The two primary methods of industrial induction heating are embodied in the coreless induction furnace and the channel induction furnace. While both use electromagnetic induction to generate heat directly within a metal, their internal construction dictates vastly different applications, from primary steelmaking to holding molten aluminum.
The essential difference lies in their function: coreless furnaces are versatile primary melters ideal for a wide range of metals, while channel furnaces are highly efficient specialists, primarily used for holding and superheating already molten, lower-temperature alloys.

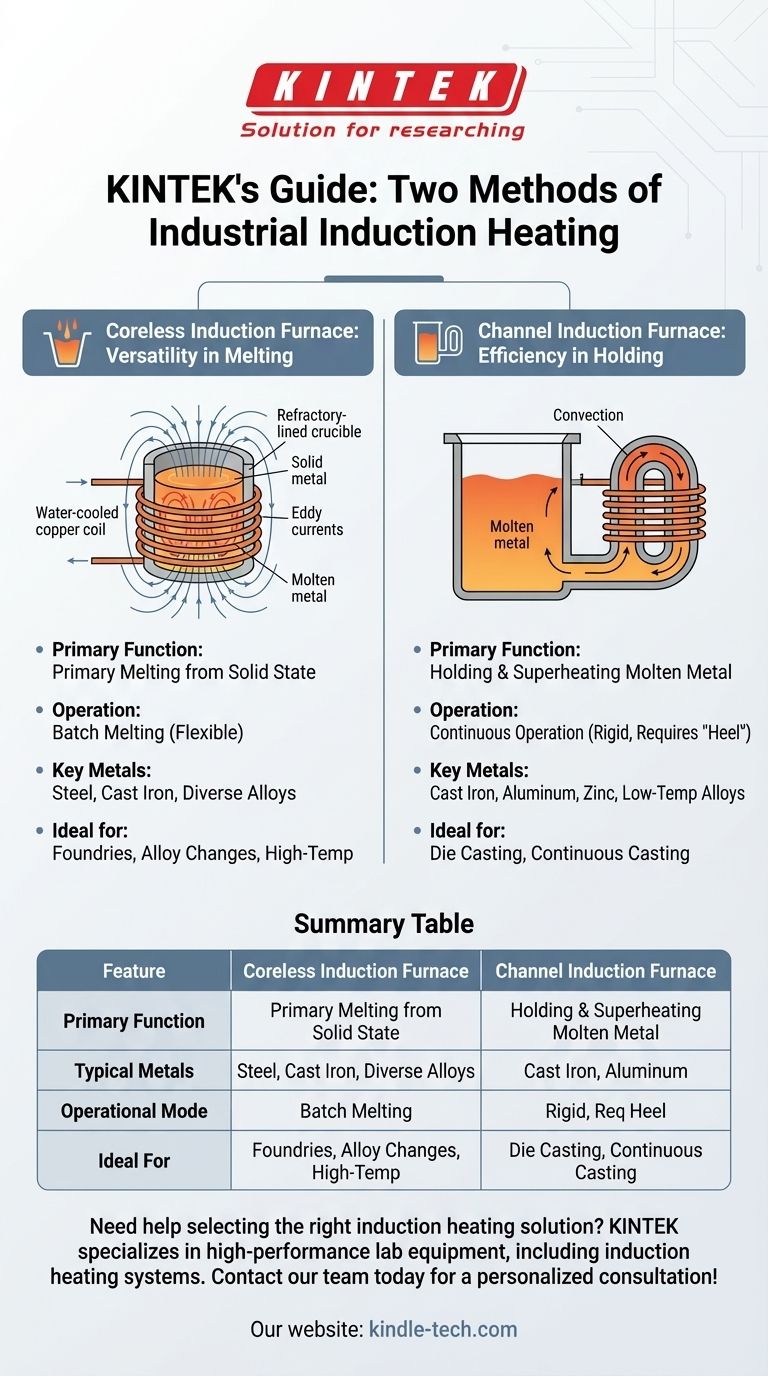
The Coreless Induction Furnace: Versatility in Melting
A coreless furnace is the more common design for melting metals from a solid state. It operates like a true transformer where the primary is the furnace's coil and the secondary is the metal charge itself.
How It Works
The furnace consists of a refractory-lined crucible which contains the metal to be melted. This crucible is surrounded by a water-cooled copper coil.
When a powerful alternating current is passed through the coil, it creates a strong, reversing magnetic field. This field induces powerful eddy currents within the metal charge, generating immense heat through electrical resistance and rapidly melting it.
Key Applications
The coreless furnace is exceptionally versatile. It is used for melting a wide range of metals, including steel, cast iron, and various non-ferrous alloys.
Its ability to start melting from a cold, solid charge makes it ideal for foundries that operate in batches or frequently change the type of alloy they are melting.
The Channel Induction Furnace: Efficiency in Holding
A channel furnace is designed less for primary melting and more for holding large volumes of molten metal at a specific temperature with high efficiency.
How It Works
This furnace has a main chamber for holding metal, connected to a smaller, looped channel made of refractory material. An induction coil is wrapped around this channel.
The molten metal inside the channel forms a closed secondary circuit. Current induced in this loop generates heat, which then circulates through the main bath of metal via natural convection, keeping the entire volume at a consistent temperature.
Key Applications
Channel furnaces excel as holding and superheating units. They are commonly used for low melting point alloys like cast iron and non-ferrous metals.
Because they must maintain a continuous molten "heel" in the channel to operate, they are best suited for continuous or semi-continuous casting operations rather than batch melting.
Understanding the Key Differences
Choosing between these two furnace types comes down to understanding the trade-offs between versatility and specialized efficiency.
Melting vs. Holding
The coreless furnace is a primary melter. Its design is optimized for taking solid metal and turning it into liquid.
The channel furnace is a holding vessel. It is far more thermally efficient at maintaining the temperature of an already-molten bath for long periods.
Application Range
The intense and direct heating of a coreless furnace makes it suitable for high-temperature alloys like steel.
The design of a channel furnace makes it better suited for lower-temperature metals. It is a workhorse in industries like aluminum and zinc die casting.
Operational Flexibility
A coreless furnace offers high flexibility. It can be started from cold and completely emptied between melts, allowing for easy alloy changes.
A channel furnace is operationally rigid. It must remain on and filled with molten metal, making it unsuitable for operations that require frequent shutdowns or alloy switches.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific industrial process will determine which furnace technology is the correct tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is melting solid steel or diverse alloys in batches: The coreless furnace provides the necessary power and flexibility.
- If your primary focus is holding large quantities of molten cast iron or aluminum at a stable temperature for casting: The channel furnace offers superior thermal efficiency for this task.
- If your primary focus is superheating or adjusting the chemistry of already-molten metal: The gentle, continuous heating of a channel furnace is the ideal solution.
Understanding the fundamental design of each furnace empowers you to select the most effective and efficient technology for your metallurgical process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Coreless Induction Furnace | Channel Induction Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Primary Melting | Holding & Superheating |
| Typical Metals | Steel, Cast Iron, Diverse Alloys | Cast Iron, Aluminum, Zinc |
| Operational Mode | Batch Melting (Flexible) | Continuous Operation (Rigid) |
| Ideal For | Foundries, Alloy Changes | Die Casting, Continuous Casting |
Need help selecting the right induction heating solution for your lab or foundry?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including induction heating systems for metallurgical processes. Whether you need the versatile melting power of a coreless furnace or the efficient holding capabilities of a channel furnace, our experts can help you identify the perfect technology to enhance your efficiency and results.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and discover the KINTEK difference!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of CCIM for titanium deoxygenation? Achieve Ultra-High Purity in Reactive Metal Melting
- What is the primary function of an induction furnace in Al-Fe-Ni alloy melting? Achieve Unmatched Chemical Homogeneity
- What are the disadvantages of coreless type induction furnace? Key Trade-offs in Flexibility vs. Efficiency
- What are the benefits of using an induction heating source for the direct conversion of methane into hydrogen?
- Can you melt gold in an induction furnace? A Guide to Clean, Efficient Gold Melting
- What is the main frequency of an induction furnace? A Guide to Optimizing Melting & Heating
- What is the temperature for induction hardening? Achieve Precise Hardness Without Compromising Part Integrity
- How does an induction melting furnace work? Unlock the Power of Non-Contact, Efficient Metal Melting



















