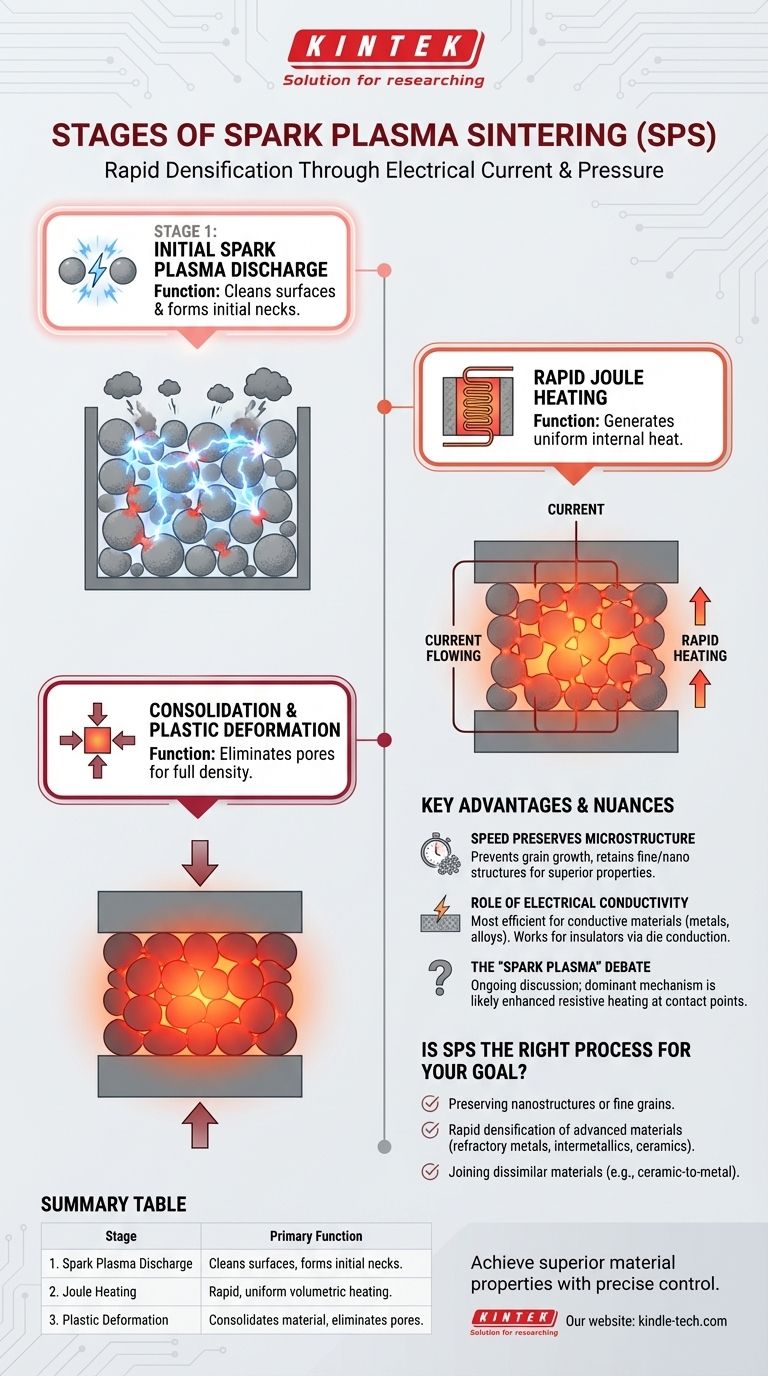
At its core, Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is a three-stage process involving an initial plasma discharge, subsequent Joule heating, and final plastic deformation. This method uses a pulsed electrical current and mechanical pressure to transform a powder into a solid, dense mass with extreme speed and control, fundamentally differing from slower, conventional furnace-based heating.
The critical insight is that SPS is not just about heating. It leverages electrical energy in two ways: first, to generate localized plasma that cleans and activates particle surfaces, and second, to produce rapid, uniform internal heat that, when combined with pressure, achieves full densification at lower temperatures and in a fraction of the time required by traditional methods.

The SPS Mechanism: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Conventional sintering relies on external heat slowly soaking into a material over many hours. Spark Plasma Sintering, also known as a Field-Assisted Sintering Technique (FAST), redefines this process by using electricity to act directly on the material at the particle level.
Stage 1: Initial Spark Plasma Discharge
At the start of the process, the powder particles are only loosely touching. When a high electrical current is applied, it cannot flow smoothly.
Instead, electrical discharges—or sparks—jump across the tiny gaps between individual particles. This creates momentary, localized pockets of plasma with temperatures reaching thousands of degrees Celsius.
This intense, localized heat serves a critical purpose: it vaporizes and cleans away surface impurities (like oxides) that would otherwise inhibit bonding. The now-purified surfaces begin to melt and fuse, forming small connections known as "necks" between particles.
Stage 2: Rapid Joule Heating
Once these initial necks have formed, the powder compact has a continuous path for electricity to flow. The process then transitions from sparking to a state of volumetric heating.
The electrical resistance of the powder compact and the graphite die generates intense, uniform heat throughout the material. This phenomenon, known as Joule heating, is what allows for the incredibly rapid heating rates (hundreds of degrees °C per minute) characteristic of SPS.
Stage 3: Consolidation and Plastic Deformation
In this final stage, the combination of high temperature and externally applied mechanical pressure forces the material to consolidate.
The heat makes the material soft and malleable. The pressure then squeezes the particles together, causing them to deform plastically and slide past one another. This action eliminates the remaining voids or pores between them.
The result is a highly dense, solid component achieved in mere minutes, rather than the many hours or even days required for conventional sintering.
Understanding the Key Advantages and Trade-offs
The unique mechanism of SPS offers distinct advantages over other methods, but it's important to understand the context in which it operates best.
Advantage: Speed Preserves Microstructure
The primary benefit of SPS is its speed. By keeping the sintering temperature lower and the duration shorter, SPS effectively prevents grain growth.
In conventional high-temperature processes, small grains tend to merge and grow larger, which can degrade the material's mechanical properties. SPS allows for the consolidation of nanopowders while preserving their fine-grained or even nanocrystalline structure, resulting in superior strength and hardness.
Consideration: The Role of Electrical Conductivity
SPS is most effective when the electrical current can pass directly through the powder being sintered. This makes the process exceptionally efficient for conductive materials like metals, alloys, and many ceramics (e.g., carbides, nitrides).
For electrically insulating ceramics, the process still works, but the heating is less direct. The current heats the conductive graphite die, which then heats the sample via conduction. While still faster than a conventional furnace, it does not leverage the full benefit of internal Joule heating.
Nuance: The "Spark Plasma" Debate
It is important to note that the term "spark plasma" is a topic of ongoing scientific discussion. While the initial discharge model is widely used for explanation, some researchers argue that a sustained plasma is not present throughout the process.
They contend that the dominant mechanism is enhanced resistive heating at the contact points between particles. Regardless of the precise physics, the outcome remains the same: a highly effective, rapid sintering technique driven by electrical current.
Is SPS the Right Process for Your Goal?
SPS is a powerful and versatile tool, but its application is goal-dependent. Use these guidelines to determine if it fits your objective.
- If your primary focus is preserving nanostructures or fine grains: SPS is the ideal choice, as its low process temperature and short duration prevent the grain coarsening seen in conventional methods.
- If your primary focus is rapid densification of advanced materials: SPS excels at consolidating difficult-to-sinter materials like refractory metals, intermetallics, and high-performance ceramics that respond poorly to traditional techniques.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials: The precise control and localized heating of SPS make it a uniquely effective method for welding materials with different properties, such as ceramic-to-metal joints.
Ultimately, Spark Plasma Sintering empowers you to create advanced materials that are simply not achievable through slower, conventional heating methods.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Spark Plasma Discharge | High-current sparks create plasma between particles. | Cleans surfaces and forms initial necks between particles. |
| 2. Joule Heating | Electrical resistance generates rapid, uniform internal heat. | Heats the entire powder compact volumetrically at high speed. |
| 3. Plastic Deformation | Applied pressure consolidates the heated, malleable material. | Eliminates pores to achieve full density and a solid mass. |
Ready to achieve superior material properties with precise control?
Spark Plasma Sintering from KINTEK enables you to densify advanced materials—from metals and alloys to high-performance ceramics—while preserving fine microstructures and nanocrystalline grains. Our SPS systems are designed for researchers and manufacturers who need rapid, low-temperature consolidation without grain growth.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our lab equipment can accelerate your materials development. Get in touch via our contact form to learn more.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the different sintering methods? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material & Application
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts
- What is the SPS process of spark plasma sintering? A Guide to Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What is the plasma sintering technique? Achieve Rapid, High-Density Material Fabrication
- What are the advantages of SPS? Achieve Superior Material Density and Performance



















