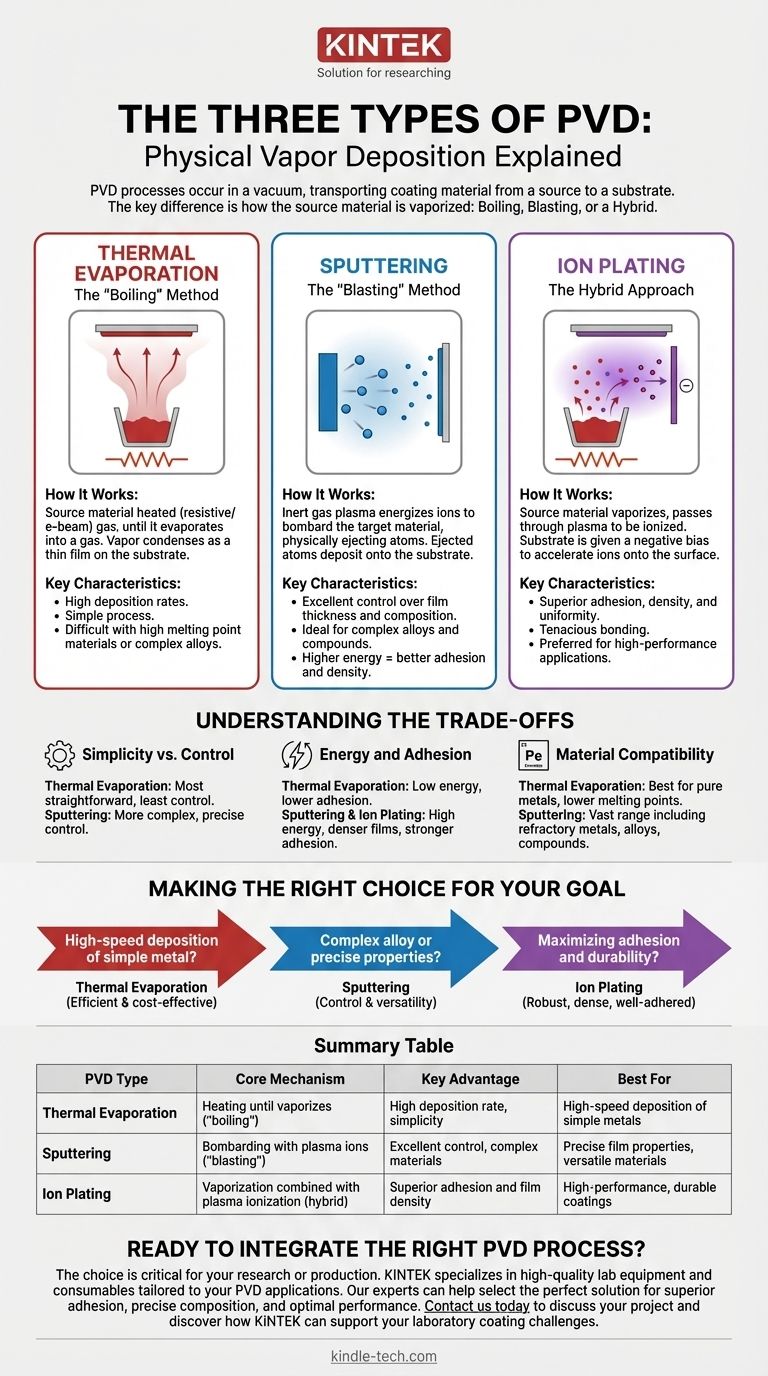
The three primary types of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) are thermal evaporation, sputtering, and ion plating. These processes all occur within a vacuum chamber but differ fundamentally in how they transport coating material from a source onto the surface of a part, known as the substrate.
The core difference between PVD methods isn't the final coating, but the technique used to vaporize the source material. Each method—essentially boiling, blasting, or a hybrid of the two—offers distinct advantages in adhesion, film density, and the types of materials that can be deposited.

Thermal Evaporation: The "Boiling" Method
Thermal evaporation is conceptually the simplest form of PVD. It involves heating a solid coating material until it evaporates into a gas within a vacuum chamber.
How It Works
The source material is placed in a crucible and heated, typically through resistive heating or with an electron beam. As the material heats, its atoms gain enough energy to transition into a vapor phase. This vapor then travels through the vacuum and condenses as a thin film on the cooler substrate.
Key Characteristics
This method is known for its high deposition rates and relative simplicity. However, it can be difficult to use with materials that have very high melting points or complex alloys, as the different elements may evaporate at different rates.
Sputtering: The "Blasting" Method
Sputtering is a more energetic process that does not rely on melting the source material. Instead, it uses a plasma to physically eject atoms from the target.
How It Works
An inert gas, like argon, is introduced into the vacuum chamber and energized to create a plasma. The positively charged ions within this plasma are accelerated and bombard the source material (called the "target"). This collision has enough energy to knock atoms loose from the target, which then travel and deposit onto the substrate.
Key Characteristics
Sputtering offers excellent control over film thickness and composition, making it ideal for depositing complex alloys and compounds. The higher energy of the deposited atoms generally results in better adhesion and a denser film compared to thermal evaporation.
Ion Plating: The Hybrid Approach
Ion plating is an advanced PVD process that combines elements of both thermal evaporation and sputtering to produce exceptionally high-quality coatings.
How It Works
Like thermal evaporation, the source material is heated until it vaporizes. However, the vaporized atoms then pass through a plasma field. This energizes the atoms, and the substrate itself is often given a negative electrical bias, which actively accelerates these newly ionized coating atoms toward its surface.
Key Characteristics
This combination results in superior film adhesion, density, and uniformity. The added energy and electrical attraction create a coating that is more tenaciously bonded to the substrate, making it a preferred method for high-performance applications like aerospace components and medical implants.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a PVD method involves balancing process complexity with the desired coating characteristics. There is no single "best" method; the choice depends entirely on the application's specific requirements.
Simplicity vs. Control
Thermal evaporation is the most straightforward process but offers the least control over the film's structure. Sputtering, on the other hand, is more complex but provides precise control over the properties of the deposited film.
Energy and Adhesion
The energy of the depositing particles is a critical factor. The low-energy nature of thermal evaporation can sometimes lead to lower adhesion. The high-energy particle bombardment in sputtering and ion plating creates much denser films with significantly stronger adhesion to the substrate.
Material Compatibility
Thermal evaporation is best suited for pure metals with lower melting points. Sputtering can deposit a vast range of materials, including refractory metals, alloys, and compounds, without concern for their melting temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate PVD process, you must first define the most critical property of the final coating.
- If your primary focus is high-speed deposition of a simple metal: Thermal evaporation offers an efficient and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is depositing a complex alloy or achieving precise film properties: Sputtering provides the control and versatility needed for advanced materials.
- If your primary focus is maximizing adhesion and durability for a critical application: Ion plating delivers the most robust, dense, and well-adhered coatings.
Ultimately, understanding these core PVD techniques empowers you to match the right physical process to your specific material and performance goals.
Summary Table:
| PVD Type | Core Mechanism | Key Advantage | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Evaporation | Heating material until it vaporizes ("boiling") | High deposition rate, simplicity | High-speed deposition of simple metals |
| Sputtering | Bombarding a target with plasma ions ("blasting") | Excellent control, deposits complex alloys/compounds | Precise film properties, versatile materials |
| Ion Plating | Vaporization combined with plasma ionization (hybrid) | Superior adhesion and film density | High-performance, durable coatings |
Ready to integrate the right PVD process into your laboratory workflow? The choice between thermal evaporation, sputtering, and ion plating is critical for achieving the specific coating properties your research or production demands. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your PVD applications. Our experts can help you select the perfect solution to ensure superior adhesion, precise film composition, and optimal performance for your substrates. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's coating challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
People Also Ask
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications



















