The primary challenge holding back graphene is the immense difficulty in producing large, perfect, and cost-effective sheets of it. While its properties are revolutionary in the laboratory, translating that potential to industrial-scale products is hindered by fundamental manufacturing problems. Current methods struggle to deliver the consistent quality and quantity needed for widespread, real-world applications.
Graphene's potential is undisputed. However, the core problem is not a failure of the material itself, but a profound manufacturing challenge. Producing the right type of high-quality graphene, consistently and at an industrial scale, remains the single greatest barrier to its adoption.

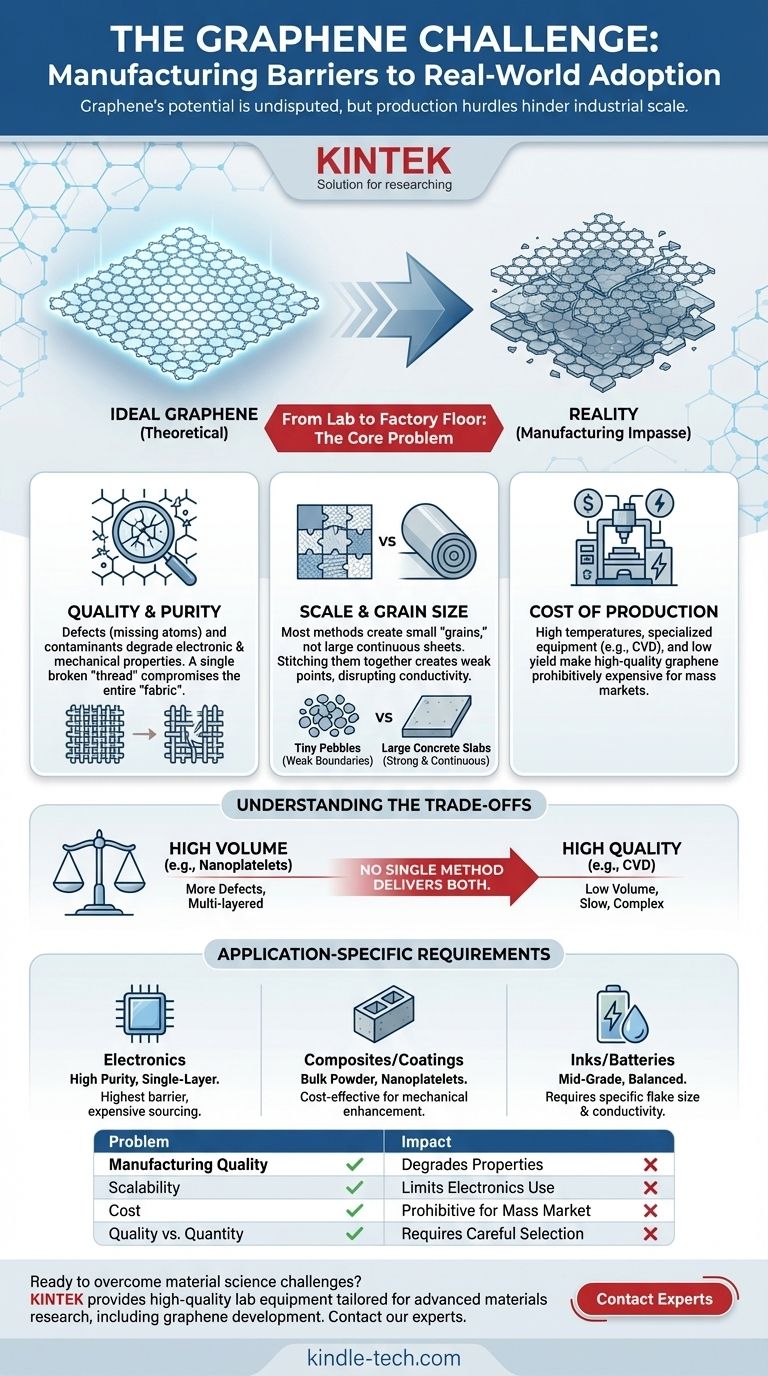
The Manufacturing Impasse: From Lab to Factory Floor
The excitement around graphene is based on its ideal, theoretical form: a perfect, single-atom-thick lattice of carbon. The reality of producing this material is far more complex and is the root cause of its slow commercialization.
The Challenge of Quality and Purity
The most common methods for making graphene often introduce defects and contaminants. A defect can be a vacancy (a missing atom) or a misplaced atom in the hexagonal lattice.
Think of it like a perfect, tightly woven piece of fabric. A single broken thread—a defect—compromises the strength and properties of the entire sheet. These imperfections drastically degrade the material's exceptional electronic and mechanical strength.
The Problem of Scale and Grain Size
For applications like electronics or transparent protective films, large, continuous sheets of graphene are required. Most production techniques create small, individual flakes, known as "grains."
Stitching these small grains together is like paving a road with tiny pebbles instead of large concrete slabs. The boundaries between the grains create weak points that disrupt electrical conductivity and reduce overall strength, negating many of the material's benefits.
The Prohibitive Cost of Production
Creating high-quality graphene is an expensive process. Techniques like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), which can grow large, high-quality sheets, require specialized equipment, high temperatures, and costly precursor materials.
The low yield and high energy consumption of these methods make the resulting graphene too expensive for all but the most niche, high-value applications. Mass-market adoption requires a dramatic reduction in these production costs.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Not All Graphene is Created Equal
The term "graphene" is often used as a catch-all, but in reality, there are many different types. The method of production dictates its form and quality, leading to a critical trade-off that every potential user must understand.
Quality vs. Quantity
Methods that can produce graphene in large volumes, such as liquid-phase exfoliation of graphite, typically yield a powder of small, multi-layered flakes with a higher number of defects. This material is often called graphene nanoplatelets.
Conversely, methods that produce high-quality, single-layer graphene (like CVD) are slow, complex, and produce much smaller quantities. There is currently no single method that delivers both high quality and high quantity at a low cost.
Application-Specific Requirements
The "best" type of graphene is entirely dependent on the end-use. For an application like strengthening concrete or plastics, adding a bulk powder of graphene nanoplatelets may be perfectly sufficient and cost-effective.
However, for a high-frequency transistor or a transparent, conductive display, only a near-perfect, single-layer sheet of graphene will do. Using the wrong type of graphene for the job is a common source of failed projects and disillusionment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Navigating the graphene landscape requires matching the material's real-world form to your specific technical and commercial goals.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics: You face the highest barrier and must source expensive, high-purity, single-layer graphene, likely produced via CVD.
- If your primary focus is bulk composites or coatings: You can likely use lower-cost, mass-produced graphene nanoplatelets to enhance the mechanical or thermal properties of a host material.
- If your primary focus is conductive inks or batteries: You will need a material that balances flake size, conductivity, and cost, often requiring a mid-grade graphene product.
Understanding these fundamental production hurdles is the key to realistically evaluating graphene's role in any future technology.
Summary Table:
| Problem | Key Challenge | Impact on Adoption |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Quality | Defects and contaminants in the carbon lattice | Degrades electronic and mechanical properties |
| Scalability | Difficulty producing large, continuous sheets | Limits use in electronics and films |
| Cost | High energy use and expensive precursors | Prohibitive for mass-market applications |
| Quality vs. Quantity Trade-off | No single method delivers high quality and high volume | Requires careful selection for specific applications |
Ready to overcome material science challenges in your lab? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored for advanced materials research, including graphene development. Our expertise can help you select the right tools for your specific production and analysis needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your innovative projects and help you navigate complex material landscapes efficiently.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Bottom Discharge Graphitization Furnace for Carbon Materials
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- What are thin films used for? Unlock Advanced Material Properties for Your Applications
- What is the purpose of using electrolytic polishing on copper foils? Optimize Your CVD Graphene & hBN Growth Surface
- How does diamond like coating work? Unlock Superior Hardness and Low Friction
- What is an example of an anti-reflective coating? Master Light Control with MgF₂ & Multi-Layer Coatings
- Are carbon nanotubes stronger than graphene? Choosing the Right Carbon Nanomaterial for Your Application
- What can carbon nanotubes replace? Upgrade Your Materials with Superior Performance
- What are the characterization techniques of carbon nanotubes? A Guide to Analyzing Quality, Structure & Purity
- What uses thin films? Discover the Invisible Tech Powering Modern Devices



















