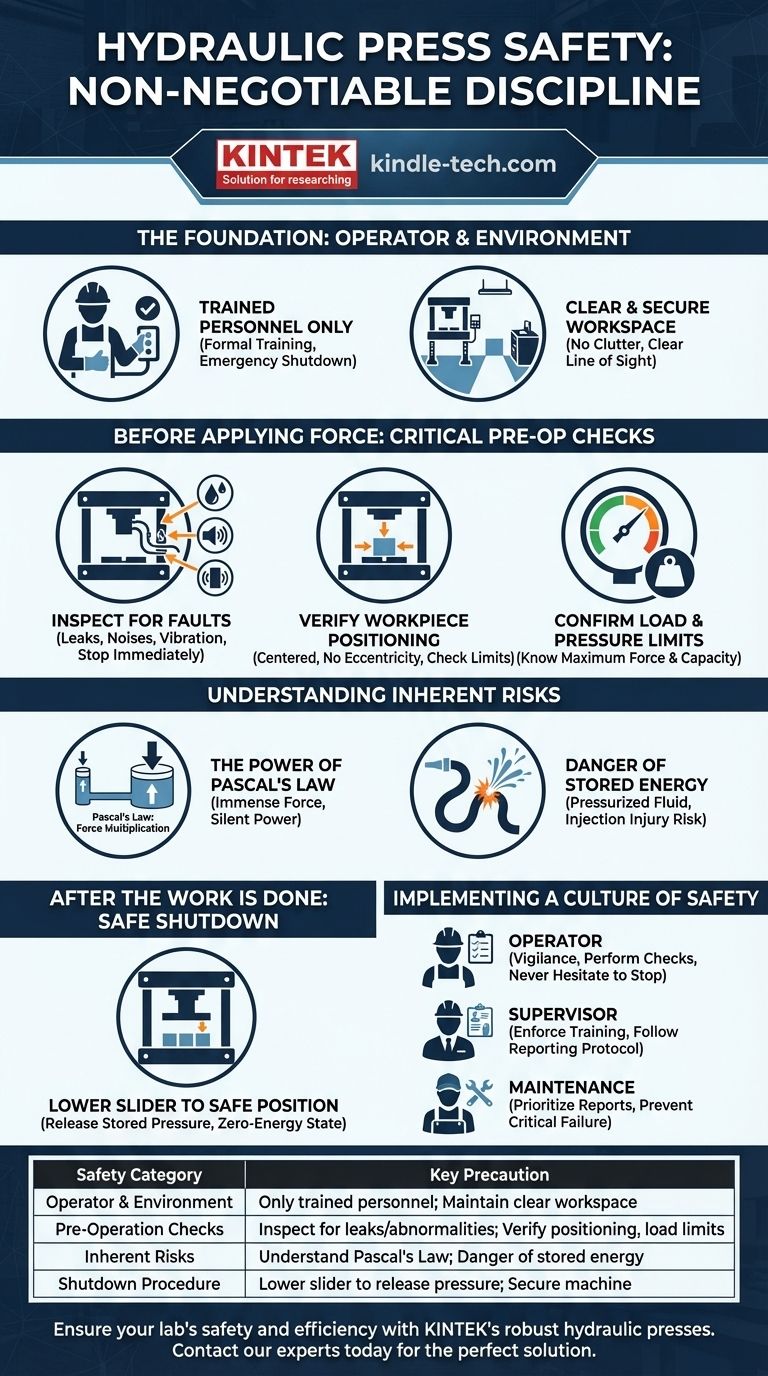
Operating a hydraulic press safely is a matter of non-negotiable discipline. The core precautions involve ensuring only trained and authorized personnel operate the machine, performing diligent pre-operation checks, and stopping immediately if any abnormalities like oil leaks, unusual noises, or excessive vibration occur. Fundamentally, safety relies on respecting the machine's immense power and adhering to established protocols without exception.
A hydraulic press multiplies force to an extreme degree. True safety, therefore, isn't just a checklist of rules, but a constant awareness of the machine's state, the security of the workpiece, and the inherent risks of stored hydraulic energy.

The Foundation: Operator and Environment
The first layer of safety begins before the machine is even turned on. It involves the person operating the press and the space around it.
Only Trained Personnel May Operate
A hydraulic press is not an intuitive tool. Operation must be restricted to individuals who have been formally trained on its specific model, its limits, and its emergency shutdown procedures. This training ensures the operator can recognize warning signs and understand the consequences of improper use.
Maintain a Clear and Secure Workspace
The area around a hydraulic press must be kept clear of all clutter, tools, and unnecessary personnel. This prevents trip hazards, ensures the operator has a clear line of sight, and provides an unobstructed path for retreat in an emergency.
Before Applying Force: Critical Pre-Operation Checks
A safe outcome is determined by the preparation you do beforehand. Never apply pressure without completing these essential checks.
Inspect the Machine for Faults
Before every use, visually inspect the press. Look for any signs of hydraulic fluid leaks on hoses, fittings, or seals. During startup, listen for any loud or unusual noises and feel for abnormal vibrations. If any of these are present, stop immediately and report the issue for maintenance.
Verify Workpiece Positioning
The workpiece must be centered securely on the press bed. An off-center load, known as eccentricity, places dangerous and uneven stress on the press frame and components. Never operate the press if the load exceeds the manufacturer's maximum limit for eccentricity, as this can lead to catastrophic structural failure.
Confirm Load and Pressure Limits
Know the maximum force your press can generate and the pressure limits of your workpiece. Applying a load beyond the capacity of either the press or the object being pressed can cause the workpiece to shatter or the machine to fail.
Understanding the Inherent Risks
The principles that make a hydraulic press so effective are also what make it so dangerous. Understanding these risks is key to avoiding complacency.
The Power of Pascal's Law
A hydraulic press works by using a confined fluid to transmit and multiply force. A small amount of pressure applied to a small piston generates immense force on a larger piston. This silent, invisible power can crush objects—and body parts—with no warning if safety procedures are ignored.
The Danger of Stored Energy
Pressurized hydraulic fluid is a form of stored energy. A sudden failure of a hose or seal can result in a violent, high-pressure release of this fluid, which can cause severe injection injuries or propel broken components at high velocity. This is why even a small leak must be treated as a serious safety issue.
After the Work is Done: Safe Shutdown
Proper procedure doesn't end when the job is complete. Securing the machine is a critical final step.
Lower the Slider to a Safe Position
After use, the machine's ram or slider should be lowered until it rests on the press bed or on secure blocks. This releases the stored pressure within the hydraulic system, placing the machine in a stable, zero-energy state and preventing accidental activation.
Implementing a Culture of Safety
To ensure long-term safety, these principles must be integrated into your operational culture.
- If you are an operator: Your primary responsibility is vigilance; perform pre-operation checks every time and never hesitate to stop if something seems wrong.
- If you are a supervisor: Your goal is to enforce that only trained personnel use the equipment and that a clear, no-fault protocol for reporting issues is established and followed.
- If you are responsible for maintenance: You must treat any report of unusual noise, vibration, or leakage with immediate priority to prevent a minor issue from becoming a critical failure.
Ultimately, a safe hydraulic press is the result of a well-trained operator who respects the machine's power with every single use.
Summary Table:
| Safety Category | Key Precaution |
|---|---|
| Operator & Environment | Only trained personnel may operate; maintain a clear workspace. |
| Pre-Operation Checks | Inspect for leaks/abnormalities; verify workpiece positioning and load limits. |
| Inherent Risks | Understand Pascal's Law and the danger of stored hydraulic energy. |
| Shutdown Procedure | Lower the slider to release stored pressure and secure the machine. |
Ensure your lab's safety and efficiency with KINTEK's robust hydraulic presses. Our equipment is designed with safety as a top priority, helping you enforce critical protocols and protect your personnel. Don't compromise on safety—contact our experts today to find the perfect hydraulic press solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
People Also Ask
- Why is a hydraulic pellet press used for FTIR? Transform Nanofillers into Clear Data
- What is the function of a laboratory hydraulic press for Li10GeP2S12 pellets? Optimize Solid-State Battery Performance
- How do laboratory hydraulic presses facilitate biomass pelletization? Optimize Biofuel Density and Prevent Slagging
- How does a laboratory manual hydraulic press facilitate the FT-IR characterization of catalysts? Master Sample Prep.
- What is the function of a bench-top laboratory hydraulic press for XRF? Maximize Accuracy in Prosopis juliflora Analysis



















