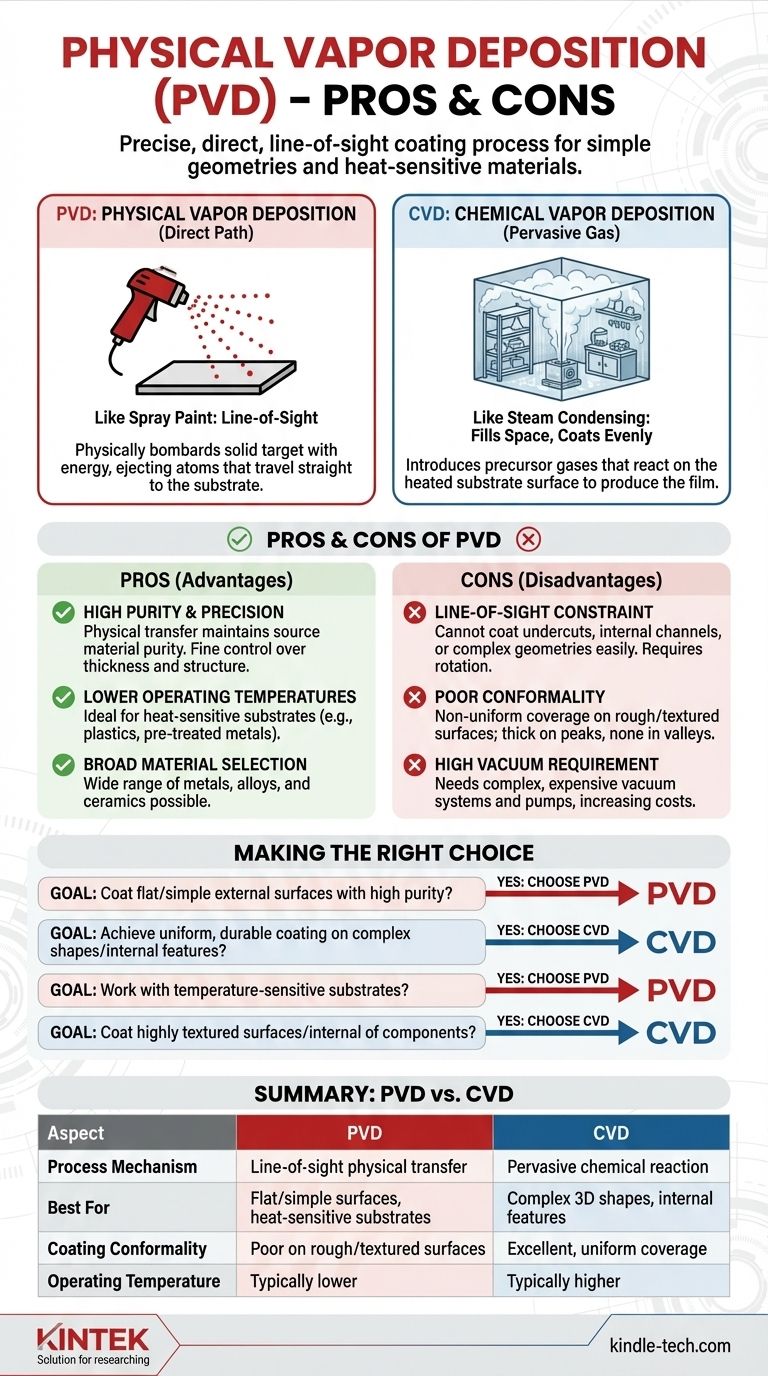
At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a highly precise and relatively straightforward process for applying thin films onto surfaces. Its primary advantage is the ability to deposit high-purity coatings with excellent control. However, its main disadvantage is that it is a "line-of-sight" process, making it poorly suited for coating complex, three-dimensional shapes with internal surfaces.
The choice between Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and its primary alternative, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), almost always comes down to one critical factor: the geometry of the part you need to coat. Understanding the fundamental difference between these two methods is the key to selecting the right one.

The Defining Principle: Line-of-Sight vs. Chemical Reaction
To understand the pros and cons of PVD, we must first compare its core mechanism to that of CVD. Their names describe their fundamental difference.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): A Direct Path
PVD works by physically bombarding a solid source material (the "target") with energy inside a vacuum chamber, causing atoms or molecules to be ejected. These ejected particles travel in a straight line until they strike the substrate, where they condense to form a thin film.
Think of it like using a can of spray paint. The paint only lands on the surfaces you can see directly from the nozzle's perspective.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): A Pervasive Gas
CVD, in contrast, introduces one or more volatile precursor gases into a reaction chamber. These gases decompose and react on the heated substrate's surface to produce the desired film.
This is more like steam condensing in a cold bathroom. The water vapor fills the entire room and condenses evenly on every surface it can reach, including the underside of shelves and the inside of a glass.
Key Advantages of PVD
The physical, line-of-sight nature of PVD gives it several distinct strengths.
High Purity and Precision
Because PVD is a physical transfer of material rather than a chemical reaction, it's often easier to maintain the purity of the source material in the final film. The process allows for extremely fine control over the thickness and structure of the coating.
Lower Operating Temperatures
PVD processes can often be run at significantly lower temperatures than many CVD processes. This makes PVD an ideal choice for coating substrates that are sensitive to heat, such as certain plastics or pre-treated metals.
Broad Material Selection
A very wide range of metals, alloys, and ceramics can be deposited using PVD. If you can make a target out of the material, you can generally use it for a PVD coating.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Limitations of PVD
The strengths of PVD are directly linked to its weaknesses, which become apparent when compared to the capabilities of CVD.
The Line-of-Sight Constraint
This is the single greatest limitation of PVD. The coating material travels in a straight line, so it cannot easily coat undercuts, sharp corners, or internal channels. Parts with complex geometries must often be rotated on intricate fixtures to achieve adequate coverage, adding complexity and cost.
Poor Conformality
A direct result of the line-of-sight issue is poor "conformality." PVD coatings do not uniformly cover rough or textured surfaces. High peaks will receive a thick coating while deep valleys may receive none at all. CVD, by contrast, excels at creating highly conformal coatings on even the most complex topographies.
Requirement for High Vacuum
PVD processes require a high vacuum environment to ensure the sputtered atoms can travel from the target to the substrate without colliding with air molecules. This necessitates expensive and complex vacuum chamber systems and pumps, which can increase capital and maintenance costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision ultimately depends on the specific demands of your component and desired outcome. Use these points as your guide.
- If your primary focus is coating flat or simple external surfaces with high purity: PVD is likely the more direct, efficient, and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving a uniform, durable coating on complex shapes with internal features: CVD's non-line-of-sight nature is almost always the superior solution.
- If your primary focus is working with temperature-sensitive substrates: PVD's typically lower process temperatures offer a significant advantage over high-temperature CVD.
- If your primary focus is coating the inside of a component or a highly textured surface: You must lean toward CVD for its ability to create a pervasive, conformal coating.
Understanding the fundamental difference between a physical, line-of-sight process and a pervasive chemical reaction is the key to making an informed and effective decision.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Mechanism | Line-of-sight physical transfer | Pervasive chemical reaction |
| Best For | Flat/simple surfaces, heat-sensitive substrates | Complex 3D shapes, internal features |
| Coating Conformality | Poor on rough/textured surfaces | Excellent, uniform coverage |
| Operating Temperature | Typically lower | Typically higher |
Still unsure if PVD or CVD is right for your project? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving all your laboratory coating needs. Our experts can help you select the ideal deposition method for your specific application, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. Contact our team today via our Contact Form for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Coating Solution for Sensitive Materials
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















