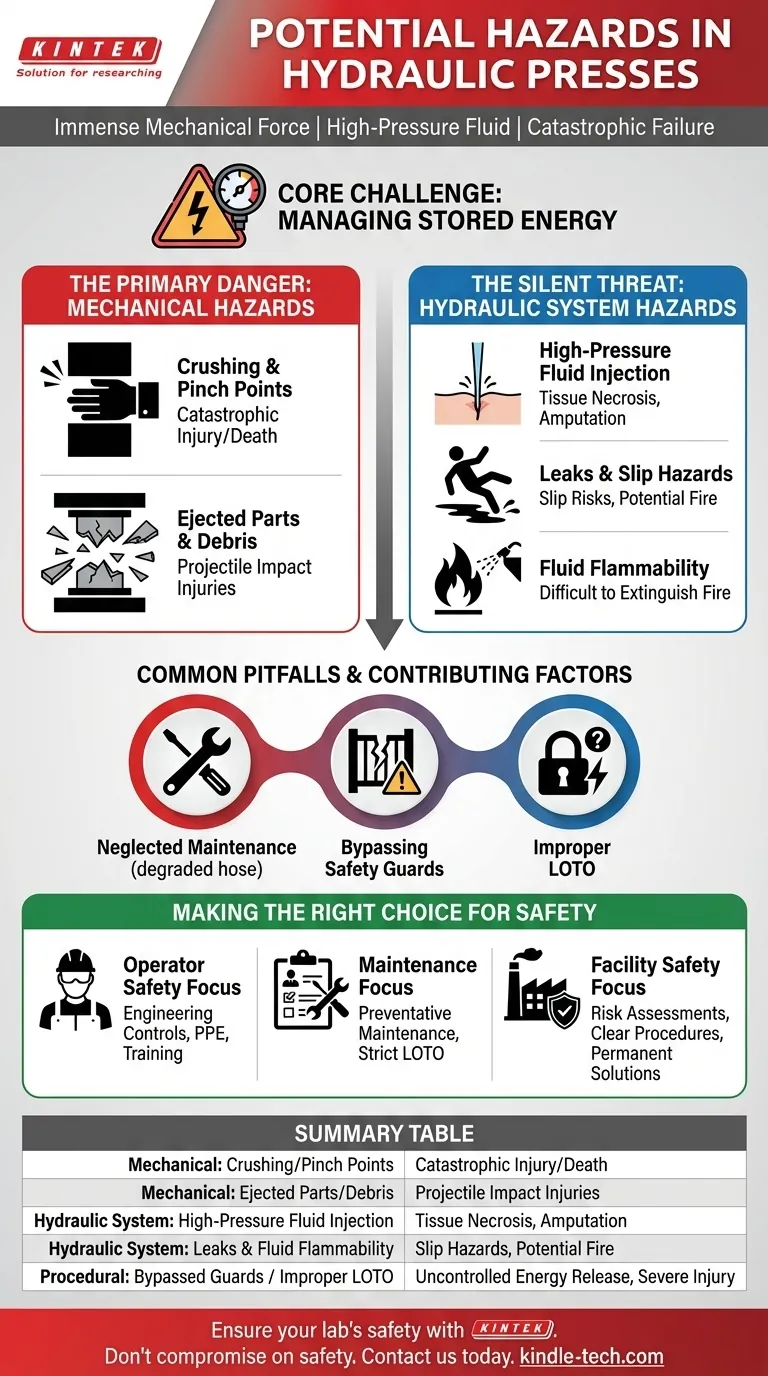
The most significant hazards of a hydraulic press stem from the immense mechanical force it generates, the high-pressure fluid that powers it, and the potential for catastrophic component failure. While many are aware of the obvious crushing danger, the risks associated with high-pressure hydraulic fluid injection and flying debris are equally severe and often underestimated.
The core challenge in hydraulic press safety is managing stored energy. Whether it's the mechanical potential energy in the raised ram or the hydraulic pressure stored in the lines, an uncontrolled release of this energy is the root cause of nearly all major incidents.
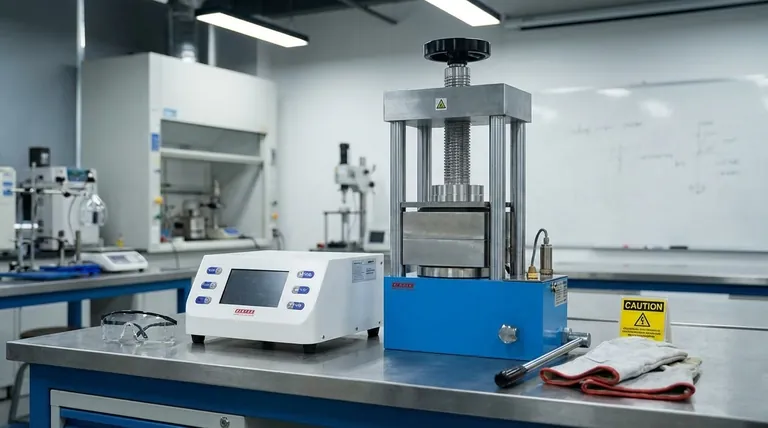

The Primary Danger: Mechanical Hazards
The defining characteristic of a hydraulic press—its ability to exert massive force—is also its primary hazard. This force can be dangerous not only at the point of operation but also through secondary effects.
Crushing and Pinch Points
The most obvious and severe hazard is the area between the ram and the press bed. Any body part caught in this "point of operation" will be subjected to immense crushing forces, leading to catastrophic injury or death. Pinch points can also exist in other moving parts of the press machinery.
Ejected Parts and Debris
The force of the press can cause the workpiece, tooling, or dies to fracture unexpectedly. This can send shards of metal or other materials flying at high velocity, creating a projectile hazard for the operator and anyone else in the vicinity.
The Silent Threat: Hydraulic System Hazards
The hydraulic system itself presents a unique set of risks that are distinct from the mechanical motion of the press. These are often less obvious to untrained personnel.
High-Pressure Fluid Injection
Hydraulic systems operate at extremely high pressures. A pinhole leak in a hose or fitting can eject a nearly invisible stream of fluid at a velocity high enough to pierce the skin. This type of injury is a severe medical emergency that can lead to amputation or death if not treated correctly, as the injected fluid can cause tissue necrosis and widespread systemic damage.
Leaks and Slip Hazards
Even low-pressure leaks are hazardous. Spilled hydraulic fluid creates a significant slip-and-fall risk on the surrounding floor. These leaks also indicate a potential point of failure in the system that could escalate.
Fluid Flammability
While many modern hydraulic fluids have high flash points, some types are flammable. A leak that sprays onto a hot surface or ignition source can result in a torch-like fire that is difficult to extinguish.
Common Pitfalls and Contributing Factors
Accidents rarely have a single cause. They are often the result of underlying issues in maintenance, procedures, or the operational environment.
Neglected Maintenance
The reference to "more maintenance is required" is critical because neglect is a direct cause of failure. Hoses, seals, and fittings degrade over time. Failure to inspect and replace these components is a leading cause of leaks and catastrophic line bursts.
Bypassing Safety Guards
Safety features like two-hand controls, light curtains, and physical guarding are there for a reason. Operators under pressure for productivity may be tempted to bypass these systems, which removes the essential layer of protection and dramatically increases the risk of a crushing injury.
Improper Lockout/Tagout (LOTO)
Performing maintenance, clearing a jam, or changing a die without properly de-energizing the press is extremely dangerous. The hydraulic system can store pressure even when the motor is off. Failure to follow strict LOTO procedures can lead to the unexpected activation of the ram, causing severe injury to maintenance personnel.
Making the Right Choice for Safety
Your safety strategy should be tailored to your specific role and responsibilities. Focus on the controls that will have the greatest impact on the risks you manage.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: Prioritize engineering controls like physical guarding and light curtains, enforce the use of PPE (especially safety glasses), and provide comprehensive training on machine-specific hazards.
- If your primary focus is maintenance and reliability: Implement a rigorous preventative maintenance schedule with a focus on hydraulic hose and component inspections, and enforce strict adherence to lockout/tagout procedures for all service tasks.
- If your primary focus is overall facility safety: Conduct regular, documented risk assessments on the press, ensure safety procedures are clear and accessible, and always favor permanent engineering solutions over reliance on operator behavior.
Ultimately, creating a safe environment around a hydraulic press depends on a proactive culture that respects the machine's inherent power.
Summary Table:
| Hazard Category | Specific Risk | Key Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical | Crushing/Pinch Points | Catastrophic injury or death |
| Mechanical | Ejected Parts/Debris | Projectile impact injuries |
| Hydraulic System | High-Pressure Fluid Injection | Tissue necrosis, amputation |
| Hydraulic System | Leaks & Fluid Flammability | Slip hazards, potential fire |
| Procedural | Bypassed Guards / Improper LOTO | Uncontrolled energy release, severe injury |
Ensure your lab's safety and operational integrity with KINTEK.
Hydraulic presses are powerful but pose significant risks if not properly maintained or operated. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment, including hydraulic presses, and the necessary consumables to keep your operations running safely and efficiently.
Our expertise helps you mitigate hazards like crushing, fluid injection, and component failure. We provide the quality equipment and support your laboratory needs to foster a proactive safety culture.
Don't compromise on safety. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and let KINTEK be your partner in laboratory safety and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Lab Heat Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What are the failures of a hydraulic press? Prevent Downtime and Ensure Safety in Your Lab
- What are the parts of a manual hydraulic press? A Guide to Its Core Components and Operation
- What is a hydraulic press in simple words? Harness Immense Force for Shaping and Crushing
- What is the conclusion of a hydraulic press? Unmatched Force for Industrial Applications
- What does a manual press do? Understand the Two Key Types for Your Lab or Industrial Needs



















