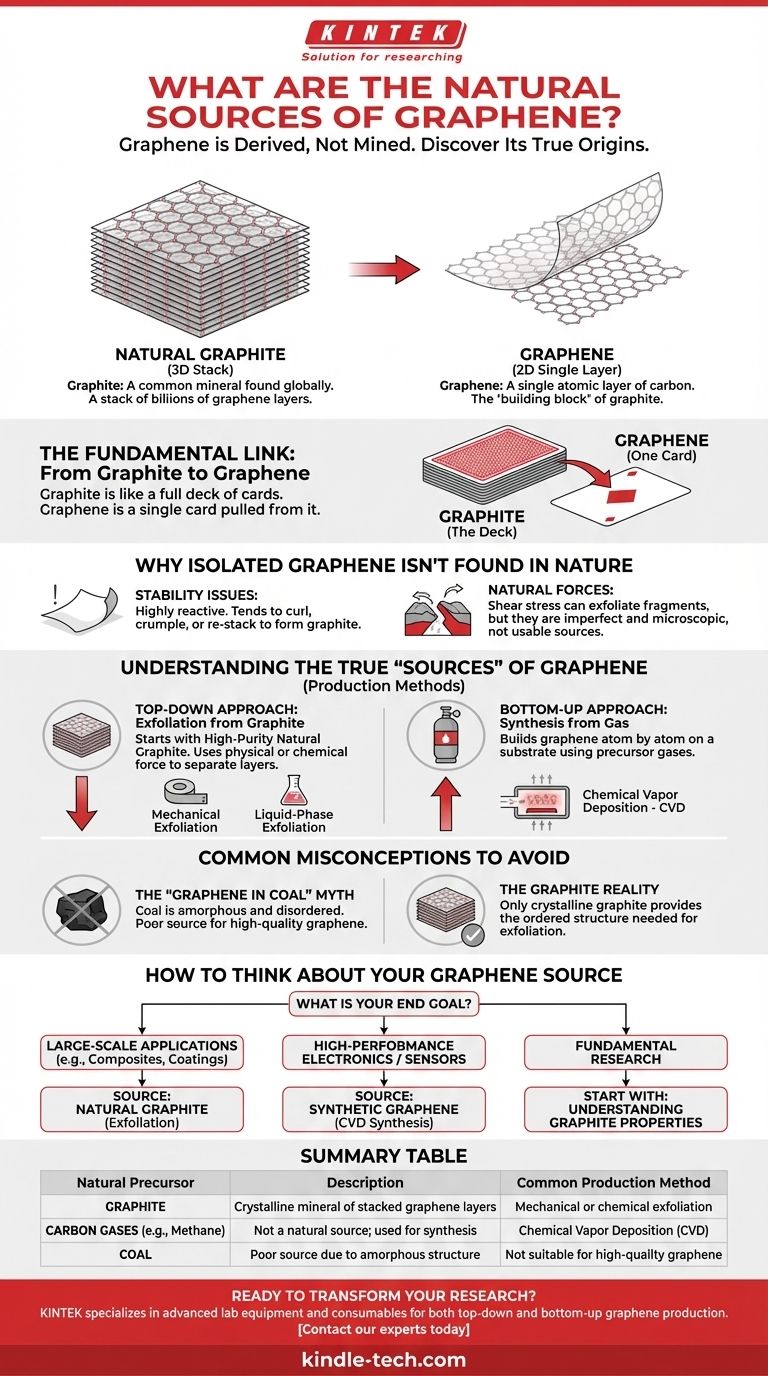
In its purest form, graphene does not have a direct natural source that can be mined or harvested. Instead, the true natural source of graphene is graphite, a common mineral found across the globe. Graphene is a single, two-dimensional atomic layer of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb lattice, and graphite is simply a three-dimensional structure made of billions of these graphene layers stacked together.
The critical distinction is that graphene is not found in nature as a standalone material but is derived from its natural precursor, graphite. The challenge and innovation in the field lie not in finding graphene, but in efficiently separating a single atomic layer from the graphite stack.

The Fundamental Link: From Graphite to Graphene
To understand why graphene isn't simply collected from the environment, it's essential to understand its relationship with graphite, its parent material.
What is Graphite?
Graphite is a naturally occurring crystalline form of carbon. It is a common mineral mined worldwide and is known for its use in pencils and lubricants.
Its structure consists of countless layers of graphene sheets held together by relatively weak forces. This layered structure is what allows the sheets to slide against each other, giving graphite its characteristic slipperiness.
The "Deck of Cards" Analogy
Think of a block of natural graphite as a full deck of playing cards. The entire deck represents graphite.
A single playing card pulled from that deck is graphene. It's still made of the same fundamental material, but its properties as an individual sheet are dramatically different from the bulk deck.
Why Isolated Graphene Isn't Found in Nature
While technically a component of a natural mineral, stable, isolated sheets of graphene are not found in the natural world for two primary reasons.
The Problem of Stability
A single, large atomic layer is thermodynamically unstable on its own in a three-dimensional world. Graphene's immense surface area relative to its volume makes it highly reactive.
An isolated sheet would prefer to minimize its energy by curling into a nanotube, crumpling into a fullerene, or re-stacking onto another surface to become graphite again.
The Reality of Natural Forces
Natural geological processes, such as shear stress, can theoretically exfoliate or peel off tiny fragments of graphene from graphite deposits.
However, these fragments would be microscopic, structurally imperfect, and not in a form that could be considered a usable "source." The 2004 isolation of graphene was achieved with scotch tape in a lab—a deliberate, artificial act of separation.
Understanding the True "Sources" of Graphene
Since graphene is not harvested directly, its "sources" are best understood as the starting materials for production methods. These methods are broadly categorized as top-down or bottom-up.
Top-Down Approach: Exfoliation from Graphite
This method starts with a bulk material and breaks it down. High-purity natural graphite is the primary source material for all exfoliation techniques.
Processes like mechanical exfoliation (the "tape method") or liquid-phase exfoliation use physical force to overcome the weak bonds holding the graphene layers together, producing graphene flakes.
Bottom-Up Approach: Synthesis from Gas
This method builds graphene atom by atom. The most common technique is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
In CVD, carbon-containing gases (like methane) are heated on a substrate (often copper foil). The gas decomposes, and the carbon atoms arrange themselves into a continuous sheet of high-quality graphene. Here, the "source" is the precursor gas, not a natural mineral.
Common Misconceptions to Avoid
Understanding the source of graphene requires sidestepping common assumptions about carbon materials.
The "Graphene in Coal" Myth
While coal is rich in carbon, it is a poor source for graphene. Coal has an amorphous structure, meaning its carbon atoms are disordered.
Graphene production via exfoliation requires the highly ordered, crystalline lattice structure found only in graphite.
Natural vs. Synthetic: A Question of Application
The quality and form of graphene depend entirely on its production source.
Graphene exfoliated from natural graphite typically comes as flakes of varying sizes and is ideal for bulk applications like composites, inks, and coatings. High-quality sheet graphene for advanced electronics must be synthesized via methods like CVD.
How to Think About Your Graphene Source
The right "source" is directly tied to your end goal. It's not about finding the material but choosing the right production pathway.
- If your primary focus is large-scale applications like composites or coatings: Your source will be high-purity natural graphite, from which graphene flakes are exfoliated.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics or sensors: You will need synthetic graphene, typically grown via CVD from precursor gases, which is not a natural process.
- If you are exploring fundamental research: The journey always begins with understanding the properties of graphite, the natural precursor to nearly all graphene production.
Understanding that graphene is a material we must purposefully create rather than discover is the key to unlocking its remarkable potential.
Summary Table:
| Natural Precursor | Description | Common Production Method |
|---|---|---|
| Graphite | A crystalline mineral of stacked graphene layers | Mechanical or chemical exfoliation |
| Carbon Gases (e.g., Methane) | Not a natural source; used for synthesis | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) |
| Coal | Poor source due to amorphous structure | Not suitable for high-quality graphene |
Ready to explore how high-quality graphene can transform your research or product development? KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for both top-down (exfoliation) and bottom-up (CVD) graphene production. Whether you're working with natural graphite precursors or synthesizing high-purity sheets, our solutions ensure precision and reliability. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs and help you achieve groundbreaking results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why does graphite not melt? Unlocking the Secrets of Its Extreme Heat Resistance
- Is graphite good for high temperature? Unlock Its Full Potential in Controlled Atmospheres
- What is the graphite furnace used for? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C in a Controlled Environment
- At what temperature does graphite melt? Understanding Its Extreme Phase Change
- What is special about graphite? Unlocking Its Unique Properties for Extreme Applications



















