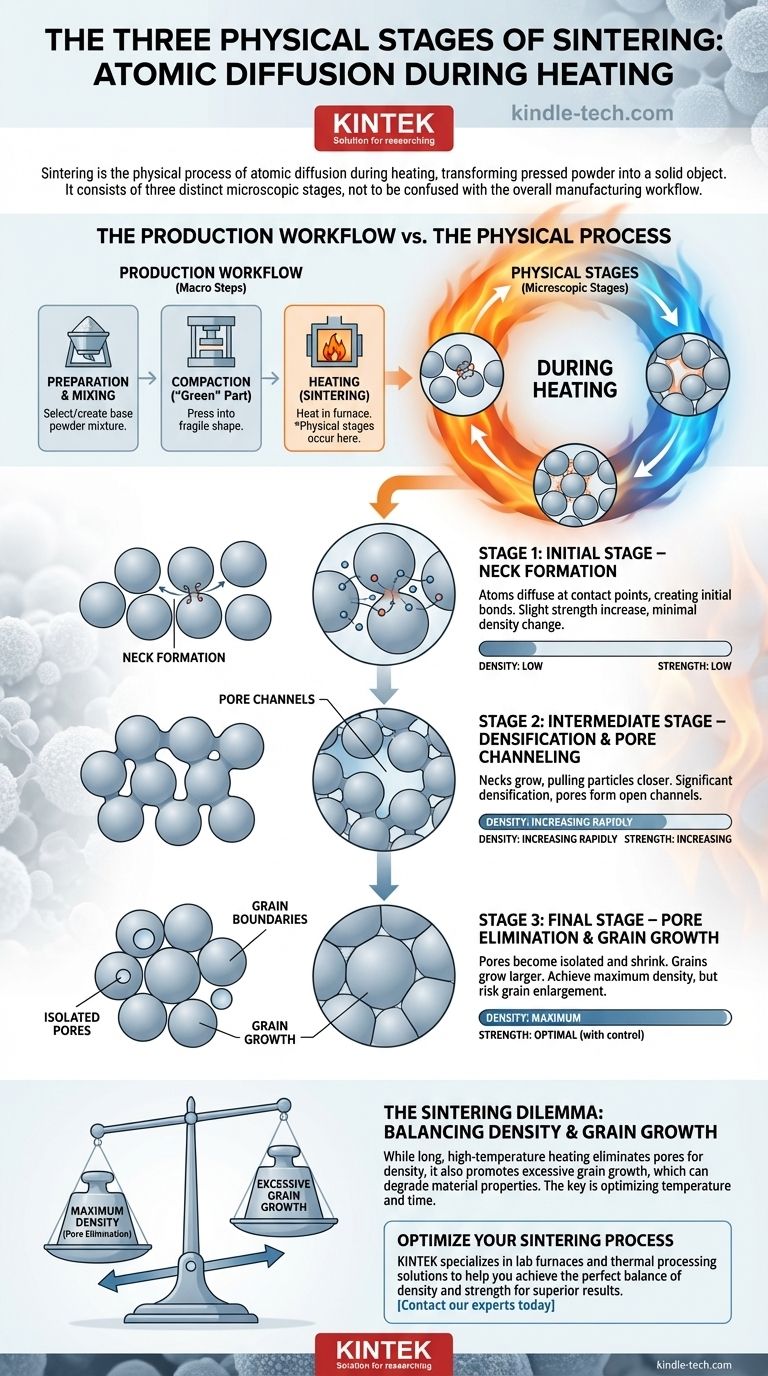
Sintering is the physical process of atomic diffusion that occurs during the heating phase, and it consists of three distinct stages: the initial stage of neck formation, the intermediate stage of densification, and the final stage of pore elimination. While many descriptions confuse the overall manufacturing steps with the physical process, these three stages describe what actually happens to the material's microstructure to transform it from a pressed powder into a solid object.
Many sources incorrectly describe the stages of sintering as powder preparation, compaction, and heating. These are the steps of the manufacturing process. The true physical stages of sintering all occur during the heating step, describing how individual particles bond and densify on a microscopic level.

The Production Workflow vs. The Physical Process
To understand sintering, it is critical to distinguish between the high-level production workflow and the microscopic physical transformation. The common three-step model describes the industrial process of creating a sintered part.
Step 1: Powder Preparation and Mixing
Before any heating occurs, a base powder is selected or created. This can involve mixing different metal or ceramic powders, along with binders or lubricants, to achieve the desired final chemical composition and processing characteristics.
Step 2: Compaction (The "Green" Part)
The prepared powder is then poured into a die and compacted under high pressure. This step presses the particles into close contact, creating a fragile, pre-sintered object known as a "green" part. This part has the desired shape but lacks strength.
Step 3: Heating (Sintering)
The green part is placed in a furnace and heated to a high temperature, typically below the material's melting point. It is during this heating step that the three physical stages of sintering take place, fusing the particles and strengthening the part.
The Three Physical Stages of Sintering (During Heating)
Sintering is driven by thermal energy, which causes atoms to move and diffuse across the boundaries of adjacent particles. This process unfolds in three overlapping stages.
Stage 1: Initial Stage – Neck Formation
As the temperature rises, atoms on the surface of the particles become more mobile. At the points where two particles touch, atoms begin to diffuse, creating a small bridge or "neck" between them. This initial bonding slightly increases the part's strength, but there is very little change in its overall density.
Stage 2: Intermediate Stage – Densification and Pore Channeling
As the heating continues, the necks between particles grow significantly wider. This process pulls the particle centers closer together, causing the entire part to shrink and its density to increase dramatically. The empty spaces (pores) between particles connect to form a continuous network of open channels. Most of the densification happens during this stage.
Stage 3: Final Stage – Pore Elimination and Grain Growth
In the final stage, the interconnected pore channels collapse and break up, forming isolated, spherical pores. These remaining pores continue to shrink and, in ideal conditions, are eventually eliminated as atoms diffuse to fill them. Simultaneously, the individual crystallites within the material, known as grains, begin to grow larger.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Sintering Dilemma
The goal of sintering is typically to achieve maximum density, but this must be balanced against a competing and often undesirable phenomenon.
Density vs. Grain Growth
The primary trade-off is between eliminating pores and preventing excessive grain growth. While a longer time at high temperature helps remove pores to increase density, it also encourages grains to grow. Overly large grains can degrade the material's mechanical properties, such as its strength and toughness.
The Role of Temperature and Time
Temperature and time are the two main levers for controlling the sintering outcome. A higher temperature accelerates all stages but can also promote rapid grain growth. The key to successful sintering is finding the optimal temperature-time profile that maximizes density while keeping grain size within an acceptable range for the desired application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these stages and trade-offs allows you to control the process to achieve specific material properties.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and performance: Your goal is to reach the final sintering stage to eliminate porosity, but you must carefully control the temperature and time to prevent excessive grain growth that could compromise the material's integrity.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production: Reaching the intermediate stage may achieve sufficient density (e.g., 92-95%) for many applications. Stopping the process here avoids the long furnace times and tight controls needed for the final stage, saving energy and cost.
- If your primary focus is creating complex shapes (e.g., via 3D printing): Sintering is the enabling technology. The goal is to ensure that necking and densification occur uniformly across the part to fuse the powdered layers into a solid, functional component.
By mastering the interplay between these stages, you can effectively engineer the microstructure of a material to meet your exact needs.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Microstructural Change |
|---|---|---|
| Initial | Neck Formation | Atoms diffuse at contact points, creating bonds between particles. |
| Intermediate | Densification | Necks grow, particles move closer, density increases sharply. |
| Final | Pore Elimination & Grain Growth | Pores become isolated and shrink; grains may grow larger. |
Need precise control over your sintering process to achieve the perfect balance of density and strength? KINTEK specializes in lab furnaces and thermal processing solutions for advanced materials. Our expertise helps you optimize temperature and time profiles for superior results, whether you're focused on maximum performance or cost-effective production. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific sintering challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs



















