The primary risks of sintering revolve around managing dimensional accuracy, ensuring consistent material properties, and navigating high operational costs and environmental regulations. These challenges stem from the process's reliance on high temperatures, which can lead to unpredictable material shrinkage and the release of regulated emissions.
Sintering is a powerful manufacturing process, but its effectiveness is a direct result of precise process control. The core challenge is not avoiding risks entirely, but rather investing in the expertise and equipment needed to manage the inherent trade-offs between part quality, cost, and compliance.
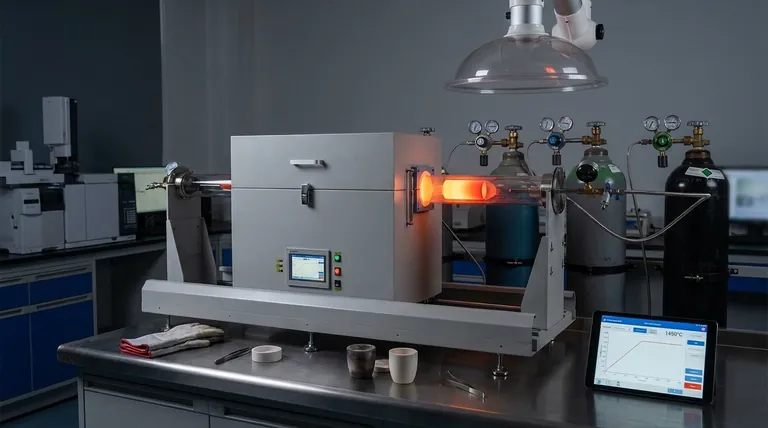

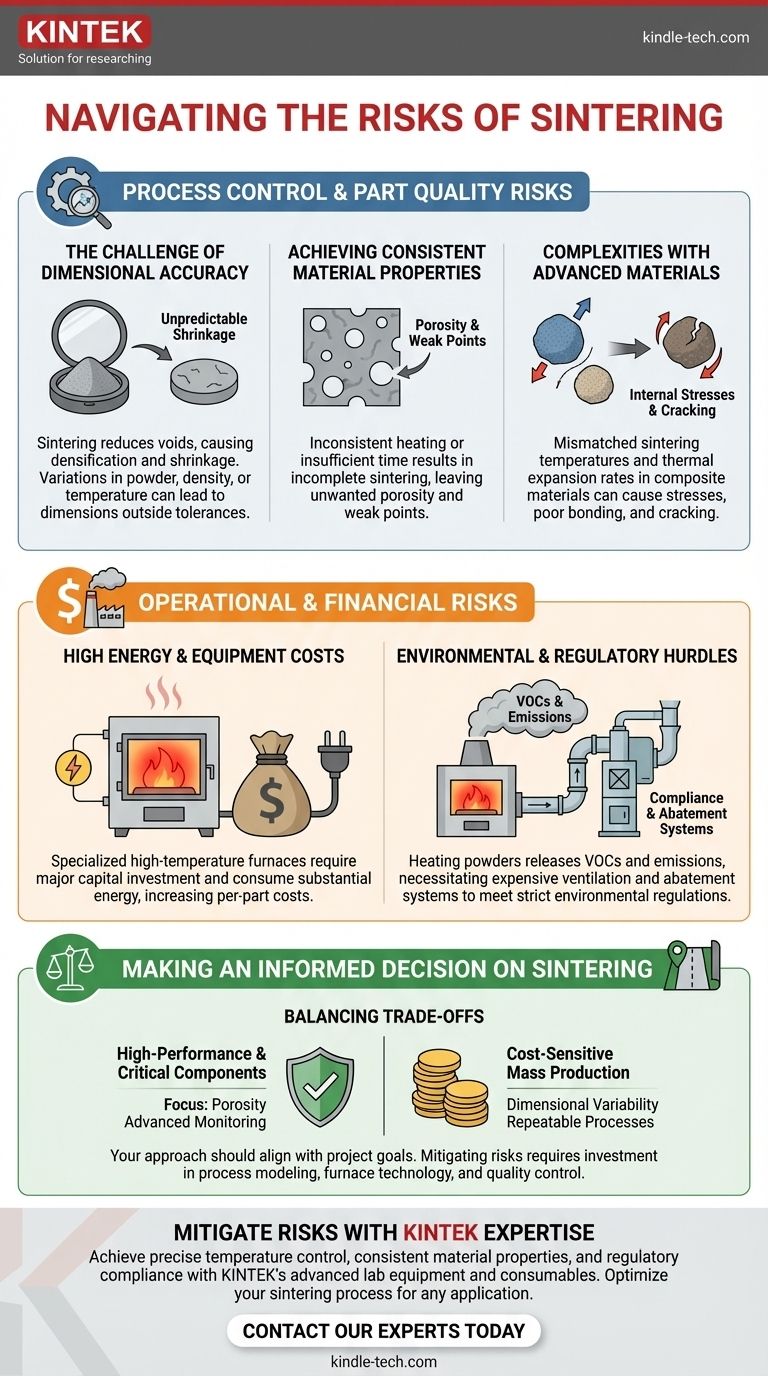
Process Control and Part Quality Risks
The most immediate risks in sintering relate to the physical and mechanical quality of the final component. Without meticulous control over the process parameters, the integrity of the part is compromised.
The Challenge of Dimensional Accuracy
Sintering fundamentally works by reducing the voids between material particles, causing the entire part to densify and shrink.
This shrinkage is necessary but can be difficult to predict and control. Variations in powder composition, green part density, or furnace temperature can lead to final dimensions falling outside of required tolerances.
Achieving Consistent Material Properties
The goal of sintering is to create a solid, homogenous mass with predictable mechanical properties.
Inconsistent heating or insufficient time at temperature can result in incomplete sintering. This leaves behind unwanted porosity, creating weak points within the material that can lead to premature component failure under stress.
Complexities with Advanced Materials
Sintering composite materials, where multiple types of powders are mixed, presents a significant challenge.
Different materials often have different sintering temperatures and rates of thermal expansion. This mismatch can create internal stresses, poor bonding between materials, or even cracking during the cooling phase.
Operational and Financial Risks
Beyond the quality of the part itself, the operational realities of running a high-temperature process introduce significant financial and regulatory hurdles.
High Energy and Equipment Costs
High-temperature sintering requires specialized furnaces capable of reaching and maintaining extreme temperatures with high precision.
These furnaces represent a major capital investment and consume substantial amounts of energy. These high operational costs directly impact the per-part cost, making the process less economical for low-volume production runs.
Environmental and Regulatory Hurdles
The process of heating material powders, especially those containing binders or lubricants, can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other potentially harmful emissions.
Governmental agencies strictly regulate these emissions. Complying with these environmental norms often requires installing expensive ventilation and abatement systems, which adds cost and complexity to the manufacturing line and can affect production rates.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the risks are significant, they must be weighed against the unique advantages of the sintering process. Understanding this balance is key to making an informed decision.
Why Sintering is Still a Dominant Process
Sintering excels at producing complex, net-shape parts from materials with very high melting points, such as ceramics and refractory metals. It also minimizes material waste compared to traditional subtractive manufacturing methods.
For many applications in the automotive, aerospace, and medical industries, sintering is the only economically viable method for mass-producing intricate, high-strength components.
The Cost of Failure vs. The Cost of Control
The risks of sintering—dimensional inaccuracy, porosity, and high costs—are not unavoidable outcomes but variables that can be managed.
Mitigating these risks requires a significant upfront investment in process modeling, advanced furnace technology, and rigorous quality control. The trade-off is between accepting a higher risk of part failure or incurring the higher cost of a tightly controlled process.
Making an Informed Decision on Sintering
Your approach to managing sintering risks should align directly with the primary goal of your project.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive mass production: Your key challenge is managing dimensional variability, which requires investing in highly repeatable processes and strict control over raw material quality.
- If your primary focus is high-performance, critical components: Your greatest risk is inconsistent material properties like porosity, necessitating advanced process monitoring and non-destructive testing to ensure part integrity.
- If your primary focus is regulatory and environmental compliance: Your main hurdle is managing process emissions, which requires careful selection of materials and investment in appropriate abatement technologies from the outset.
By understanding these risks as controllable variables, you can effectively leverage sintering's unique capabilities for your specific manufacturing goals.
Summary Table:
| Risk Category | Key Challenges | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Part Quality | Unpredictable shrinkage, inconsistent heating, material mismatch | Dimensional inaccuracy, porosity, weak points, cracking |
| Operational & Financial | High energy use, expensive furnace equipment, emission control systems | Increased per-part cost, major capital investment |
| Regulatory | Release of VOCs and other emissions during heating | Need for costly abatement systems, compliance hurdles |
Mitigate your sintering risks with KINTEK's expertise. Our advanced lab equipment and consumables are designed to help you achieve precise temperature control, consistent material properties, and compliance with environmental standards. Whether you're in mass production or developing high-performance components, KINTEK provides the reliable solutions you need to optimize your sintering process. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why use quartz tubes and vacuum sealing for sulfide solid-state electrolytes? Ensure Purity & Stoichiometry
- What is the function of quartz tubes and vacuum sealing systems? Secure Your High-Purity Solid Solution Synthesis
- What are the primary functions of high-precision tube furnaces in graphene growth? Achieve Defect-Free GS Synthesis
- What is the role of a tube furnace in the thermal treatment of argyrodite electrolytes? Master Ionic Conductivity
- What is the primary function of quartz tubes in halide electrolyte synthesis? Ensure Purity & Precise Stoichiometry



















