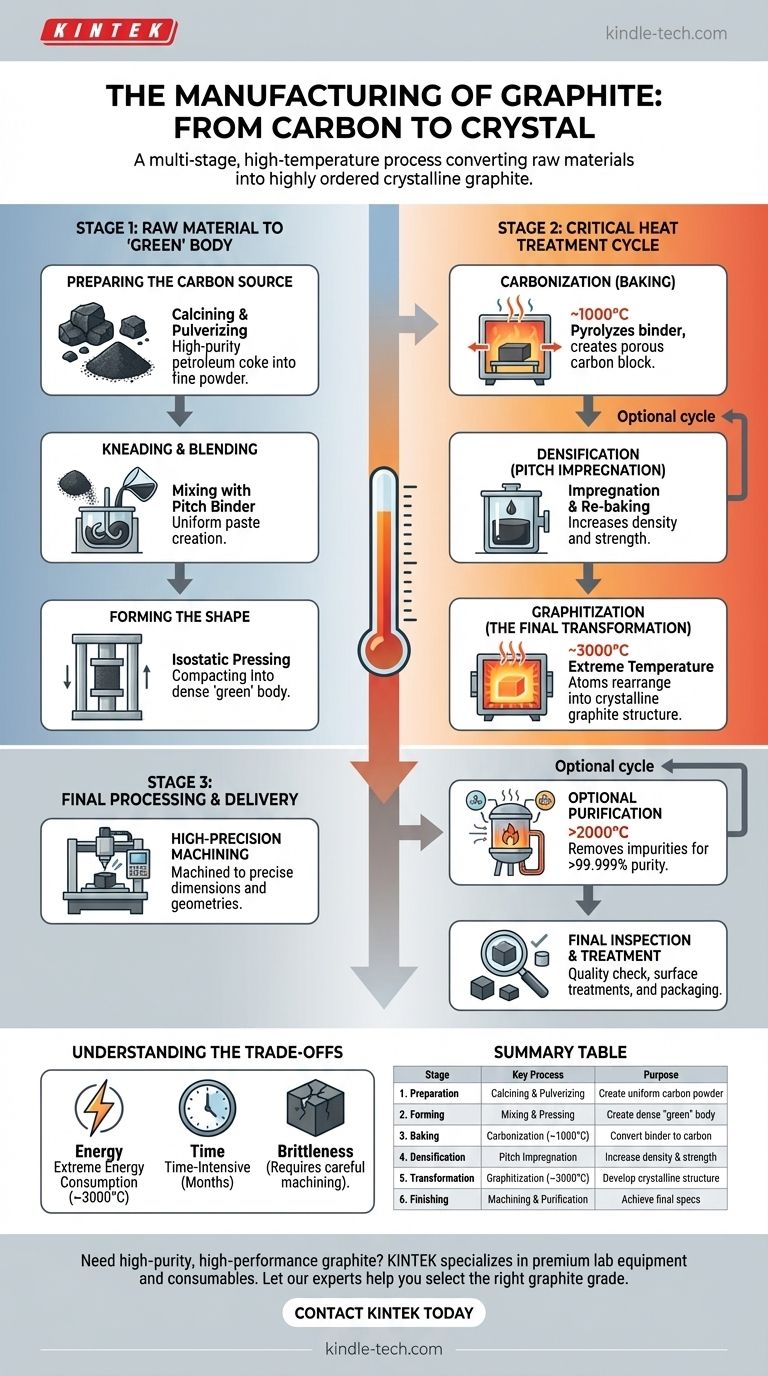
Manufacturing synthetic graphite is a multi-stage, high-temperature process designed to transform raw carbon materials into a highly ordered, crystalline final product. The core stages involve preparing a carbon source like petroleum coke, mixing it with a binder, forming it into a block, and then subjecting it to a two-part heat treatment: a lower-temperature carbonization (baking) followed by an extremely high-temperature graphitization around 3000°C. This final heat treatment is what develops graphite's signature properties.
The production of graphite is not simple fabrication; it is a controlled transformation at the atomic level. The entire process is engineered to convert disordered, amorphous carbon into the precisely ordered crystalline structure that gives graphite its exceptional thermal and electrical conductivity.

From Raw Material to Formed "Green" Body
The initial stages are focused on creating a dense, uniform block of carbon material, known as a "green" body, that is ready for heat treatment.
Preparing the Carbon Source
The primary raw material is typically high-purity petroleum coke. This coke is first calcined (heated) to remove volatile compounds and then pulverized into a fine powder, or "flour." The particle size of this powder is critical as it influences the density and grain structure of the final product.
Kneading and Blending
The carbon powder is then mixed with a binder, usually coal-tar pitch. This mixture is heated and kneaded into a uniform, paste-like consistency. The quality of this mixing step ensures that the binder is evenly distributed, which is essential for creating a strong, homogenous final product.
Forming the Shape
The most common method for forming high-density graphite is isostatic pressing. The carbon-pitch mixture is placed in a flexible mold and subjected to extremely high, uniform pressure from all sides. This compacts the material into a dense, solid block, which is referred to as a "green" artifact.
The Critical Heat Treatment Cycle
This is the heart of the manufacturing process, where the material is chemically and structurally transformed from a simple carbon block into crystalline graphite.
Carbonization (Baking)
The green body is slowly heated in an oxygen-free furnace to approximately 1000°C. This baking process pyrolyzes the pitch binder, converting it into solid carbon and driving off volatile gases. The result is a hard, brittle, and porous carbon block with a fixed shape.
Densification (Pitch Impregnation)
To increase density and strength, the porous carbon block may undergo a pitch impregnation cycle. It is placed in a vacuum chamber, which is then filled with liquid pitch to fill the internal pores. The block is then re-baked (re-carbonized) to convert the new pitch into carbon. This cycle can be repeated multiple times to achieve higher densities.
Graphitization (The Final Transformation)
This is the most crucial and energy-intensive step. The carbonized block is heated in a specialized electric furnace to temperatures approaching 3000°C. At this extreme temperature, the disordered carbon atoms rearrange themselves into the ordered, layered, hexagonal crystalline structure of graphite. This is what unlocks the material's high thermal and electrical conductivity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The unique properties of synthetic graphite come with inherent manufacturing challenges and costs that are important to recognize.
Extreme Energy Consumption
The graphitization step requires immense electrical energy to maintain temperatures near 3000°C. This makes it the single largest cost driver in the manufacturing process and a significant factor in the final price of the material.
Time-Intensive Process
This is not a fast process. The heating and cooling cycles for both carbonization and graphitization must be done very slowly to prevent thermal shock and cracking. The entire manufacturing timeline, from raw material to finished block, can take several months.
Brittleness and Machining
While strong under compression, graphite is a brittle material. Machining it into complex final parts requires specialized CNC equipment, careful handling, and dust control to prevent chipping, cracking, and contamination.
Final Processing and Delivery
Once the graphite block has cooled, it undergoes final steps to meet customer requirements.
High-Precision Machining
The large graphitized blocks are cut and machined to the precise dimensions and geometries specified by the end-user. This can range from simple blocks to highly intricate components for industries like aerospace or semiconductor manufacturing.
Optional Purification
For applications requiring extreme purity, such as in semiconductor crystal growth, the machined graphite undergoes a final high-temperature purification process. Halogen gases are used at over 2000°C to react with and remove residual metallic impurities, achieving purities greater than 99.999%.
Final Inspection and Treatment
All finished components are inspected for dimensional accuracy and material integrity. They may also receive specific surface treatments to enhance performance before being carefully packaged for shipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the manufacturing process helps you select the right material for your needs.
- If your primary focus is performance-critical applications (e.g., semiconductors, EDM): Prioritize grades that have undergone purification and controlled graphitization, as these steps directly govern electrical conductivity and purity.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for mechanical or thermal use: A lower-density grade that has undergone fewer impregnation cycles may be sufficient and more economical.
- If your primary focus is complex geometries: Engage with your supplier early about machining capabilities and tolerances, as the brittleness of graphite makes this a critical manufacturing consideration.
By understanding these stages, you can better specify the exact grade of graphite you require, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency for your application.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Calcining & Pulverizing Petroleum Coke | Create uniform carbon powder |
| 2. Forming | Mixing with Pitch Binder & Isostatic Pressing | Create dense 'green' body |
| 3. Baking | Carbonization (~1000°C) | Convert binder to solid carbon |
| 4. Densification | Pitch Impregnation & Re-baking (Optional) | Increase density and strength |
| 5. Transformation | Graphitization (~3000°C) | Develop crystalline structure |
| 6. Finishing | Precision Machining & Purification | Achieve final dimensions and purity |
Need high-purity, high-performance graphite components for your lab or production process?
The complex manufacturing of graphite requires expertise to ensure the final material meets your exact specifications for thermal management, electrical conductivity, or structural integrity.
KINTEK specializes in providing premium lab equipment and consumables, including high-quality graphite products. We understand the critical role material properties play in your application's success. Let our experts help you select the right graphite grade for optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is the graphite furnace method? Achieve Ultra-High Temperatures with Purity & Speed
- What does a graphite furnace do? Achieve Extreme Heat and Ultra-Sensitive Analysis
- Why is a high-vacuum graphite heating element furnace used for HAp sintering? Achieve Pure, High-Bond Coatings
- What is the temperature of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C
- What is the temperature range of a graphite furnace? Unlock up to 3000°C for advanced materials processing.



















